Different techniques used in cytogenetics
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
37 likes•16,419 views
This document discusses various cytogenetic techniques used to analyze chromosomes, including karyotyping, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), and molecular cytogenetics. It provides details on the slide preparation and analysis steps for karyotyping and FISH. It also notes that a skilled cytogeneticist is still needed to accurately classify banded chromosomes, despite advances in automated analysis systems.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
CYTOGENETICS.pptx

This document discusses cytogenetics and chromosome analysis techniques. It begins with an introduction to human chromosomes and chromosomal abnormalities. It then describes various types of chromosomal mutations and abnormalities that can be detected through karyotyping and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). The document provides detailed procedures for chromosome sample preparation from bone marrow and blood cultures, as well as staining and analysis techniques like Giemsa staining and G-banding. The importance of chromosomal studies for diagnosing conditions like Turner syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome is also highlighted.
Cytogenetic techniques

This document discusses various cytogenetic techniques used to study chromosomes, including their structure and abnormalities. It describes karyotyping to analyze all chromosomes for changes, as well as techniques like fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), comparative genomic hybridization (CGH), spectral karyotyping (SKY), and multicolor FISH (M-FISH) that use fluorescent probes to detect DNA sequences on chromosomes. It also discusses banding techniques like G-banding and Q-banding that identify chromosomes based on dark and light bands corresponding to GC-rich and AT-rich regions. These techniques are used to diagnose chromosomal abnormalities and further cytogenetic research.
Cytogenetics 

The document discusses cytogenetics, which involves the study of chromosomes through cell culture and karyotyping. Chromosomes can be analyzed for their number and structure to detect abnormalities. Specific staining techniques like Q-, G-, R-, and C-banding produce distinct banding patterns that allow identification of each chromosome type. Karyotyping involves organizing chromosomes based on these patterns to detect any abnormalities associated with diseases.
Chromosomal banding technique

A cytological technique to detect the nature of adjacent chromosomal regions by using different staining technique assisted with some pre treatment of metaphase chromosomes prepared on the slides
Advanced Techniques In Molecular Cytogenetics Karyotyping, FISH, CGH, SKY

Molecular cytogenetics involves combining molecular biology techniques with cytogenetics. This document discusses several molecular cytogenetic techniques including karyotyping, FISH, CGH, and SKY. Karyotyping allows visualization of whole chromosome sets but cannot detect small structural abnormalities. FISH uses fluorescent probes to detect specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. CGH analyzes copy number variations by comparing test and reference DNA samples hybridized to probes. SKY simultaneously visualizes all chromosome pairs in different colors, making abnormalities easy to identify. These techniques are useful for detecting chromosomal abnormalities that can cause genetic disorders and economic losses if spread within animal populations. Preventing the dissemination of abnormalities through genetic testing is important.
fish- Fluorescence in situ hybridization 

FISH is a technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to complementary DNA sequences on chromosomes to detect chromosomal abnormalities. It allows detection of structural changes like deletions and duplications not visible under a microscope. FISH gained recognition supporting genome mapping efforts. It involves labeling probes, denaturing probe and target DNA, and allowing hybridization. Results are then viewed under a fluorescence microscope. FISH has applications in detecting abnormalities, identifying marker chromosomes, and monitoring therapy. It provides advantages over traditional cytogenetics like rapid analysis of non-dividing cells.
Chromosome analysis

Chromosome analysis evaluates the number and structure of a person's chromosomes to detect abnormalities. It can detect both numerical changes, such as an abnormal number of chromosomes, and structural changes, such as deletions or duplications. Techniques for chromosome analysis include fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH), comparative genomic hybridization (CGH), and array comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH). FISH uses fluorescent probes to detect specific chromosome segments or genes, while CGH and array CGH compare DNA samples to detect copy number variations between them. Chromosome analysis is used to diagnose conditions like Down syndrome, leukemia, and Prader-Willi syndrome.
Feulgen stain

The Feulgen stain is a histological technique discovered in 1924 that uses acid hydrolysis and Schiff's reagent to specifically identify chromosomal material and DNA. It involves hydrolyzing tissue samples in hydrochloric acid to cleave nitrogen bases from DNA and form aldehyde groups, then staining the samples with Schiff's reagent to form a purple compound where aldehydes are present, selectively identifying DNA. The staining intensity is proportional to the DNA concentration and it allows DNA to be visualized microscopically.
Recommended
CYTOGENETICS.pptx

This document discusses cytogenetics and chromosome analysis techniques. It begins with an introduction to human chromosomes and chromosomal abnormalities. It then describes various types of chromosomal mutations and abnormalities that can be detected through karyotyping and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). The document provides detailed procedures for chromosome sample preparation from bone marrow and blood cultures, as well as staining and analysis techniques like Giemsa staining and G-banding. The importance of chromosomal studies for diagnosing conditions like Turner syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome is also highlighted.
Cytogenetic techniques

This document discusses various cytogenetic techniques used to study chromosomes, including their structure and abnormalities. It describes karyotyping to analyze all chromosomes for changes, as well as techniques like fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), comparative genomic hybridization (CGH), spectral karyotyping (SKY), and multicolor FISH (M-FISH) that use fluorescent probes to detect DNA sequences on chromosomes. It also discusses banding techniques like G-banding and Q-banding that identify chromosomes based on dark and light bands corresponding to GC-rich and AT-rich regions. These techniques are used to diagnose chromosomal abnormalities and further cytogenetic research.
Cytogenetics 

The document discusses cytogenetics, which involves the study of chromosomes through cell culture and karyotyping. Chromosomes can be analyzed for their number and structure to detect abnormalities. Specific staining techniques like Q-, G-, R-, and C-banding produce distinct banding patterns that allow identification of each chromosome type. Karyotyping involves organizing chromosomes based on these patterns to detect any abnormalities associated with diseases.
Chromosomal banding technique

A cytological technique to detect the nature of adjacent chromosomal regions by using different staining technique assisted with some pre treatment of metaphase chromosomes prepared on the slides
Advanced Techniques In Molecular Cytogenetics Karyotyping, FISH, CGH, SKY

Molecular cytogenetics involves combining molecular biology techniques with cytogenetics. This document discusses several molecular cytogenetic techniques including karyotyping, FISH, CGH, and SKY. Karyotyping allows visualization of whole chromosome sets but cannot detect small structural abnormalities. FISH uses fluorescent probes to detect specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. CGH analyzes copy number variations by comparing test and reference DNA samples hybridized to probes. SKY simultaneously visualizes all chromosome pairs in different colors, making abnormalities easy to identify. These techniques are useful for detecting chromosomal abnormalities that can cause genetic disorders and economic losses if spread within animal populations. Preventing the dissemination of abnormalities through genetic testing is important.
fish- Fluorescence in situ hybridization 

FISH is a technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to complementary DNA sequences on chromosomes to detect chromosomal abnormalities. It allows detection of structural changes like deletions and duplications not visible under a microscope. FISH gained recognition supporting genome mapping efforts. It involves labeling probes, denaturing probe and target DNA, and allowing hybridization. Results are then viewed under a fluorescence microscope. FISH has applications in detecting abnormalities, identifying marker chromosomes, and monitoring therapy. It provides advantages over traditional cytogenetics like rapid analysis of non-dividing cells.
Chromosome analysis

Chromosome analysis evaluates the number and structure of a person's chromosomes to detect abnormalities. It can detect both numerical changes, such as an abnormal number of chromosomes, and structural changes, such as deletions or duplications. Techniques for chromosome analysis include fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH), comparative genomic hybridization (CGH), and array comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH). FISH uses fluorescent probes to detect specific chromosome segments or genes, while CGH and array CGH compare DNA samples to detect copy number variations between them. Chromosome analysis is used to diagnose conditions like Down syndrome, leukemia, and Prader-Willi syndrome.
Feulgen stain

The Feulgen stain is a histological technique discovered in 1924 that uses acid hydrolysis and Schiff's reagent to specifically identify chromosomal material and DNA. It involves hydrolyzing tissue samples in hydrochloric acid to cleave nitrogen bases from DNA and form aldehyde groups, then staining the samples with Schiff's reagent to form a purple compound where aldehydes are present, selectively identifying DNA. The staining intensity is proportional to the DNA concentration and it allows DNA to be visualized microscopically.
Demonstration of protein and nucleic acids

This document discusses proteins and nucleic acids in tissues and various methods for demonstrating them. It covers:
1. Protein composition and types including structural, enzymes, and complement proteins.
2. Methods for demonstrating proteins including immunohistochemistry, histochemical staining of amino acids or enzymes, and physical properties.
3. Nucleic acid composition, structure of DNA and RNA, and their functions in storage of genetic information and protein coding.
4. Techniques for demonstrating DNA including Feulgen reaction, fluorescent staining, and in situ hybridization. Methods for RNA include methyl green-pyronin staining and enzymatic digestion.
Nucleic acid stains

This document discusses several techniques for staining and demonstrating nucleic acids and proteins under a light microscope. It describes two types of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, and how their composition allows them to be stained using dyes that bind to phosphate groups or react with sugar groups. Specific staining methods mentioned include Fuelgen stain for DNA, methyl green pyronin for both DNA and RNA, and acridine orange. Extraction techniques are also summarized that can separate DNA and RNA for individual staining. The document also covers protein staining techniques like Ninhydrin-Schiff for amino acids and Millon's reaction for detecting tyrosine.
Ppt on karyotyping, chromosome banding and chromosome painting.

This document provides an overview of karyotyping, chromosome banding, and chromosome painting techniques. It discusses how karyotyping involves arranging chromosomes based on size and centromere position. Different banding techniques like Q, G, N, and C banding stain chromosomes to reveal structural features. Chromosome painting uses fluorescent probes to identify chromosomes and chromosomal abnormalities. These techniques allow studying chromosome structure, identifying defects, and analyzing evolutionary changes.
Cytogenetic analysis

Chromosomes consist of DNA, proteins, and structures like telomeres and centromeres. Chromosomal abnormalities can include aneuploidy (extra or missing chromosomes) and polyploidy (extra sets of chromosomes). These abnormalities can be detected through techniques like amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, and analyzing fetal cells in maternal blood, which allow chromosomal analysis to screen for conditions like Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome. Nondisjunction during cell division can result in aneuploidies, while errors in meiosis can also produce chromosomal abnormalities.
Presentation on Fluorescence in-Situ Hybridization (FISH)

Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes to identify specific sequences on chromosomes. FISH allows researchers to detect the presence, absence, and location of gene sequences without having to culture cells. The process involves labeling probes with fluorescent dyes, applying the probes to intact cells on a slide, and visualizing where the probes bind to complementary DNA sequences under a microscope. FISH has applications in gene mapping, identifying chromosomal abnormalities, and analyzing structural chromosome changes.
Cryostat and frozen section

Frozen sections of tissue are prepared using a cryostat to quickly obtain thin sections for histological examination and diagnosis. A cryostat maintains tissue at freezing temperatures to allow sectioning without ice crystal formation. Tissue is mounted on a chuck and placed in the cryostat, then sectioned and mounted on slides for staining. Frozen sections allow rapid diagnosis but have poorer morphology and staining than fixed tissue sections.
Fixation of tissues

This document discusses tissue fixation, which involves using chemicals to preserve tissue samples for examination. It defines fixation as preventing post-mortem changes while maintaining tissue characteristics. The goals of fixation are to prevent autolysis and putrefaction, penetrate tissues rapidly and evenly, harden tissues, and not interfere with staining. Common fixatives discussed include formalin, glutaraldehyde, Bouin's solution, and Zenker's solution. Factors that influence fixation such as temperature, specimen size, fixation time, and choice of fixative are also reviewed.
Flow cytometry

This document provides an overview of flow cytometry. It begins by defining flow cytometry as a technique for quantitative single cell analysis that counts, examines, and sorts cells based on optical properties like light scattering and fluorescence. It then describes the basic principles, components, and working of a flow cytometer. Key components include lasers, optical filters, and detectors. Cells in suspension pass through the laser one by one, with signals detected by photodiodes and photomultiplier tubes. Applications discussed include cell sorting, apoptosis analysis using markers like Annexin V and PI, and cell cycle analysis using DNA binding dyes or BrdU incorporation. Clinical uses involve hematologic malignancy diagnosis, residual disease detection, and monitoring treatments.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)

Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) is a cytogenetic technique that can be used to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes.
Mounting media

The document discusses mounting media used to embed specimens on microscope slides under a coverslip. There are two main categories of mounting media: resinous (organic) media, which are dissolved in solvents like xylene and harden through evaporation, and aqueous media for specimens mounted in water. The ideal mounting medium is transparent, colorless, protects specimens from damage, and has a refractive index close to that of glass. Common mounting media include Canada balsam, Euparal, glycerin jelly, and aqueous solutions. Proper mounting techniques help prevent air bubbles between the specimen and coverslip.
Fixation & fixatives in histopathology, dr naveen reddy

This document provides an overview of tissue fixation techniques. It defines fixation as a process that preserves tissues in a state close to how they appeared when living. This is achieved by preventing autolysis and maintaining cellular morphology. The document discusses various types of fixatives including aldehydes, alcohols, and oxidizing agents. It also covers the aims of fixation, how different fixatives work, commonly used fixatives for different tissue and cellular components, and potential artifacts. Fixation is essential for histological examination and aims to maintain tissues for further analysis.
Staining by hematoxylin and eosin

Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is the most common histology stain. Hematoxylin stains cell nuclei blue by binding to DNA and RNA, while eosin stains cytoplasm and extracellular components pink. The staining process involves deparaffinizing tissue sections, staining with hematoxylin, differentiating with acid to remove excess stain, staining with eosin, and mounting for examination. Hematoxylin is extracted from logwood and oxidized to hematin, which binds tissue as a cationic dye with a mordant like alum. Eosin Y is the typical counterstain used to visualize cytoplasm. Together, H&E staining provides excellent contrast to study cell and
Cytogenetic abnormalities 

1. Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and abnormalities involving changes in number or structure. Key milestones included the discovery and counting of chromosomes and development of techniques like karyotyping.
2. Cytogenetic analysis involves culturing cells, arresting cell division, staining and analyzing chromosomes to identify abnormalities. It is used to diagnose conditions like Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome which are caused by gains or losses of whole chromosomes.
3. Chromosomal abnormalities can be numerical, involving extra or missing chromosomes, or structural with changes like translocations, deletions, or duplications. These abnormalities are associated with developmental delays, birth defects,
Kell blood group system

Kell blood group system most important blood group system following to ABO and Rh blood group system, particularly RhD as far as immunogenicity is concerned and Its clinical importance.
Flow cytometry

Flow cytometry allows for the quantitative and qualitative analysis of cell properties as cells flow in a fluid stream through a laser. Cells are labeled with fluorescent markers and pass through the laser one by one. Light scattering and fluorescence emission are converted to digital signals which provide information on cell size, granularity, and marker expression. Data is displayed as histograms, dot plots, or density plots to identify cell populations and phenotypes.
Frozen section and cryostat

This document discusses frozen sections and cryostats. Frozen sections are prepared without dehydration or embedding to enable rapid diagnosis within 10 minutes. They have applications in intraoperative diagnosis, enzyme histochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and other techniques. Tissue is frozen using liquid nitrogen or other cryogenic methods, turning water within the tissue to ice which acts as an embedding medium for sectioning. Cryostats maintain low temperatures, typically -20 to -30°C, for sectioning frozen tissue blocks. Optimal cutting temperatures vary by tissue type and whether the tissue is fixed.
Histochemistry

This document provides an overview of histochemistry from Sourabh Tiwary's class presentation. It defines histochemistry as identifying tissue chemical constituents using stains and microscopy. The goals of histochemistry are to present normal chemical composition and distribution with specific, detectable, and insoluble reaction products. Related disciplines like cytochemistry, enzyme histochemistry, immunocytochemistry, and in situ hybridization are discussed. Common methods for detecting substances like ions, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and saccharides are described along with applications and examples. Enzyme histochemistry and immunocytochemistry techniques are also summarized.
Fixatives 

This document discusses tissue fixation in pathology. It begins by describing the overall tissue processing steps and importance of fixation. The main types of fixatives are then outlined, including coagulant, cross-linking, and compound fixatives. Formalin and glutaraldehyde fixation are discussed in depth. Key factors that influence fixation quality like buffer pH, fixation duration, tissue size, and temperature are also summarized. The document provides a comprehensive overview of fixation in pathology.
Histopatholgy staining by suchit kumar

The document summarizes a seminar presentation on histopathology staining techniques. It discusses the routine H&E stain and provides details on the principle, reagents, and procedure. It also describes special stains used to identify substances like carbohydrates, amyloid, nucleic acids, and lipids. Specific stains covered include periodic acid Schiff, Congo red, Feulgen, methyl green pyronin, and Oil red O. The document aims to inform attendees about common and special staining methods in histopathology.
Special stains bmlt

This document discusses special stains used in histopathology, specifically stains used to identify lipids. It describes the Oil Red O and Sudan Black B stains. Oil Red O stains neutral triglycerides and lipids red and nuclei blue. It is used to identify tumors containing fat cells and fatty emboli. Sudan Black B stains fats blue-black and nuclei red. It can identify phospholipids and is used to differentiate myeloblasts from lymphoblasts in hematological disorders. Special stains are important tools to identify tissue components not visible with routine H&E staining.
Intorduction to Cytogenetics

Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, number, and abnormalities. Key techniques include karyotyping, G-banding, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and molecular cytogenetics. Several clinical cases were presented involving abnormalities detected by cytogenetic analysis, such as Down syndrome, chronic myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and acute promyelocytic leukemia. A total of 55 conventional cytogenetics studies and 15 bone marrow cytogenetics studies were performed, with various abnormalities identified. Future plans include expanding FISH and PCR testing.
Genetic Series Cytogenetics.pptx

Karyotyping involves growing cells in culture, arresting them in metaphase using colchicine, staining the chromosomes, and arranging them into a standardized pattern for analysis. The main steps are sample collection, cell culture, harvesting metaphase cells, staining (typically using Giemsa banding), and arranging the chromosomes into a karyotype based on length, centromere position, and banding pattern. Karyotyping is used for clinical diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities, prenatal testing, and research applications like identifying cancer-related translocations.
More Related Content
What's hot
Demonstration of protein and nucleic acids

This document discusses proteins and nucleic acids in tissues and various methods for demonstrating them. It covers:
1. Protein composition and types including structural, enzymes, and complement proteins.
2. Methods for demonstrating proteins including immunohistochemistry, histochemical staining of amino acids or enzymes, and physical properties.
3. Nucleic acid composition, structure of DNA and RNA, and their functions in storage of genetic information and protein coding.
4. Techniques for demonstrating DNA including Feulgen reaction, fluorescent staining, and in situ hybridization. Methods for RNA include methyl green-pyronin staining and enzymatic digestion.
Nucleic acid stains

This document discusses several techniques for staining and demonstrating nucleic acids and proteins under a light microscope. It describes two types of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, and how their composition allows them to be stained using dyes that bind to phosphate groups or react with sugar groups. Specific staining methods mentioned include Fuelgen stain for DNA, methyl green pyronin for both DNA and RNA, and acridine orange. Extraction techniques are also summarized that can separate DNA and RNA for individual staining. The document also covers protein staining techniques like Ninhydrin-Schiff for amino acids and Millon's reaction for detecting tyrosine.
Ppt on karyotyping, chromosome banding and chromosome painting.

This document provides an overview of karyotyping, chromosome banding, and chromosome painting techniques. It discusses how karyotyping involves arranging chromosomes based on size and centromere position. Different banding techniques like Q, G, N, and C banding stain chromosomes to reveal structural features. Chromosome painting uses fluorescent probes to identify chromosomes and chromosomal abnormalities. These techniques allow studying chromosome structure, identifying defects, and analyzing evolutionary changes.
Cytogenetic analysis

Chromosomes consist of DNA, proteins, and structures like telomeres and centromeres. Chromosomal abnormalities can include aneuploidy (extra or missing chromosomes) and polyploidy (extra sets of chromosomes). These abnormalities can be detected through techniques like amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, and analyzing fetal cells in maternal blood, which allow chromosomal analysis to screen for conditions like Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome. Nondisjunction during cell division can result in aneuploidies, while errors in meiosis can also produce chromosomal abnormalities.
Presentation on Fluorescence in-Situ Hybridization (FISH)

Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes to identify specific sequences on chromosomes. FISH allows researchers to detect the presence, absence, and location of gene sequences without having to culture cells. The process involves labeling probes with fluorescent dyes, applying the probes to intact cells on a slide, and visualizing where the probes bind to complementary DNA sequences under a microscope. FISH has applications in gene mapping, identifying chromosomal abnormalities, and analyzing structural chromosome changes.
Cryostat and frozen section

Frozen sections of tissue are prepared using a cryostat to quickly obtain thin sections for histological examination and diagnosis. A cryostat maintains tissue at freezing temperatures to allow sectioning without ice crystal formation. Tissue is mounted on a chuck and placed in the cryostat, then sectioned and mounted on slides for staining. Frozen sections allow rapid diagnosis but have poorer morphology and staining than fixed tissue sections.
Fixation of tissues

This document discusses tissue fixation, which involves using chemicals to preserve tissue samples for examination. It defines fixation as preventing post-mortem changes while maintaining tissue characteristics. The goals of fixation are to prevent autolysis and putrefaction, penetrate tissues rapidly and evenly, harden tissues, and not interfere with staining. Common fixatives discussed include formalin, glutaraldehyde, Bouin's solution, and Zenker's solution. Factors that influence fixation such as temperature, specimen size, fixation time, and choice of fixative are also reviewed.
Flow cytometry

This document provides an overview of flow cytometry. It begins by defining flow cytometry as a technique for quantitative single cell analysis that counts, examines, and sorts cells based on optical properties like light scattering and fluorescence. It then describes the basic principles, components, and working of a flow cytometer. Key components include lasers, optical filters, and detectors. Cells in suspension pass through the laser one by one, with signals detected by photodiodes and photomultiplier tubes. Applications discussed include cell sorting, apoptosis analysis using markers like Annexin V and PI, and cell cycle analysis using DNA binding dyes or BrdU incorporation. Clinical uses involve hematologic malignancy diagnosis, residual disease detection, and monitoring treatments.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)

Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) is a cytogenetic technique that can be used to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes.
Mounting media

The document discusses mounting media used to embed specimens on microscope slides under a coverslip. There are two main categories of mounting media: resinous (organic) media, which are dissolved in solvents like xylene and harden through evaporation, and aqueous media for specimens mounted in water. The ideal mounting medium is transparent, colorless, protects specimens from damage, and has a refractive index close to that of glass. Common mounting media include Canada balsam, Euparal, glycerin jelly, and aqueous solutions. Proper mounting techniques help prevent air bubbles between the specimen and coverslip.
Fixation & fixatives in histopathology, dr naveen reddy

This document provides an overview of tissue fixation techniques. It defines fixation as a process that preserves tissues in a state close to how they appeared when living. This is achieved by preventing autolysis and maintaining cellular morphology. The document discusses various types of fixatives including aldehydes, alcohols, and oxidizing agents. It also covers the aims of fixation, how different fixatives work, commonly used fixatives for different tissue and cellular components, and potential artifacts. Fixation is essential for histological examination and aims to maintain tissues for further analysis.
Staining by hematoxylin and eosin

Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is the most common histology stain. Hematoxylin stains cell nuclei blue by binding to DNA and RNA, while eosin stains cytoplasm and extracellular components pink. The staining process involves deparaffinizing tissue sections, staining with hematoxylin, differentiating with acid to remove excess stain, staining with eosin, and mounting for examination. Hematoxylin is extracted from logwood and oxidized to hematin, which binds tissue as a cationic dye with a mordant like alum. Eosin Y is the typical counterstain used to visualize cytoplasm. Together, H&E staining provides excellent contrast to study cell and
Cytogenetic abnormalities 

1. Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and abnormalities involving changes in number or structure. Key milestones included the discovery and counting of chromosomes and development of techniques like karyotyping.
2. Cytogenetic analysis involves culturing cells, arresting cell division, staining and analyzing chromosomes to identify abnormalities. It is used to diagnose conditions like Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome which are caused by gains or losses of whole chromosomes.
3. Chromosomal abnormalities can be numerical, involving extra or missing chromosomes, or structural with changes like translocations, deletions, or duplications. These abnormalities are associated with developmental delays, birth defects,
Kell blood group system

Kell blood group system most important blood group system following to ABO and Rh blood group system, particularly RhD as far as immunogenicity is concerned and Its clinical importance.
Flow cytometry

Flow cytometry allows for the quantitative and qualitative analysis of cell properties as cells flow in a fluid stream through a laser. Cells are labeled with fluorescent markers and pass through the laser one by one. Light scattering and fluorescence emission are converted to digital signals which provide information on cell size, granularity, and marker expression. Data is displayed as histograms, dot plots, or density plots to identify cell populations and phenotypes.
Frozen section and cryostat

This document discusses frozen sections and cryostats. Frozen sections are prepared without dehydration or embedding to enable rapid diagnosis within 10 minutes. They have applications in intraoperative diagnosis, enzyme histochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and other techniques. Tissue is frozen using liquid nitrogen or other cryogenic methods, turning water within the tissue to ice which acts as an embedding medium for sectioning. Cryostats maintain low temperatures, typically -20 to -30°C, for sectioning frozen tissue blocks. Optimal cutting temperatures vary by tissue type and whether the tissue is fixed.
Histochemistry

This document provides an overview of histochemistry from Sourabh Tiwary's class presentation. It defines histochemistry as identifying tissue chemical constituents using stains and microscopy. The goals of histochemistry are to present normal chemical composition and distribution with specific, detectable, and insoluble reaction products. Related disciplines like cytochemistry, enzyme histochemistry, immunocytochemistry, and in situ hybridization are discussed. Common methods for detecting substances like ions, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and saccharides are described along with applications and examples. Enzyme histochemistry and immunocytochemistry techniques are also summarized.
Fixatives 

This document discusses tissue fixation in pathology. It begins by describing the overall tissue processing steps and importance of fixation. The main types of fixatives are then outlined, including coagulant, cross-linking, and compound fixatives. Formalin and glutaraldehyde fixation are discussed in depth. Key factors that influence fixation quality like buffer pH, fixation duration, tissue size, and temperature are also summarized. The document provides a comprehensive overview of fixation in pathology.
Histopatholgy staining by suchit kumar

The document summarizes a seminar presentation on histopathology staining techniques. It discusses the routine H&E stain and provides details on the principle, reagents, and procedure. It also describes special stains used to identify substances like carbohydrates, amyloid, nucleic acids, and lipids. Specific stains covered include periodic acid Schiff, Congo red, Feulgen, methyl green pyronin, and Oil red O. The document aims to inform attendees about common and special staining methods in histopathology.
Special stains bmlt

This document discusses special stains used in histopathology, specifically stains used to identify lipids. It describes the Oil Red O and Sudan Black B stains. Oil Red O stains neutral triglycerides and lipids red and nuclei blue. It is used to identify tumors containing fat cells and fatty emboli. Sudan Black B stains fats blue-black and nuclei red. It can identify phospholipids and is used to differentiate myeloblasts from lymphoblasts in hematological disorders. Special stains are important tools to identify tissue components not visible with routine H&E staining.
What's hot (20)
Ppt on karyotyping, chromosome banding and chromosome painting.

Ppt on karyotyping, chromosome banding and chromosome painting.
Presentation on Fluorescence in-Situ Hybridization (FISH)

Presentation on Fluorescence in-Situ Hybridization (FISH)
Fixation & fixatives in histopathology, dr naveen reddy

Fixation & fixatives in histopathology, dr naveen reddy
Similar to Different techniques used in cytogenetics
Intorduction to Cytogenetics

Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, number, and abnormalities. Key techniques include karyotyping, G-banding, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and molecular cytogenetics. Several clinical cases were presented involving abnormalities detected by cytogenetic analysis, such as Down syndrome, chronic myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and acute promyelocytic leukemia. A total of 55 conventional cytogenetics studies and 15 bone marrow cytogenetics studies were performed, with various abnormalities identified. Future plans include expanding FISH and PCR testing.
Genetic Series Cytogenetics.pptx

Karyotyping involves growing cells in culture, arresting them in metaphase using colchicine, staining the chromosomes, and arranging them into a standardized pattern for analysis. The main steps are sample collection, cell culture, harvesting metaphase cells, staining (typically using Giemsa banding), and arranging the chromosomes into a karyotype based on length, centromere position, and banding pattern. Karyotyping is used for clinical diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities, prenatal testing, and research applications like identifying cancer-related translocations.
Karyotyping.pptx

Karyotyping is the process by which photographs of chromosomes are taken in order to determine the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities.
The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species or in an individual organism and for a test that detects this complement or measures the number.
Flow cytometry

This document provides an overview of flow cytometry, including its history, components, principles, and applications. Flow cytometry involves passing cells in suspension through a laser beam to measure physical properties like size and granularity, as well as cell markers detected by fluorescent antibodies. This allows identification of cell types, lineages, and abnormalities. The document discusses sample preparation, common specimens analyzed, immunophenotyping using multiple fluorochromes, and applications like DNA content analysis, erythrocyte analysis, and reticulocyte counting.
MOLECULAR AND CYTOGENETIC ANALYSIS -BMLS GENERAL &HBT-1.pptx

Molecular and cytogenetic analysis are essential techniques for diagnosing and managing hematological disorders. Key methods include DNA extraction, PCR, FISH, and next generation sequencing. Clinical applications involve investigating diseases like sickle cell anemia, thalassemias, leukemias, lymphomas, and coagulation disorders. Molecular analysis allows identification of genetic mutations and translocations that underlie these conditions and guides treatment decisions. While providing critical diagnostic information, these techniques also have limitations like risk of infection and interference from therapies.
Cytogenetics in diagnosis of disease

Chromosome abnormalities are common, occurring in 1-2% of live births and are an important cause of congenital anomalies and intellectual disability. Cytogenetic testing identifies these abnormalities and involves culturing cells to grow and arrest in metaphase, staining chromosomes for analysis. Specific indications for testing include advanced maternal age, multiple fetal abnormalities, and multiple congenital anomalies in the newborn. Analysis techniques include karyotyping, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and comparative genomic hybridization to identify abnormalities such as aneuploidies, deletions, and translocations. Common aneuploid syndromes discussed are Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome
GENETICS.pptx

This document discusses genetics and cytogenetics. It explains that human somatic cells are normally diploid containing 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. Gametes are haploid containing either 23 chromosomes. Karyotyping involves culturing cells, arresting them in metaphase, staining and analyzing chromosomes to identify pairs based on size and banding patterns. Chromosomal abnormalities can cause conditions like Down syndrome. Molecular techniques like polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and in situ hybridization are used in diagnostic pathology for conditions like cancer and genetic disorders.
Flow cytometry for cell componenet analysis

Flow cytometry is a technique that uses lasers and fluorescence to analyze physical and chemical characteristics of cells as they flow in a fluid stream. It allows simultaneous analysis of thousands of cells per second based on parameters like cell size, granularity, and detection of cell surface antigens using specific antibodies labeled with fluorochromes of different colors. Specimens suitable for analysis include blood, bone marrow, body fluids, and cell suspensions generated from tissues. Flow cytometry has various applications like immunophenotyping, DNA analysis, diagnosis of conditions like PNH, reticulated cell counting, and blood bank testing.
Molecular testing techniques in cytology specimens

Molecular testing techniques can be used on cytology specimens to facilitate cancer patient management. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is well-suited for detecting genomic abnormalities in cytology specimens. FISH involves hybridizing fluorescent probes to target sequences to visualize locations. It can detect gains, losses, amplifications, and rearrangements. A variety of cytology specimens can be used for FISH, including smears, cell blocks, and liquid-based preparations. FISH has applications in detecting abnormalities in cancers like urothelial carcinoma, breast cancer, and lymphoma.
Ezhil Final. Ppt

1. The document describes a study that isolated hepatic stem cells from human fetal liver tissue and characterized them by examining expression of liver-specific markers.
2. CD34-positive stem cells were isolated from fetal liver cells using magnetic sorting. These cells were characterized for viability, proliferation rate, and expression of alpha-fetoprotein, albumin, and cytokeratins 18 and 19.
3. The results demonstrate that the isolated CD34-positive cells expressed markers characteristic of hepatic stem cells, showing their potential for use in research and cell-based therapies for liver diseases.
Laboratory diagnosis of neoplasm

This document discusses various methods used in pathologic diagnosis of tumors, including histological examination of biopsy samples, cytological methods like exfoliative cytology and fine needle aspiration cytology, special staining techniques, immunohistochemistry, electron microscopy, tumor markers, and modern techniques like flow cytometry, in situ hybridization, and molecular diagnostic methods. The key information provided is an overview of the major diagnostic tools and techniques used in pathological analysis of tumors.
HLA typing.ppt

The document discusses HLA typing methods. It describes the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) which contains the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes. HLA typing is important for transplant matching. Methods include serology using lymphocyte cytotoxicity, as well as molecular techniques like PCR with sequence-specific primers or probes and sequence-based typing for highest resolution. Each method has advantages and limitations in resolution and reliance on viable cells. Combining methods can resolve discrepancies.
CYTOGENETICS cytogenetics abnormality.pptx

This document provides information on cytogenetics, which is the study of chromosomes and chromosome abnormalities. It begins with defining cytogenetics and outlining milestones in the field. It then describes different types of chromosomes based on centromere location. The document outlines the process of karyotyping, including sample collection, cell culturing, staining, and analysis. It also discusses other cytogenetic techniques like in situ hybridization, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and spectral karyotyping. The document concludes by covering common chromosomal abnormalities including numerical abnormalities like aneuploidy and structural abnormalities.
Genotoxicity Study (Micronucleus Test).docx

It consists of information about the in-vitro and in-vivo micronucleus test for Genotoxicity testing.
Cytogenetics iscn

This document provides an overview of cytogenetic analysis and its history and applications. It discusses how cytogenetics has evolved from microscopic analysis using banding techniques to current hybrid techniques incorporating fluorescence in situ hybridization and array-based genomic analysis. It outlines some key developments in the field including the discovery of the correct human chromosome number, identification of chromosomal abnormalities associated with conditions like Down syndrome and cancer, and advances in banding and staining techniques that enabled better chromosome identification. It concludes by describing some common indications for cytogenetic analysis and providing details on normal human karyotypes and heteromorphisms.
Applications of Flow Cytometry | Cell Analysis

Flow cytometry can be used for a variety of applications including medical research, diagnostics, and basic science. It allows for precise quantification of multiple antigens on individual cells through fluorescent labeling and detection. Key uses of flow cytometry include cell counting, sorting, analysis of characteristics and function, detection of microorganisms, biomarker analysis, and protein engineering detection. It is a routine technique in research, clinical practice, and clinical trials.
immunohistochemically and in situ hybridizati.pptx

This document discusses immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization detection of COX2 in salivary gland tumors. It provides background on immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization techniques. It then describes a study that examined COX2 expression in pleomorphic adenoma and mucoepidermoid carcinoma salivary gland tumor samples using immunohistochemistry. The study found higher COX2 expression in mucoepidermoid carcinoma samples compared to pleomorphic adenoma samples.
immunohistochemically and in situ hybridizati.pptx

This document discusses immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization detection of COX2 in salivary gland tumors. It provides background on immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization techniques. It then describes a study that examined COX2 expression in pleomorphic adenoma and mucoepidermoid carcinoma salivary gland tumor samples using immunohistochemistry. The study found higher COX2 expression in mucoepidermoid carcinoma samples compared to pleomorphic adenoma samples.
Liquid biopsy

Recent diagnostics and pathophysiology of various cancers are seen from the perspective of molecular biology.
Internship - FMRI, Gurgaon (Dec '18 - Jan '19) 

This is a presentation detailing the knowledge I acquired at my observational internship in the Clinical Pathology laboratory at Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon, India.
Similar to Different techniques used in cytogenetics (20)
MOLECULAR AND CYTOGENETIC ANALYSIS -BMLS GENERAL &HBT-1.pptx

MOLECULAR AND CYTOGENETIC ANALYSIS -BMLS GENERAL &HBT-1.pptx
Molecular testing techniques in cytology specimens

Molecular testing techniques in cytology specimens
immunohistochemically and in situ hybridizati.pptx

immunohistochemically and in situ hybridizati.pptx
immunohistochemically and in situ hybridizati.pptx

immunohistochemically and in situ hybridizati.pptx
Recently uploaded
waterlessdyeingtechnolgyusing carbon dioxide chemicalspdf

The technology uses reclaimed CO₂ as the dyeing medium in a closed loop process. When pressurized, CO₂ becomes supercritical (SC-CO₂). In this state CO₂ has a very high solvent power, allowing the dye to dissolve easily.
EWOCS-I: The catalog of X-ray sources in Westerlund 1 from the Extended Weste...

Context. With a mass exceeding several 104 M⊙ and a rich and dense population of massive stars, supermassive young star clusters
represent the most massive star-forming environment that is dominated by the feedback from massive stars and gravitational interactions
among stars.
Aims. In this paper we present the Extended Westerlund 1 and 2 Open Clusters Survey (EWOCS) project, which aims to investigate
the influence of the starburst environment on the formation of stars and planets, and on the evolution of both low and high mass stars.
The primary targets of this project are Westerlund 1 and 2, the closest supermassive star clusters to the Sun.
Methods. The project is based primarily on recent observations conducted with the Chandra and JWST observatories. Specifically,
the Chandra survey of Westerlund 1 consists of 36 new ACIS-I observations, nearly co-pointed, for a total exposure time of 1 Msec.
Additionally, we included 8 archival Chandra/ACIS-S observations. This paper presents the resulting catalog of X-ray sources within
and around Westerlund 1. Sources were detected by combining various existing methods, and photon extraction and source validation
were carried out using the ACIS-Extract software.
Results. The EWOCS X-ray catalog comprises 5963 validated sources out of the 9420 initially provided to ACIS-Extract, reaching a
photon flux threshold of approximately 2 × 10−8 photons cm−2
s
−1
. The X-ray sources exhibit a highly concentrated spatial distribution,
with 1075 sources located within the central 1 arcmin. We have successfully detected X-ray emissions from 126 out of the 166 known
massive stars of the cluster, and we have collected over 71 000 photons from the magnetar CXO J164710.20-455217.
Randomised Optimisation Algorithms in DAPHNE

Slides from talk:
Aleš Zamuda: Randomised Optimisation Algorithms in DAPHNE .
Austrian-Slovenian HPC Meeting 2024 – ASHPC24, Seeblickhotel Grundlsee in Austria, 10–13 June 2024
https://ashpc.eu/
Shallowest Oil Discovery of Turkiye.pptx

The Petroleum System of the Çukurova Field - the Shallowest Oil Discovery of Türkiye, Adana
ESR spectroscopy in liquid food and beverages.pptx

With increasing population, people need to rely on packaged food stuffs. Packaging of food materials requires the preservation of food. There are various methods for the treatment of food to preserve them and irradiation treatment of food is one of them. It is the most common and the most harmless method for the food preservation as it does not alter the necessary micronutrients of food materials. Although irradiated food doesn’t cause any harm to the human health but still the quality assessment of food is required to provide consumers with necessary information about the food. ESR spectroscopy is the most sophisticated way to investigate the quality of the food and the free radicals induced during the processing of the food. ESR spin trapping technique is useful for the detection of highly unstable radicals in the food. The antioxidant capability of liquid food and beverages in mainly performed by spin trapping technique.
(June 12, 2024) Webinar: Development of PET theranostics targeting the molecu...

(June 12, 2024) Webinar: Development of PET theranostics targeting the molecu...Scintica Instrumentation
Targeting Hsp90 and its pathogen Orthologs with Tethered Inhibitors as a Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategy for cancer and infectious diseases with Dr. Timothy Haystead.在线办理(salfor毕业证书)索尔福德大学毕业证毕业完成信一模一样

学校原件一模一样【微信:741003700 】《(salfor毕业证书)索尔福德大学毕业证》【微信:741003700 】学位证,留信认证(真实可查,永久存档)原件一模一样纸张工艺/offer、雅思、外壳等材料/诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本,帮您解决无法毕业带来的各种难题!外壳,原版制作,诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本。行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备。十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,包您满意。
本公司拥有海外各大学样板无数,能完美还原。
1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问Q/微741003700
【主营项目】
一.毕业证【q微741003700】成绩单、使馆认证、教育部认证、雅思托福成绩单、学生卡等!
二.真实使馆公证(即留学回国人员证明,不成功不收费)
三.真实教育部学历学位认证(教育部存档!教育部留服网站永久可查)
四.办理各国各大学文凭(一对一专业服务,可全程监控跟踪进度)
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证【q/微741003700】
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
The debris of the ‘last major merger’ is dynamically young

The Milky Way’s (MW) inner stellar halo contains an [Fe/H]-rich component with highly eccentric orbits, often referred to as the
‘last major merger.’ Hypotheses for the origin of this component include Gaia-Sausage/Enceladus (GSE), where the progenitor
collided with the MW proto-disc 8–11 Gyr ago, and the Virgo Radial Merger (VRM), where the progenitor collided with the
MW disc within the last 3 Gyr. These two scenarios make different predictions about observable structure in local phase space,
because the morphology of debris depends on how long it has had to phase mix. The recently identified phase-space folds in Gaia
DR3 have positive caustic velocities, making them fundamentally different than the phase-mixed chevrons found in simulations
at late times. Roughly 20 per cent of the stars in the prograde local stellar halo are associated with the observed caustics. Based
on a simple phase-mixing model, the observed number of caustics are consistent with a merger that occurred 1–2 Gyr ago.
We also compare the observed phase-space distribution to FIRE-2 Latte simulations of GSE-like mergers, using a quantitative
measurement of phase mixing (2D causticality). The observed local phase-space distribution best matches the simulated data
1–2 Gyr after collision, and certainly not later than 3 Gyr. This is further evidence that the progenitor of the ‘last major merger’
did not collide with the MW proto-disc at early times, as is thought for the GSE, but instead collided with the MW disc within
the last few Gyr, consistent with the body of work surrounding the VRM.
11.1 Role of physical biological in deterioration of grains.pdf

Storagedeteriorationisanyformoflossinquantityandqualityofbio-materials.
Themajorcausesofdeteriorationinstorage
•Physical
•Biological
•Mechanical
•Chemical
Storageonlypreservesquality.Itneverimprovesquality.
Itisadvisabletostartstoragewithqualityfoodproduct.Productwithinitialpoorqualityquicklydepreciates
ESA/ACT Science Coffee: Diego Blas - Gravitational wave detection with orbita...

ESA/ACT Science Coffee: Diego Blas - Gravitational wave detection with orbita...Advanced-Concepts-Team
Presentation in the Science Coffee of the Advanced Concepts Team of the European Space Agency on the 07.06.2024.
Speaker: Diego Blas (IFAE/ICREA)
Title: Gravitational wave detection with orbital motion of Moon and artificial
Abstract:
In this talk I will describe some recent ideas to find gravitational waves from supermassive black holes or of primordial origin by studying their secular effect on the orbital motion of the Moon or satellites that are laser ranged.Applied Science: Thermodynamics, Laws & Methodology.pdf

When I was asked to give a companion lecture in support of ‘The Philosophy of Science’ (https://shorturl.at/4pUXz) I decided not to walk through the detail of the many methodologies in order of use. Instead, I chose to employ a long standing, and ongoing, scientific development as an exemplar. And so, I chose the ever evolving story of Thermodynamics as a scientific investigation at its best.
Conducted over a period of >200 years, Thermodynamics R&D, and application, benefitted from the highest levels of professionalism, collaboration, and technical thoroughness. New layers of application, methodology, and practice were made possible by the progressive advance of technology. In turn, this has seen measurement and modelling accuracy continually improved at a micro and macro level.
Perhaps most importantly, Thermodynamics rapidly became a primary tool in the advance of applied science/engineering/technology, spanning micro-tech, to aerospace and cosmology. I can think of no better a story to illustrate the breadth of scientific methodologies and applications at their best.
8.Isolation of pure cultures and preservation of cultures.pdf

Isolation of pure culture, its various method.
The binding of cosmological structures by massless topological defects

Assuming spherical symmetry and weak field, it is shown that if one solves the Poisson equation or the Einstein field
equations sourced by a topological defect, i.e. a singularity of a very specific form, the result is a localized gravitational
field capable of driving flat rotation (i.e. Keplerian circular orbits at a constant speed for all radii) of test masses on a thin
spherical shell without any underlying mass. Moreover, a large-scale structure which exploits this solution by assembling
concentrically a number of such topological defects can establish a flat stellar or galactic rotation curve, and can also deflect
light in the same manner as an equipotential (isothermal) sphere. Thus, the need for dark matter or modified gravity theory is
mitigated, at least in part.
Compexometric titration/Chelatorphy titration/chelating titration

Classification
Metal ion ion indicators
Masking and demasking reagents
Estimation of Magnisium sulphate
Calcium gluconate
Complexometric Titration/ chelatometry titration/chelating titration, introduction, Types-
1.Direct Titration
2.Back Titration
3.Replacement Titration
4.Indirect Titration
Masking agent, Demasking agents
formation of complex
comparition between masking and demasking agents,
Indicators/Metal ion indicators/ Metallochromic indicators/pM indicators,
Visual Technique,PM indicators (metallochromic), Indicators of pH, Redox Indicators
Instrumental Techniques-Photometry
Potentiometry
Miscellaneous methods.
Complex titration with EDTA.
The cost of acquiring information by natural selection

This is a short talk that I gave at the Banff International Research Station workshop on Modeling and Theory in Population Biology. The idea is to try to understand how the burden of natural selection relates to the amount of information that selection puts into the genome.
It's based on the first part of this research paper:
The cost of information acquisition by natural selection
Ryan Seamus McGee, Olivia Kosterlitz, Artem Kaznatcheev, Benjamin Kerr, Carl T. Bergstrom
bioRxiv 2022.07.02.498577; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.02.498577
Katherine Romanak - Geologic CO2 Storage.pdf

Presented at June 6-7 Texas Alliance of Groundwater Districts Business Meeting
20240520 Planning a Circuit Simulator in JavaScript.pptx

Evaporation step counter work. I have done a physical experiment.
(Work in progress.)
Recently uploaded (20)
waterlessdyeingtechnolgyusing carbon dioxide chemicalspdf

waterlessdyeingtechnolgyusing carbon dioxide chemicalspdf
EWOCS-I: The catalog of X-ray sources in Westerlund 1 from the Extended Weste...

EWOCS-I: The catalog of X-ray sources in Westerlund 1 from the Extended Weste...
ESR spectroscopy in liquid food and beverages.pptx

ESR spectroscopy in liquid food and beverages.pptx
(June 12, 2024) Webinar: Development of PET theranostics targeting the molecu...

(June 12, 2024) Webinar: Development of PET theranostics targeting the molecu...
The debris of the ‘last major merger’ is dynamically young

The debris of the ‘last major merger’ is dynamically young
aziz sancar nobel prize winner: from mardin to nobel

aziz sancar nobel prize winner: from mardin to nobel
11.1 Role of physical biological in deterioration of grains.pdf

11.1 Role of physical biological in deterioration of grains.pdf
ESA/ACT Science Coffee: Diego Blas - Gravitational wave detection with orbita...

ESA/ACT Science Coffee: Diego Blas - Gravitational wave detection with orbita...
Applied Science: Thermodynamics, Laws & Methodology.pdf

Applied Science: Thermodynamics, Laws & Methodology.pdf
8.Isolation of pure cultures and preservation of cultures.pdf

8.Isolation of pure cultures and preservation of cultures.pdf
The binding of cosmological structures by massless topological defects

The binding of cosmological structures by massless topological defects
Compexometric titration/Chelatorphy titration/chelating titration

Compexometric titration/Chelatorphy titration/chelating titration
The cost of acquiring information by natural selection

The cost of acquiring information by natural selection
20240520 Planning a Circuit Simulator in JavaScript.pptx

20240520 Planning a Circuit Simulator in JavaScript.pptx
Different techniques used in cytogenetics
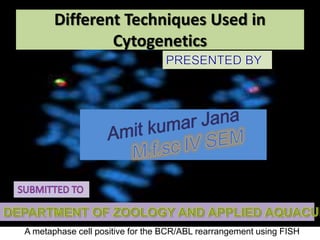
- 1. A metaphase cell positive for the BCR/ABL rearrangement using FISH Different Techniques Used in Cytogenetics
- 2. Introduction & Definition • Cytogenetics is a branch of genetics that is concerned with the study of the structure and function of the cell, especially the chromosomes. It includes routine analysis of G- banded chromosomes, other cytogenetic banding techniques, as well as molecular cytogenetics such as Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) and Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH).
- 3. History • Chromosomes were first observed in plant cells by Karl Wilhelm von Nägeli in 1842. Their behavior in animal (salamander) cells was described by Walther Flemming, the discoverer of mitosis, in 1882. The name was coined by another German anatomist, von Waldeyer in 1888. • In science books, the number of human chromosomes remained at 48 for over thirty years. New techniques were needed to correct this error. Joe Hin Tjio working in Albert Levan’s lab was responsible for finding the approach: • Using cells in culture • Pre-treating cells in a hypotonic solution, which swells them and spreads the chromosomes • Arresting mitosis in metaphase by a solution of colchicine • Squashing the preparation on the slide forcing the chromosomes into a single plane • Cutting up a photomicrograph and arranging the result into an indisputable karyogram.It took until 1956 until it became generally accepted that the karyotype of man included only 46 chromosomes.Rather interestingly, the greatapes have 48 chromosomes. Human chromosome 2was formed by a merger of ancestral chromosomes, reducing the number.
- 4. Techniques 1. Karyotyping 1. Slide preparation 2. Analysis 2. Fluorescent in situ hybridization 1. Slide preparation 2. Analysis
- 5. Techniques Karyotyping • Routine chromosome analysis (Karyotyping) refers to analysis of metaphase chromosomes which have been banded using trypsin followed by Giemsa, Leishmanns, or a mixture of the two. Several chromosome-banding techniques are used in cytogenetics laboratories. Quinacrine banding (Q-banding) was the first staining method used to produce specific banding patterns. This method requires a fluorescence microscope and is no longer as widely used as Giemsa banding (G-banding). Reverse banding, or R-banding, requires heat treatment and reverses the usual black-and-white pattern that is seen in G-bands and Q-bands. This method is particularly helpful for staining the distal ends of chromosomes. Other staining techniques include C-banding.
- 6. Slide Preparation • Cells from bone marrow, blood, amniotic fluid, cord blood, tumor, and tissues (including skin, umbilical cord, chorionic villi, liver, and many other organs) can be cultured using standard cell culture techniques in order to increase their number. • A mitotic inhibitor (colchicine, colcemid) is then added to the culture. This stops cell division at mitosis which allows an increased yield of mitotic cells for analysis. The cells are then centrifuged and media and mitotic inhibitor are removed, and replaced with a hypotonic solution. This causes the white blood cells or fibroblasts to swell so that the chromosomes will spread when added to a slide as well as lyses the red blood cells. After the cells have been allowed to sit in hypotonic solution, Carnoy's fixative (3:1 methanol to glacial acetic acid) is added. This kills the cells and hardens the nuclei of the remaining white blood cells. The cells are generally fixed repeatedly to remove any debris or remaining red blood cells. The cell suspension is then dropped onto specimen slides. After aging the slides in an oven or waiting a few days they are ready for banding and analysis.
- 7. Analysis Analysis of banded chromosomes is done at a microscope by a clinical laboratory specialist in cytogenetics (CLSp(CG)). Generally 20 cells are analyzed which is enough to rule out mosaicism to an acceptable level. The results are summarized and given to a board-certified cytogeneticist for review, and to write an interpretation taking into account the patients previous history and other clinical findings.
- 8. Fluorescent in situ hybridization Fluorescent in situ hybridization refers to using fluorescently labeled probe to hybridize to cytogenetic cell preparations. In addition to standard preparations FISH can also be performed on: 1. bone marrow smears 2. blood smears 3. paraffin embedded tissue preparations 4. enzymatically dissociated tissue samples 5. uncultured bone marrow 6. uncultured amniocytes 7. cytospin preparations Fig of FSH
- 9. Slide preparation • The slide is aged using a salt solution usually consisting of 2X SSC (salt, sodium citrate). The slides are then dehydrated in ethanol, and the probe mixture is added. The sample DNA and the probe DNA are then co-denatured using a heated plate and allowed to re-anneal for at least 4 hours. The slides are then washed to remove excess unbound probe, and counterstained with 4',6-Diamidino-2- phenylindole (DAPI) or propidium iodide.
- 10. Analysis • Analysis of FISH specimens is done by fluorescence microscopy by a clinical laboratory specialist in cytogenetics. For oncology generally a large number of interphase cells are scored in order to rule out low-level residual disease, generally between 200 and 1,000 cells are counted and scored. For congenital problems usually 20 metaphase cells are scored.
- 11. Future of cytogenetics • Advances now focus on molecular cytogenetics including automated systems for counting the results of standard FISH preparations and techniques for virtual karyotyping, such as comparative genomic hybridization arrays, CGH and Single nucleotide polymorphism arrays.
- 12. Conclusion • So far, no system can classify banded chromosomes as robustly and accurately as a skilled cytogeneticist, despite the millions of dollars that have been invested in automated karyotype analysis since 1968. Currently cytogenetics is paving its way into the molecular approaches in deciphering the structure, function and evolution of chromosomes. Still,conventional cytogenetics where routine banding techniques are employed remains a simple and popular technique to get an overview of the human genome. Routine banded karyotype analysiscan now be combined with M-FISH and other molecular techniques leading to moreprecise detection of various syndromes in children.