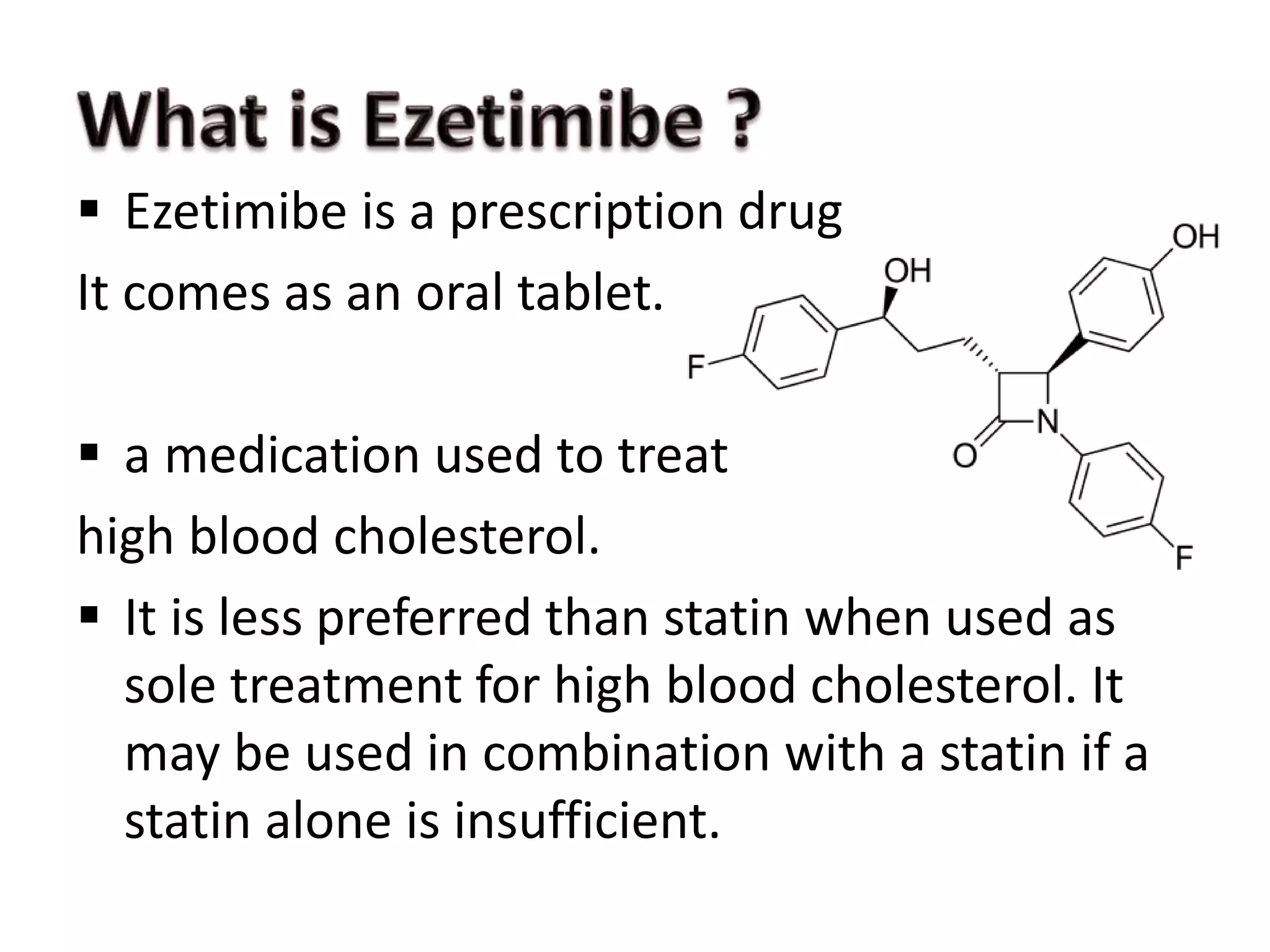
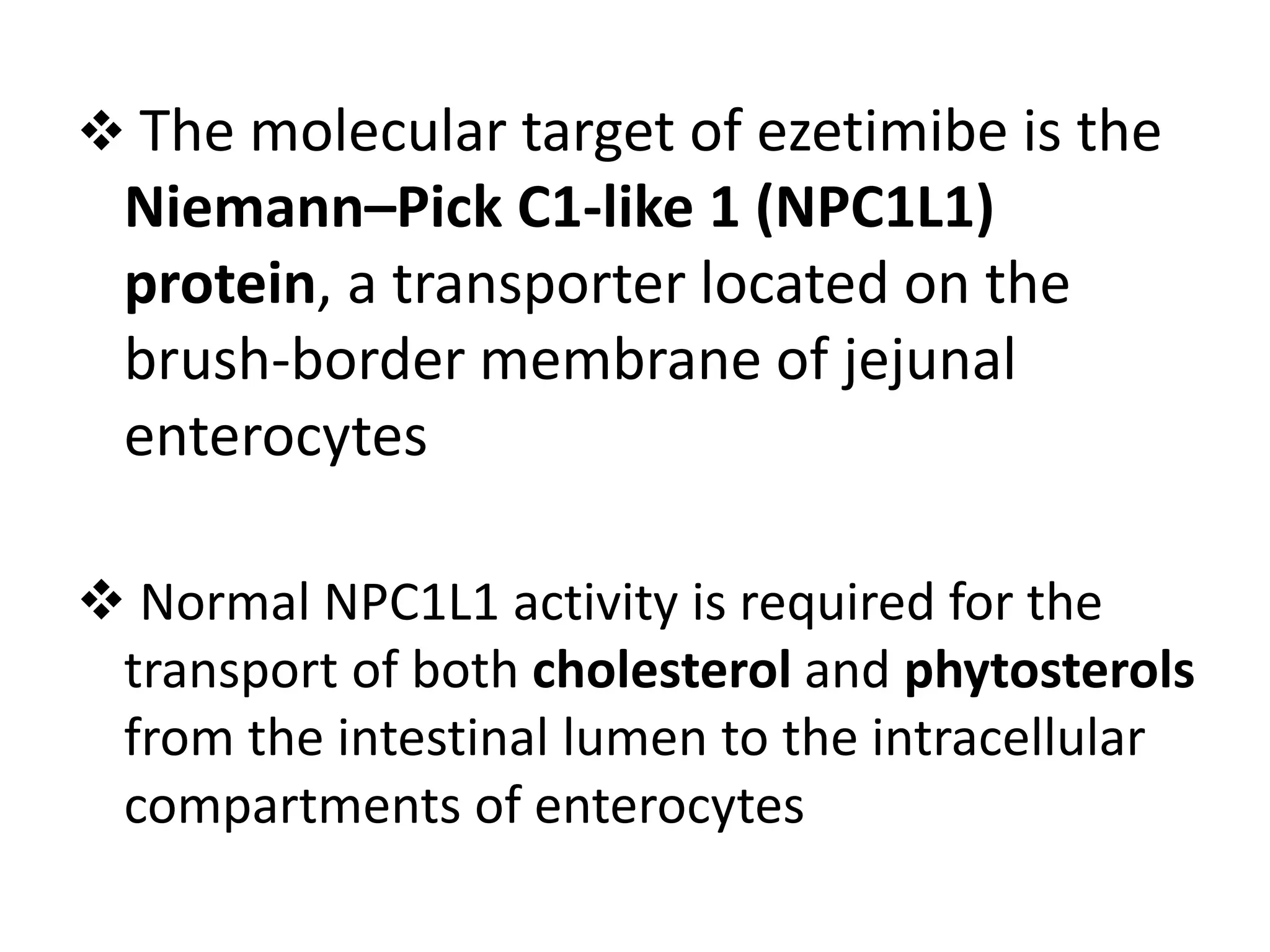
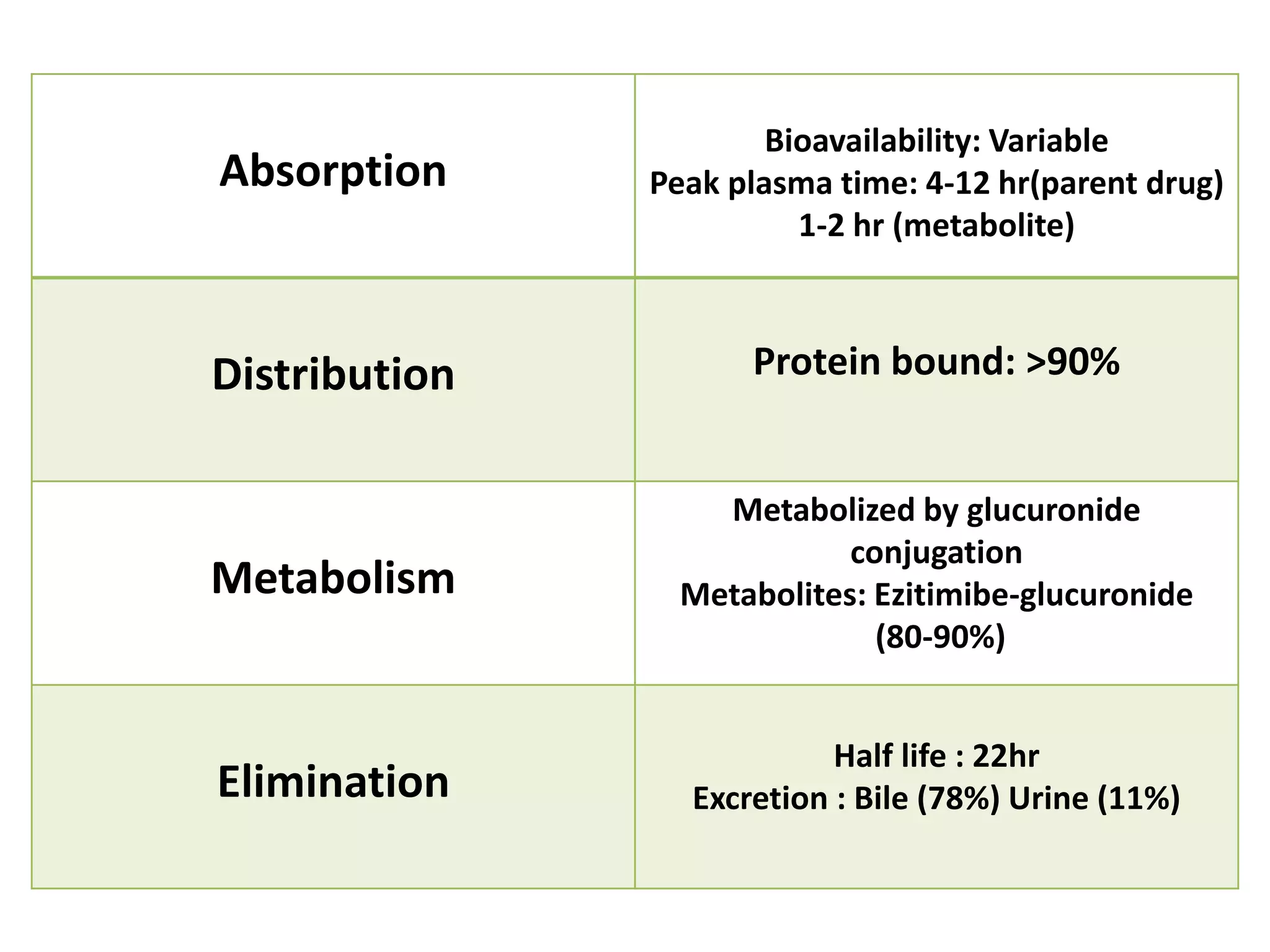
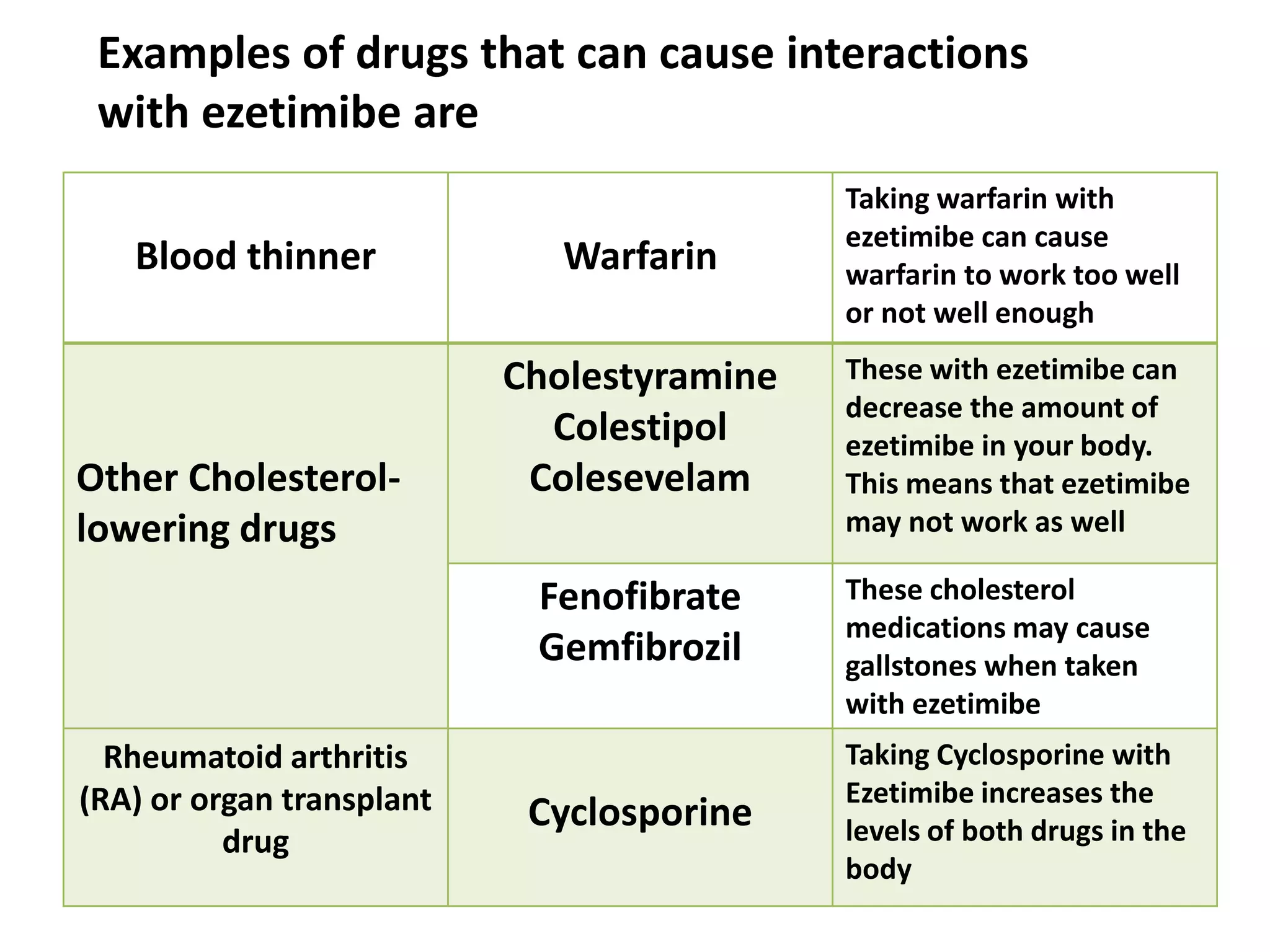
Ezetimibe is a medication used to treat high cholesterol. It works by inhibiting the absorption of cholesterol from the small intestine. Common side effects include diarrhea and stuffy nose. Serious side effects include liver problems and muscle damage. Ezetimibe should not be used in pregnant women or children under 10 due to lack of safety studies. It may interact with other cholesterol medications or blood thinners, so monitoring is required when taking multiple drugs.