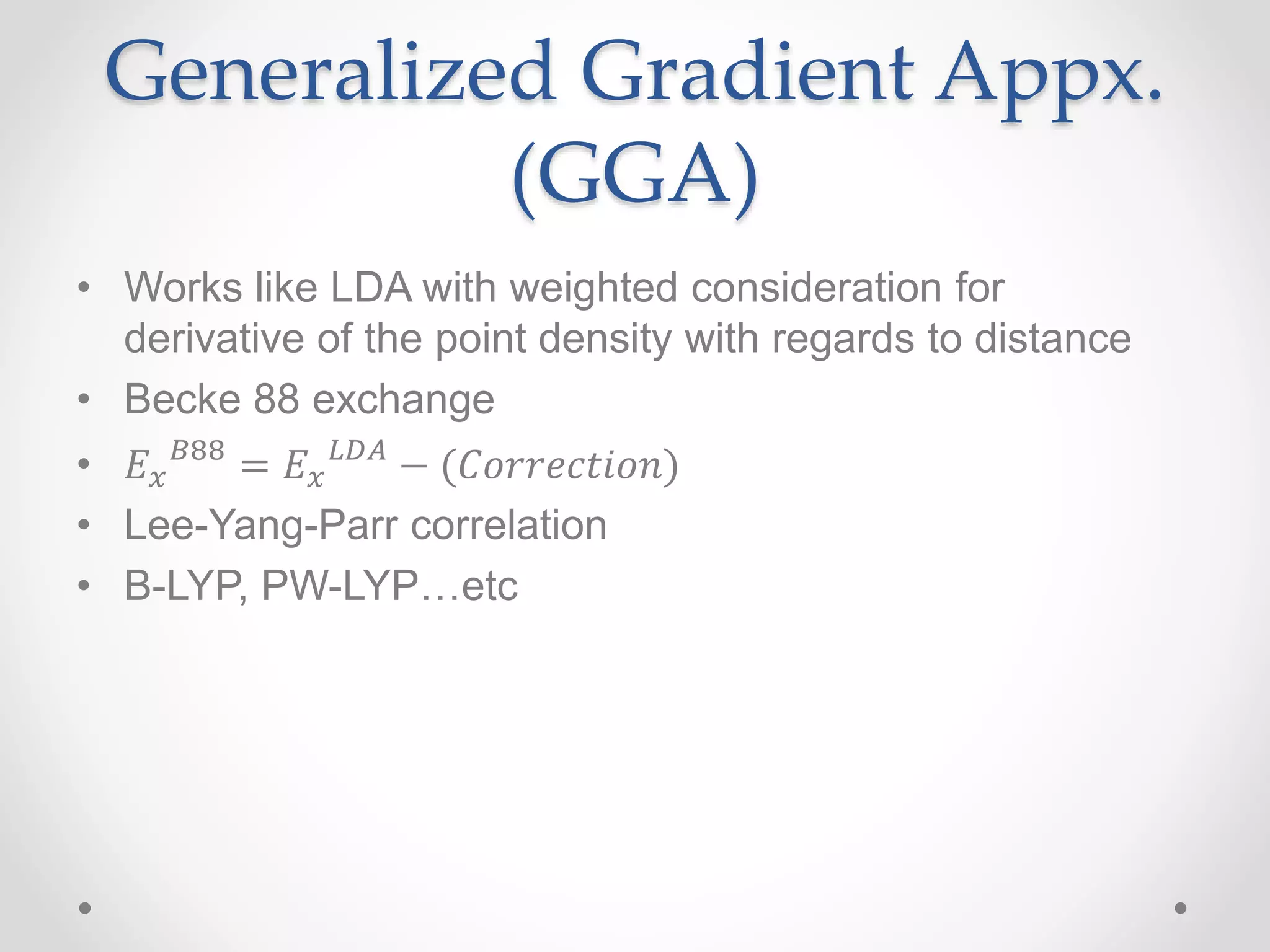
Density functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanics modeling method used in physics and chemistry to investigate the electronic structure of molecules and condensed phases. DFT was awarded the 1998 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. DFT approximates the complex quantum many-body problem by considering electron density as a basic variable instead of wave functions. Common approximations include the local density approximation (LDA) and generalized gradient approximation (GGA), which include additional information about the density gradient. DFT is widely used today due to its good accuracy and scaling better than other computational methods.



![Mathematical Model
• SE: Ĥψ= [T+V+U]ψ= Eψ
• T=e kinetic Energy
• V=e-N attraction
• Electron-electron interaction (U) prevents separation into
single particle wave function for exact solution
• (HK)DFT: E=Ê[ρ(→v)]
• Ê is a single unique functional, but probably extremely
complex
• Approximated functionals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e45a329a-f368-408e-873f-71889a0e4f38-170119090638/75/Density-Functional-Theory-5-2048.jpg)