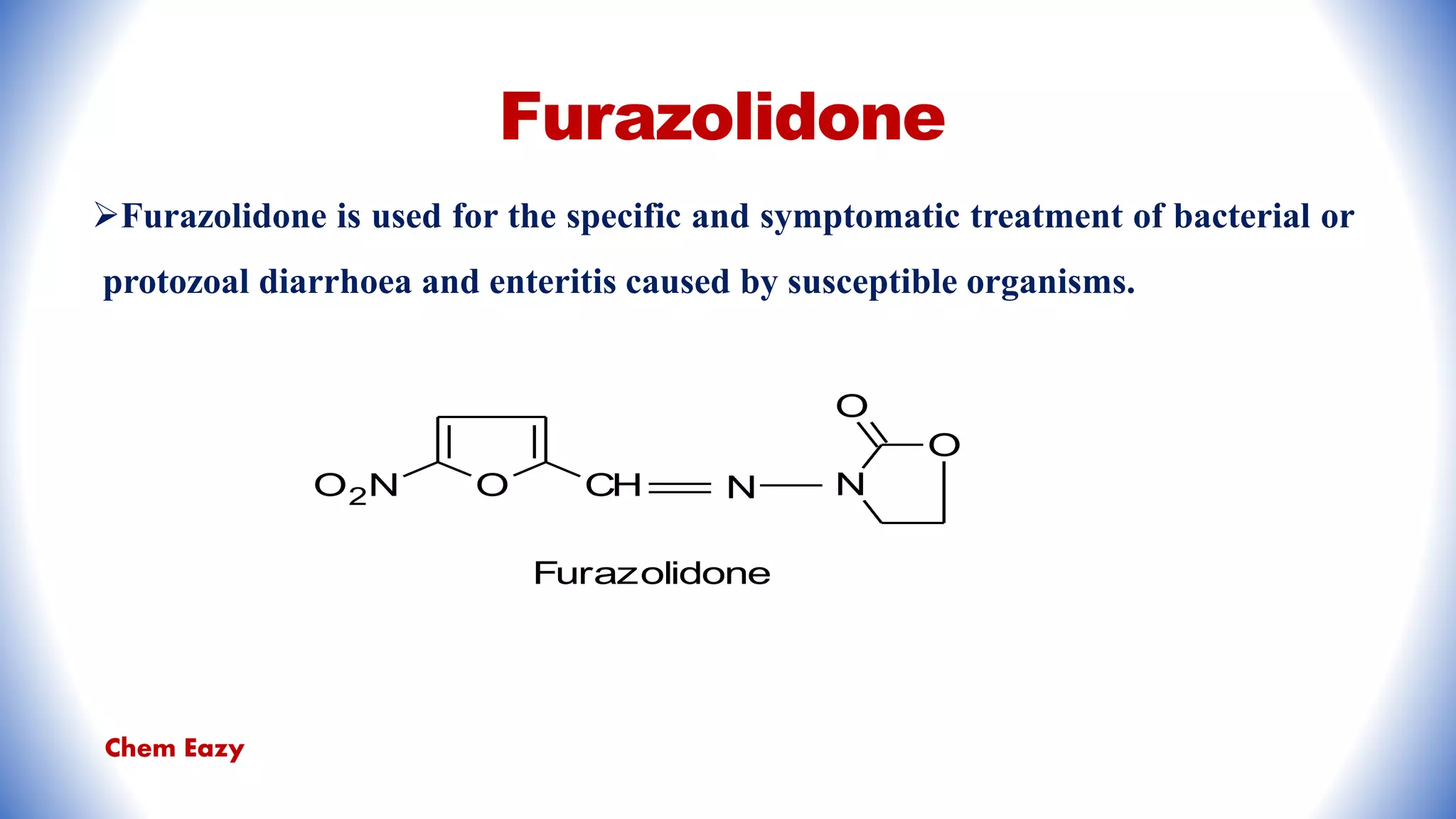
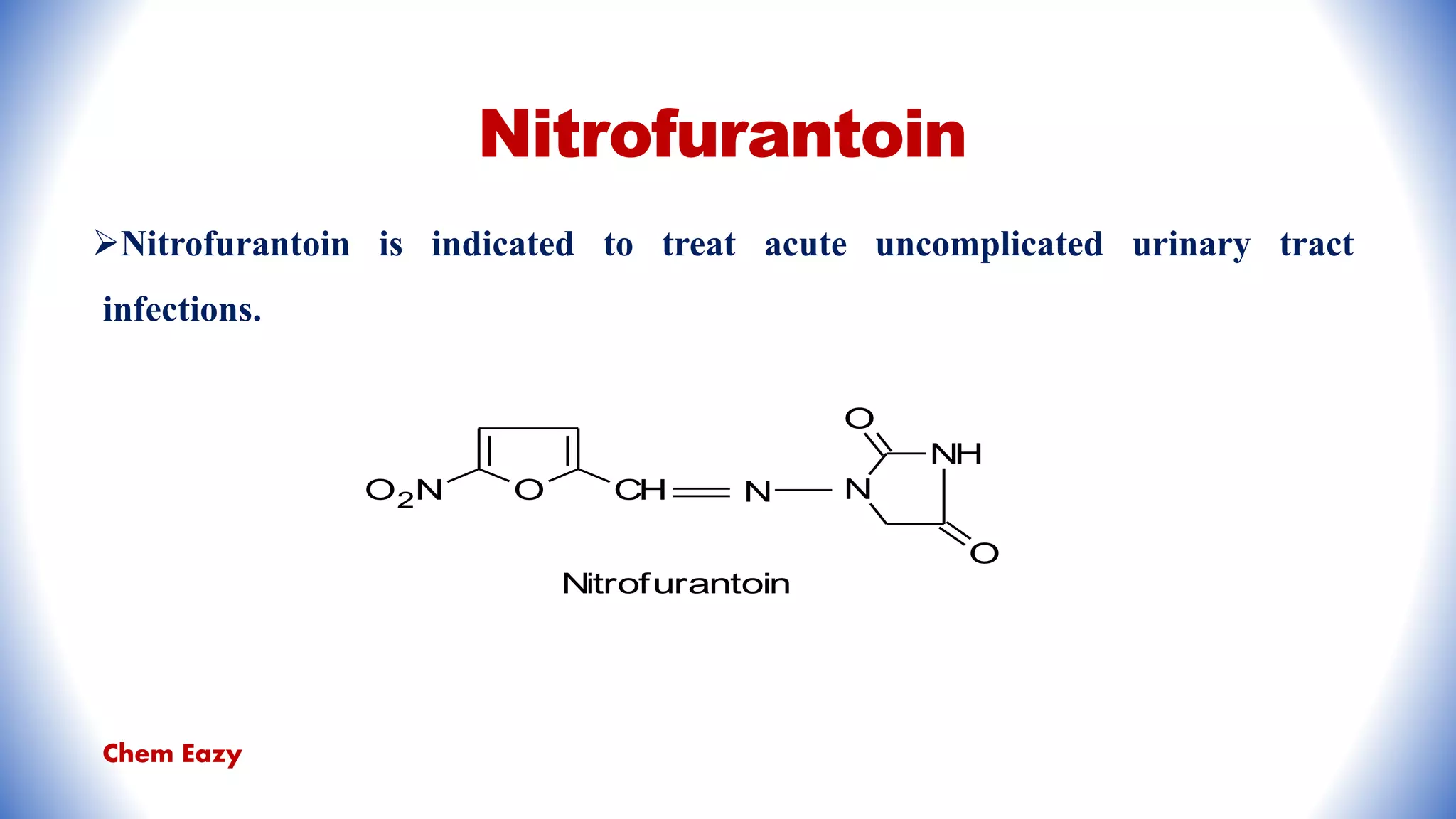
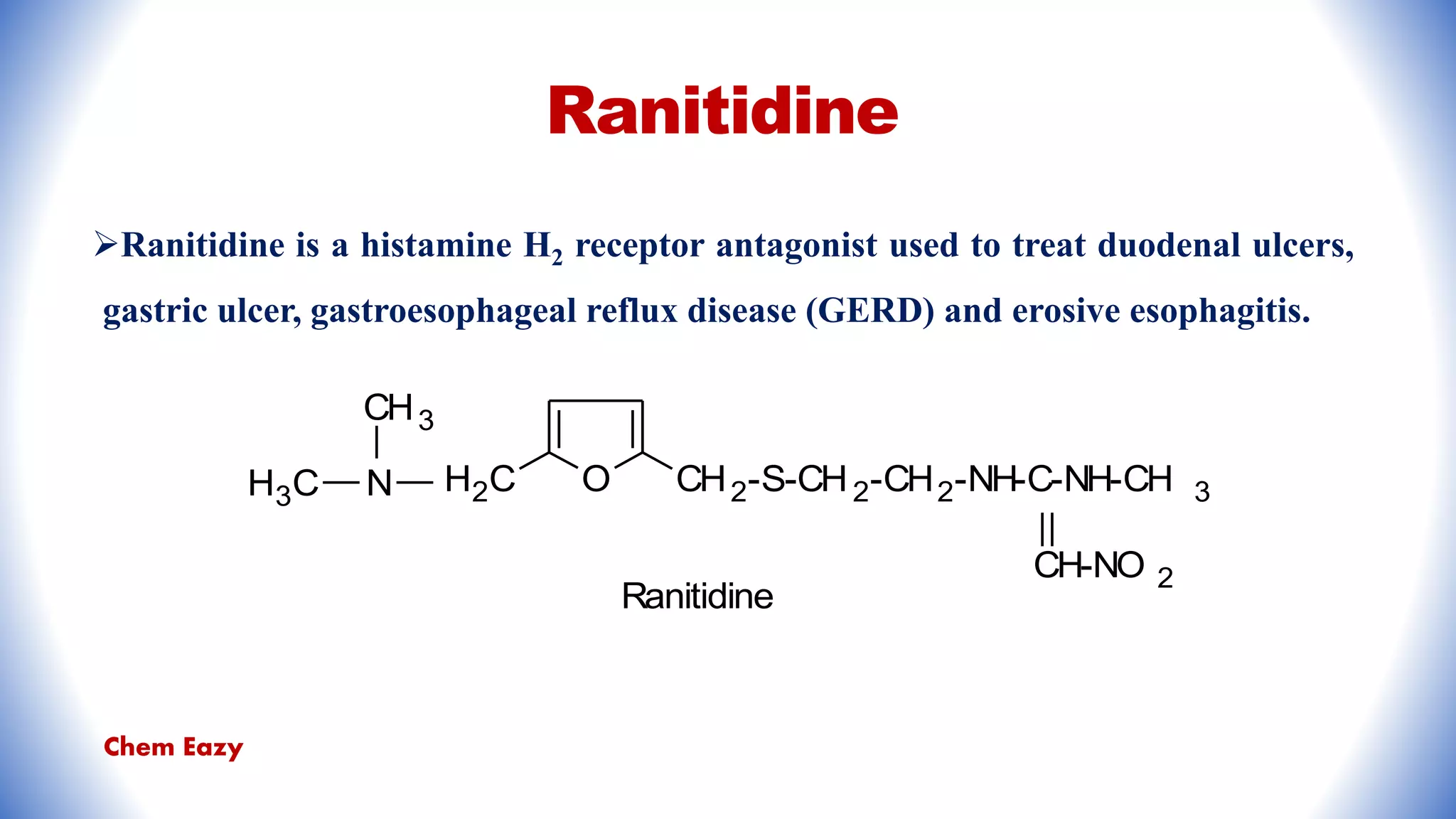
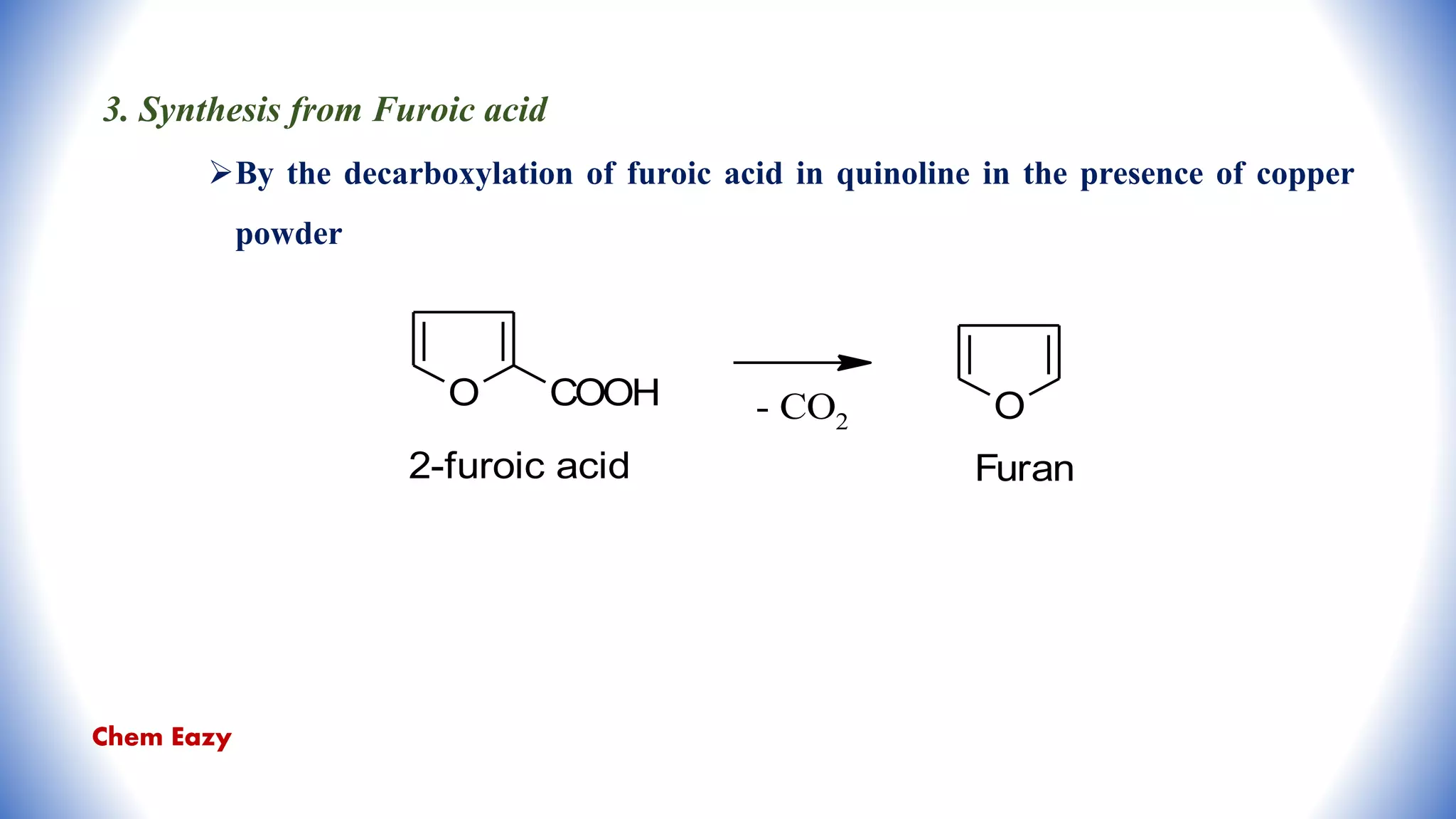
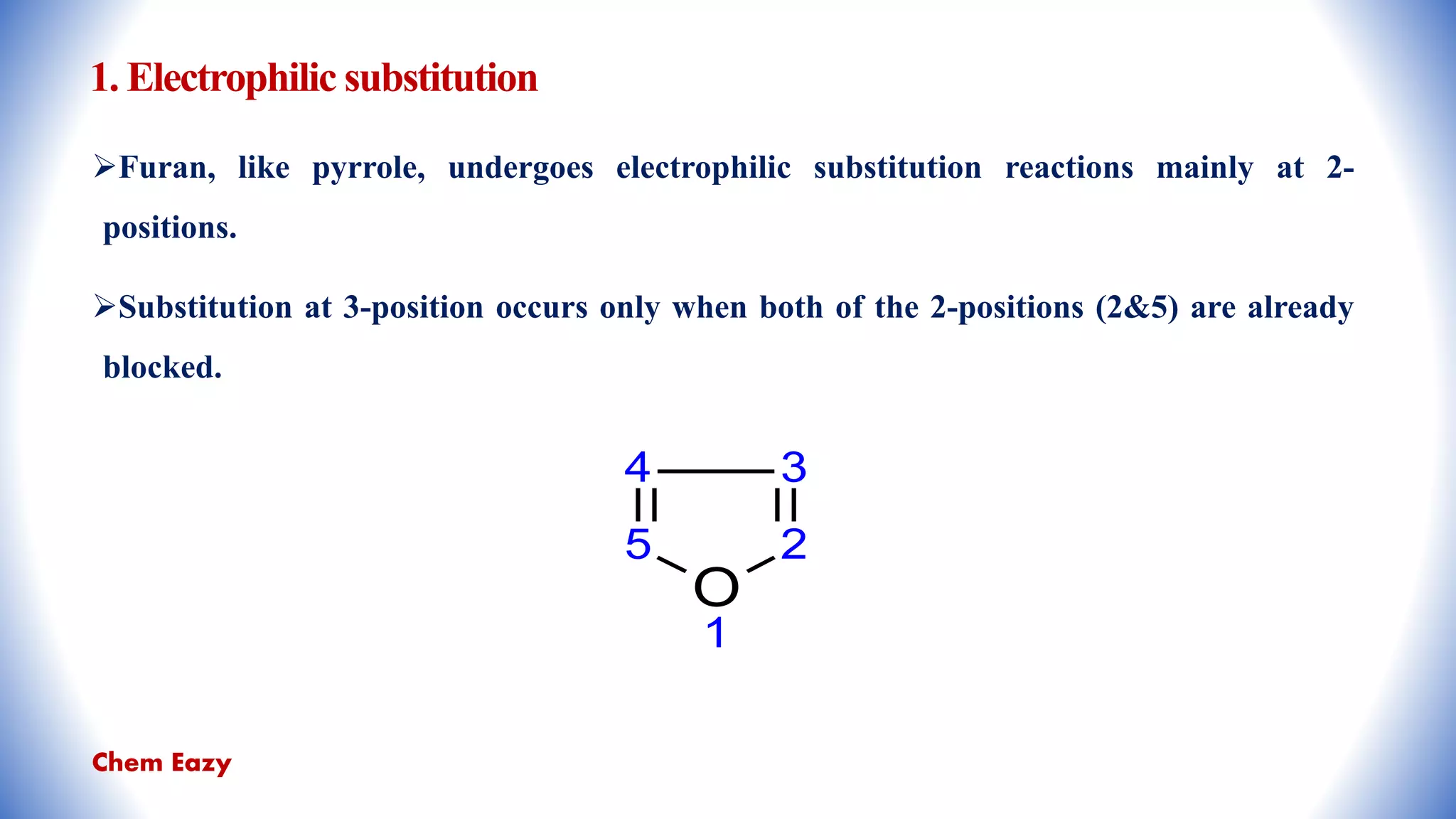
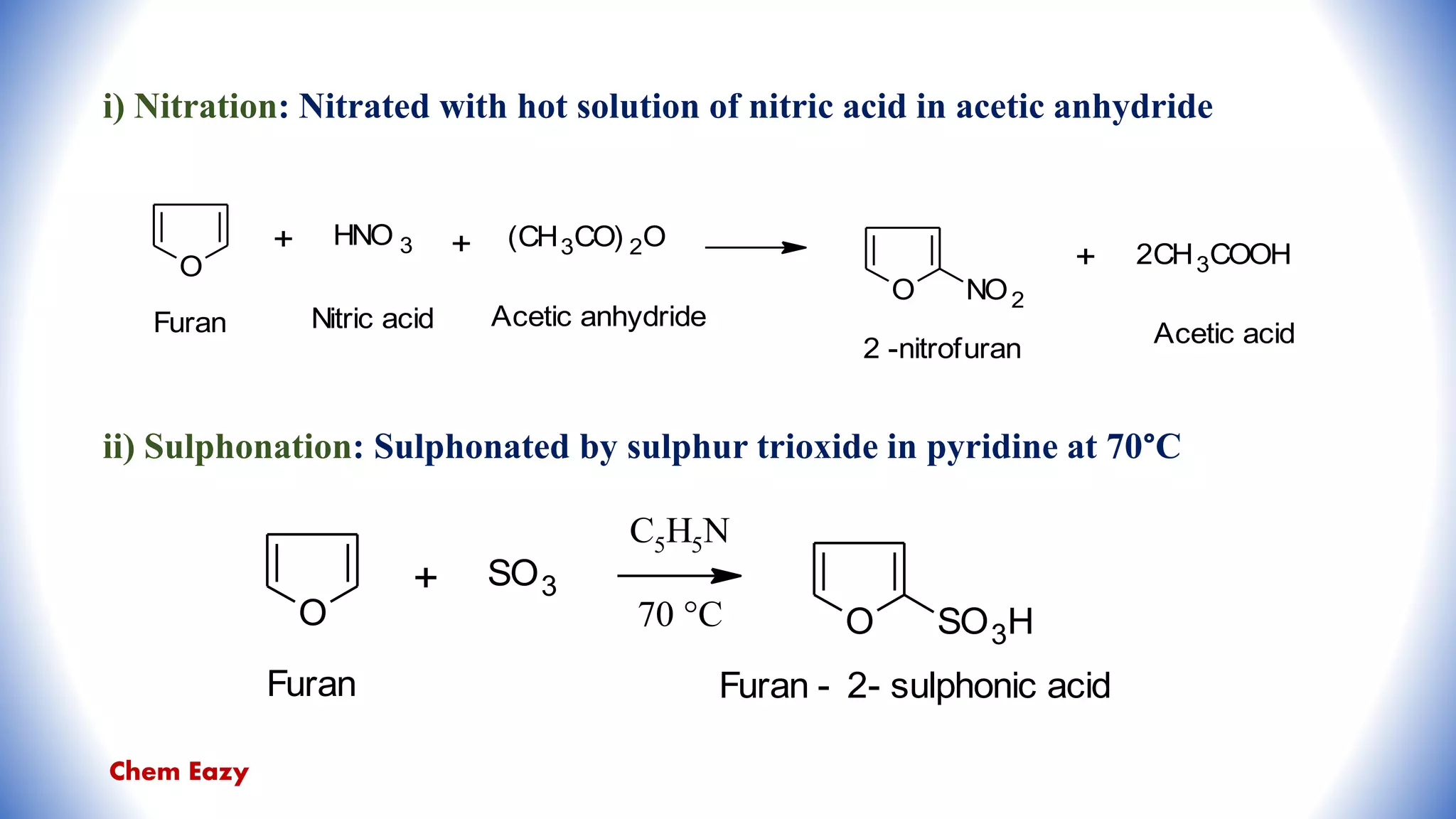
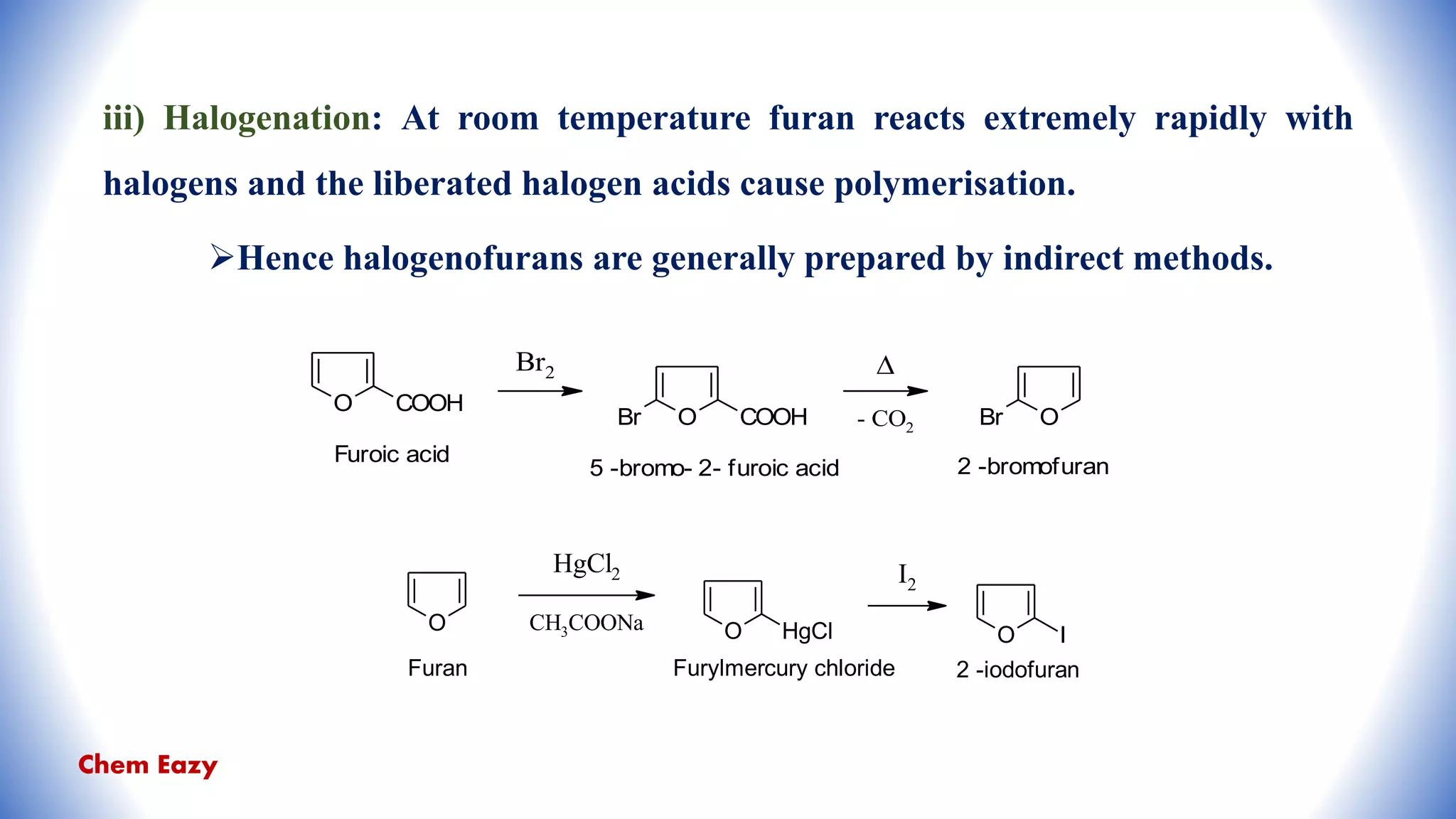
The document outlines the synthesis, reactions, and medicinal uses of furan, a heterocyclic compound. It details various synthesis methods including those from mucic acid, furfural, and furoic acid, and describes characteristic reactions such as electrophilic substitutions and oxidation. Additionally, it lists medicinal applications of furan derivatives such as furazolidone, nitrofurazone, nitrofurantoin, ranitidine, and furosemide.

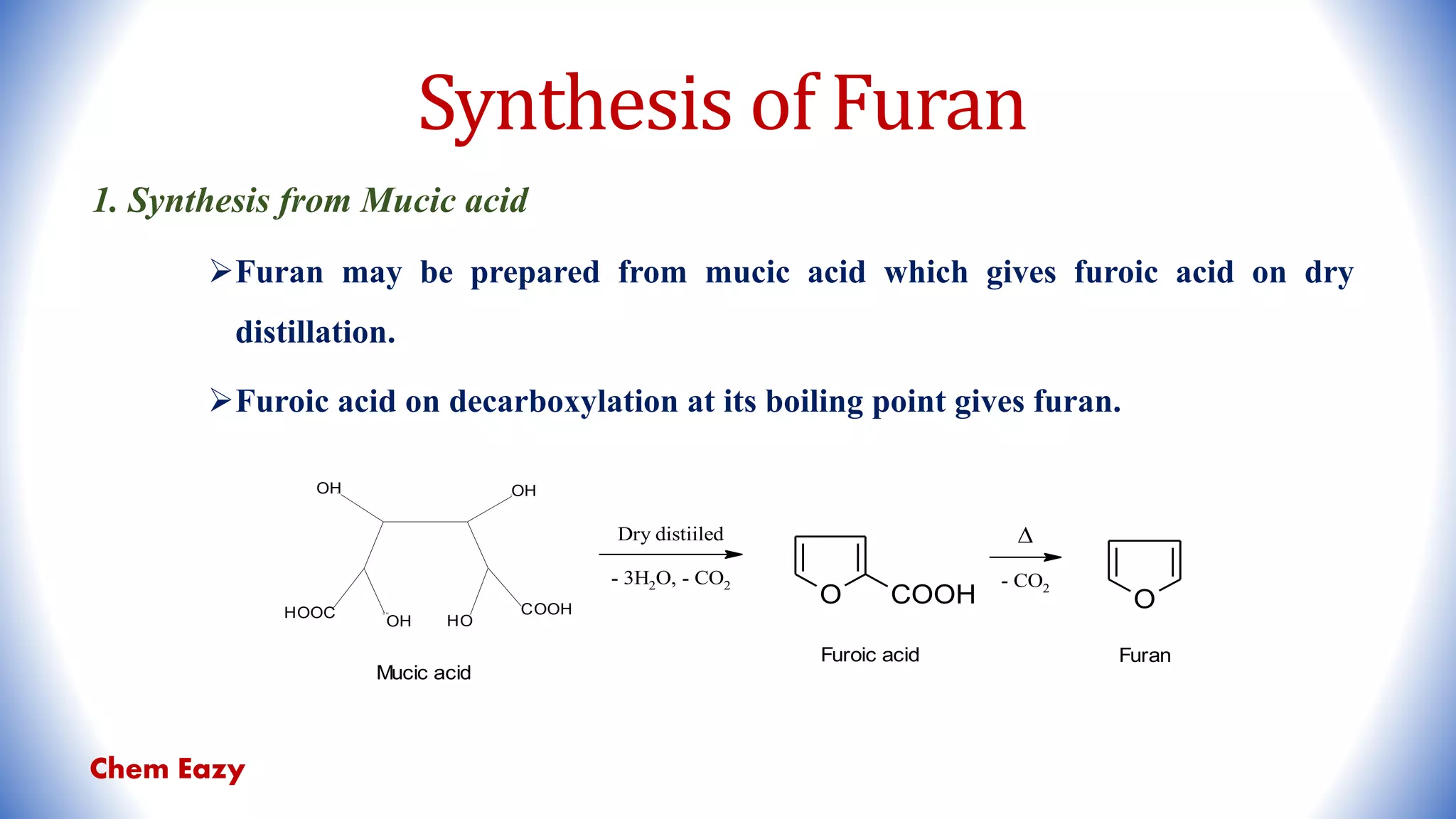
![2. Synthesis from Furfural
Furfural on oxidation with potassium dichromate gives furoic acid which on
subsequent decarboxylation at 200 - 300°C yields furan.
By decarboxylation of furfural in steam in the presence of silver oxide catalyst.
O CHO
[O]
K2Cr2O7/H+
O COOH
2-furoic acid
Furfural
- CO2 O
Furan
O CHO
Furfural
Ag2O
- CO O
Furan
Chem Eazy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heterocycliccompounds-furan-synthesisoffuran-characteristicreactionsoffuran-medicinalusesoffuran-210813152706/75/Heterocyclic-compounds-Furan-Synthesis-of-furan-Characteristic-reactions-of-furan-Medicinal-uses-of-furan-3-2048.jpg)


![iv) Acylation [Friedel-Craft’s reaction]:
Reaction of furan with acetic anhydride in the presence of boron trifluoride at 0°C
undergoes acylation.
v) Mercuration:
Furan on reaction with mercuric chloride in sodium acetate gives 2-furylmercury
chloride.
O
Furan
+ (CH3CO) 2O
Acetic anhydride
O COCH 3
+ CH3COOH
2 -acetylfuran
BF3
0 °C
O
Furan
O HgCl
HgCl2
CH3COONa
2 -furylmercury chloride
Chem Eazy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heterocycliccompounds-furan-synthesisoffuran-characteristicreactionsoffuran-medicinalusesoffuran-210813152706/75/Heterocyclic-compounds-Furan-Synthesis-of-furan-Characteristic-reactions-of-furan-Medicinal-uses-of-furan-10-2048.jpg)