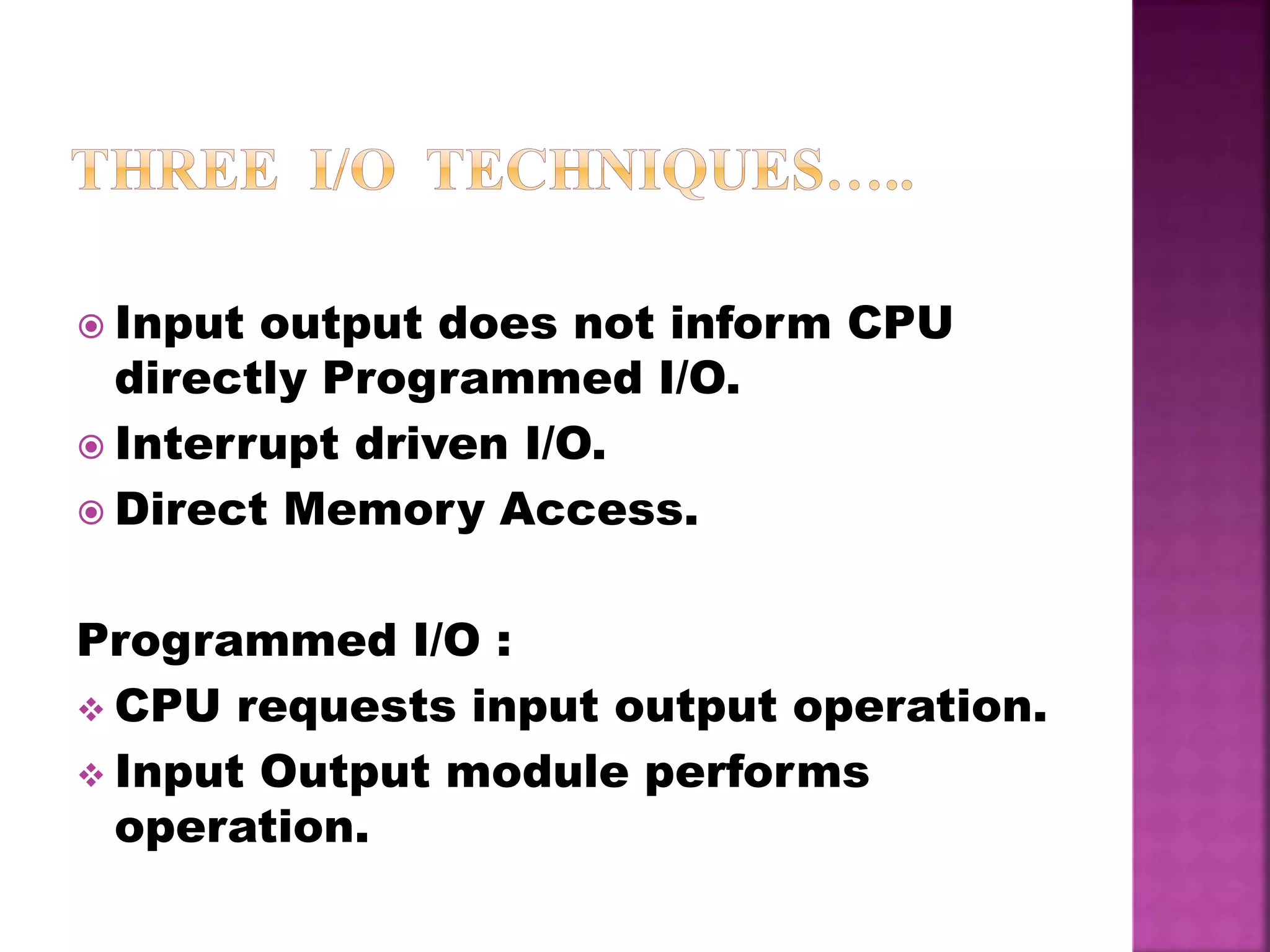
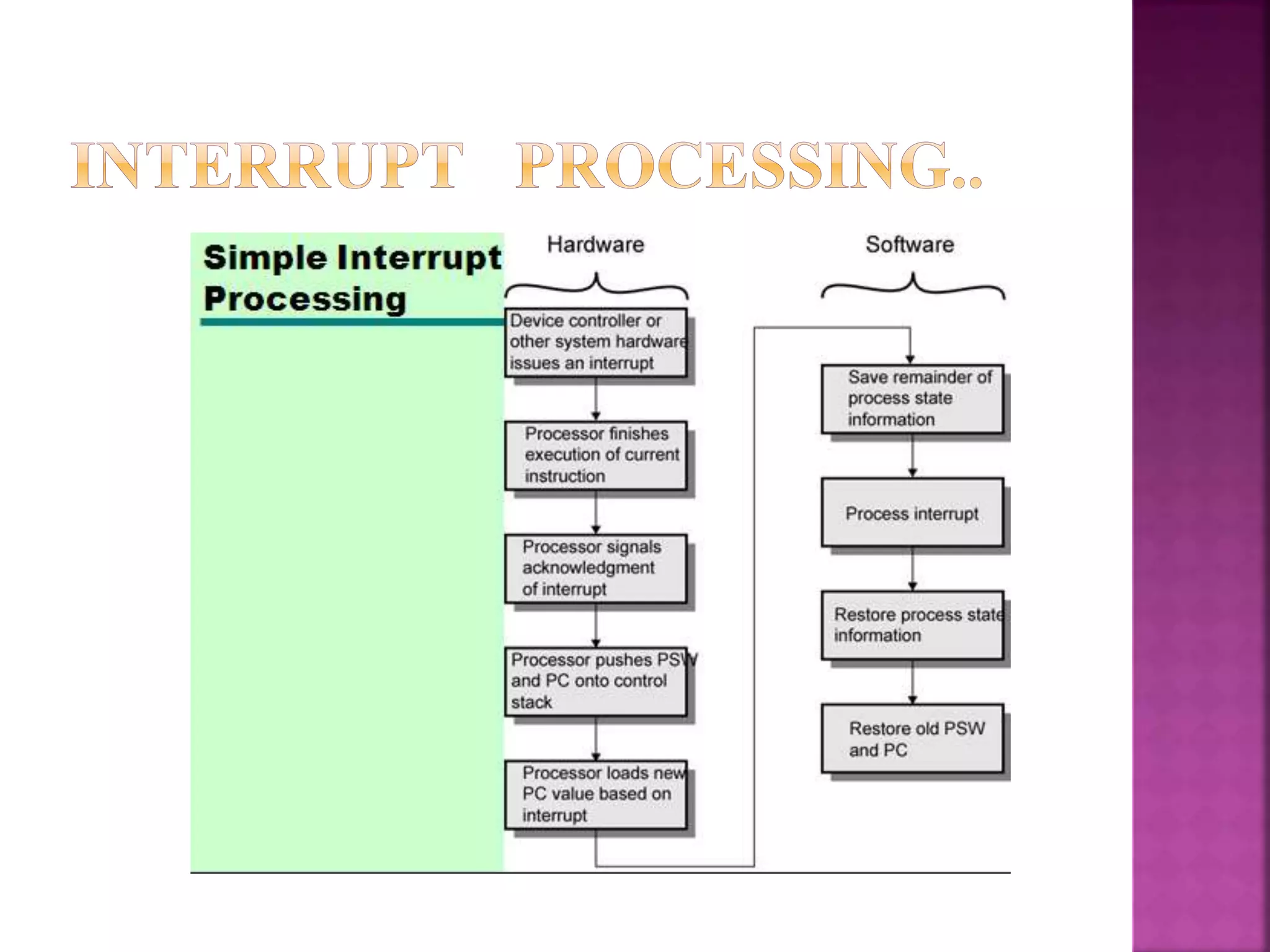
This document discusses input/output (I/O) devices and how they connect to computers. It explains that peripheral devices connect to an I/O module, which acts as an interface between the computer and external devices. It also describes different types of I/O, including programmed I/O where the CPU requests operations, interrupt-driven I/O which notifies the CPU when an operation is done, and direct memory access (DMA) where a DMA controller handles I/O instead of the CPU. Finally, it discusses channel I/O which uses special instructions to perform asynchronous I/O through a channel.