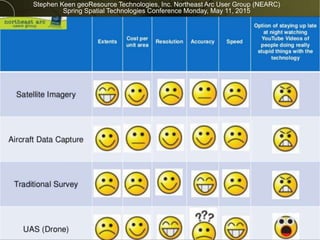
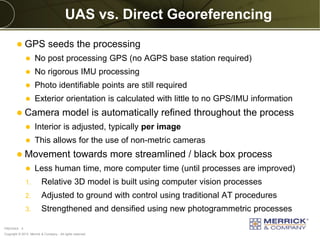
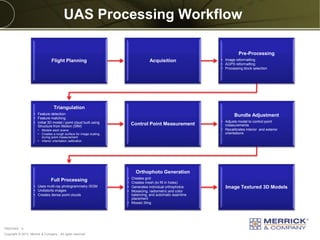
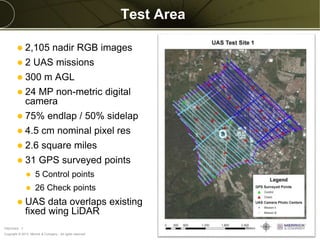
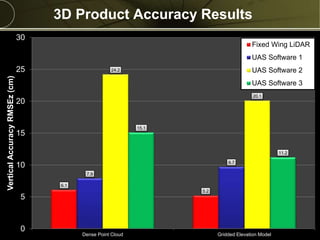
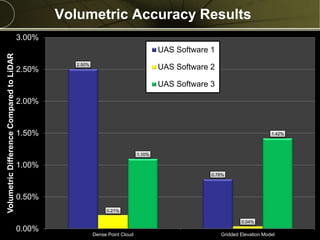
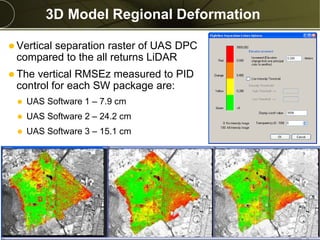
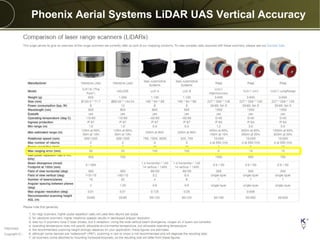
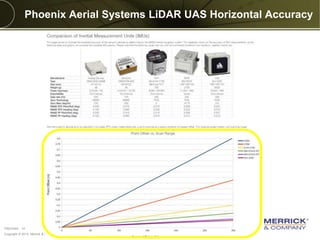
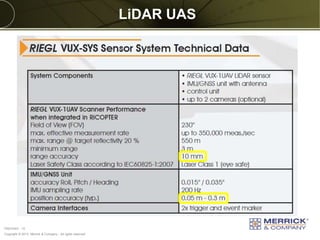
The document discusses the capabilities and performance metrics of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) in geospatial solutions, focusing on data quality and accuracy. It outlines the UAS processing workflow, factors influencing accuracy, and presents results from various tests comparing UAS-generated data to existing LIDAR datasets. Additionally, it provides metrics on horizontal and vertical accuracy, highlighting that optimal accuracies are often related to pixel resolution in non-obstructed environments.