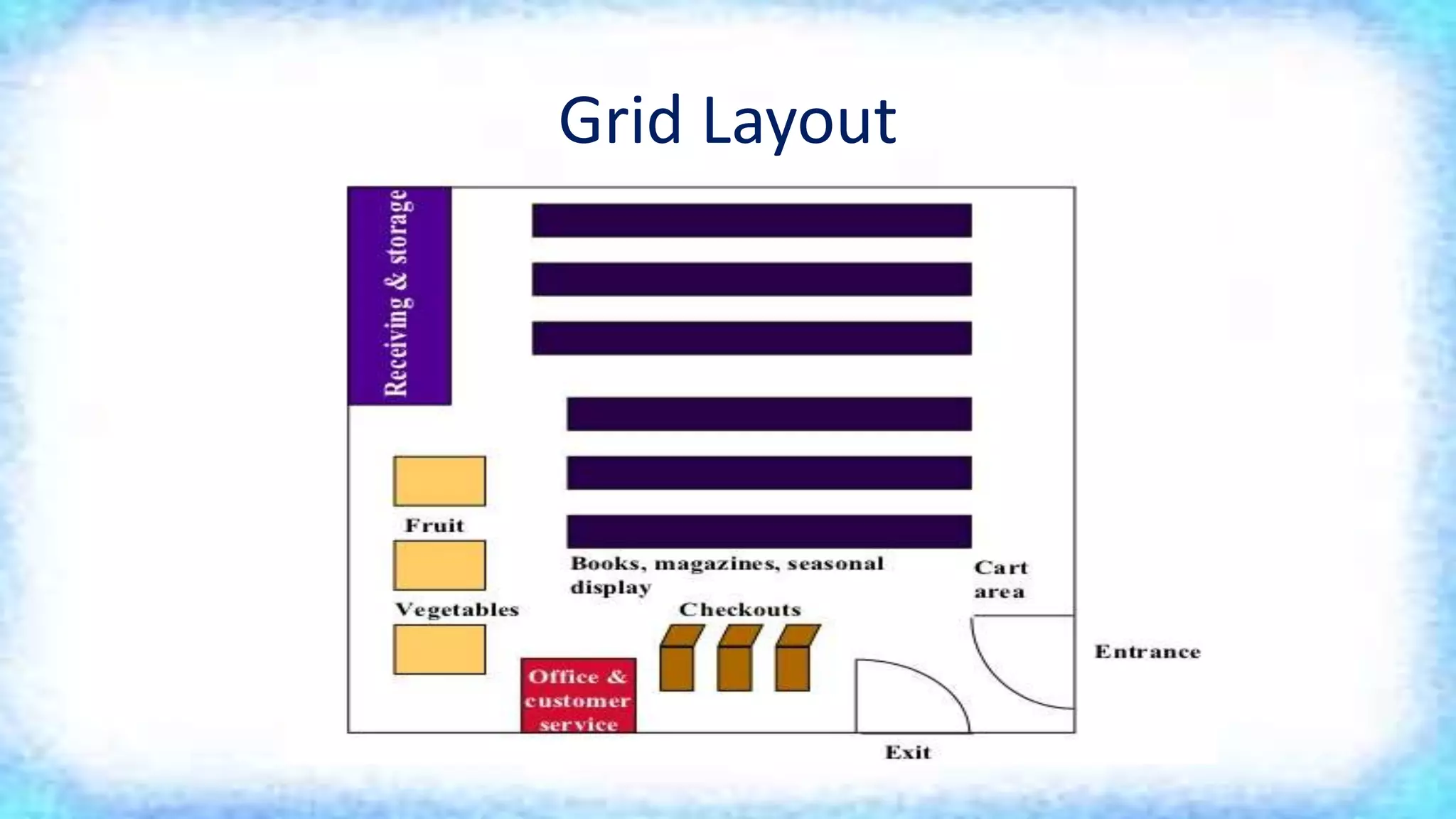
The document discusses different types of store layouts and factors to consider when designing a store layout. It describes four main types of layouts: grid layout, racetrack/loop layout, free form layout, and spine layout. A store's layout is important to create a desired store image, influence customer behavior, and maximize the use of selling space. An effective layout breaks the store into logical areas, guides customers to merchandise, and arranges lighting and music to suit shoppers.