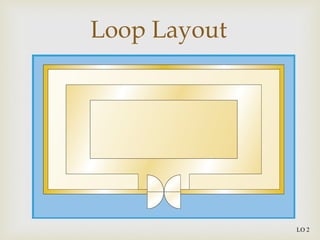
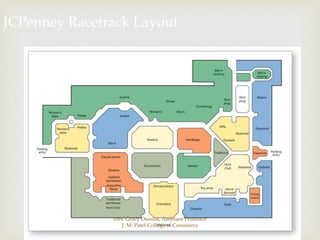
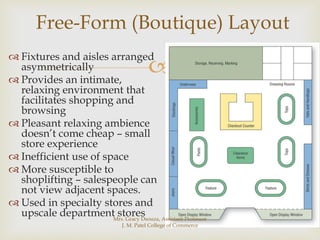
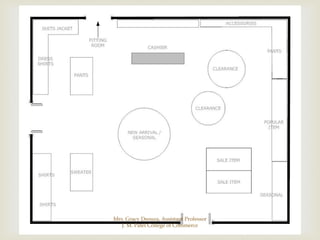
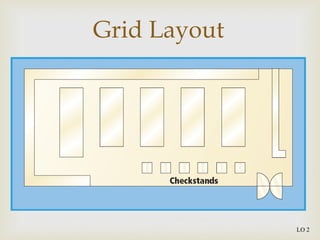
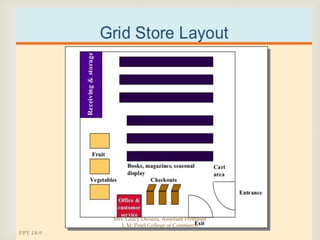
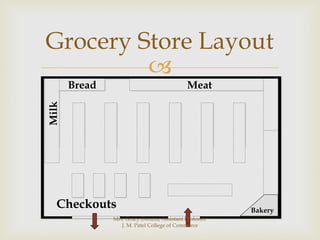
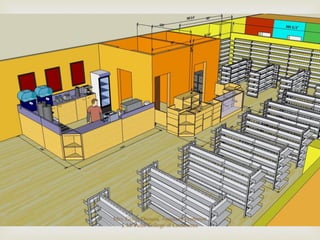
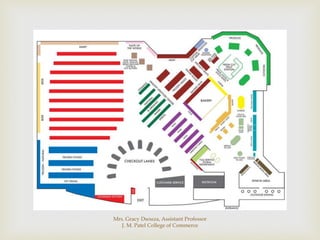
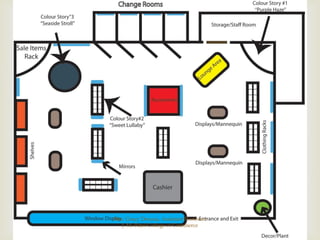
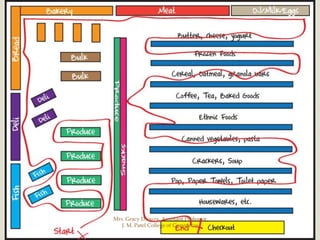
The document discusses different types of store layouts including grid, loop/racetrack, free form, and spine layouts. It provides descriptions of each layout type, examples of well-known stores that use each layout, and pros and cons of the different approaches. The grid layout arranges fixtures and aisles in straight rows, while the loop/racetrack layout forms a looping main aisle through the store. Free form layouts place fixtures asymmetrically and allow more browsing, though use space inefficiently. A spine layout features a central main aisle with departments on either side.