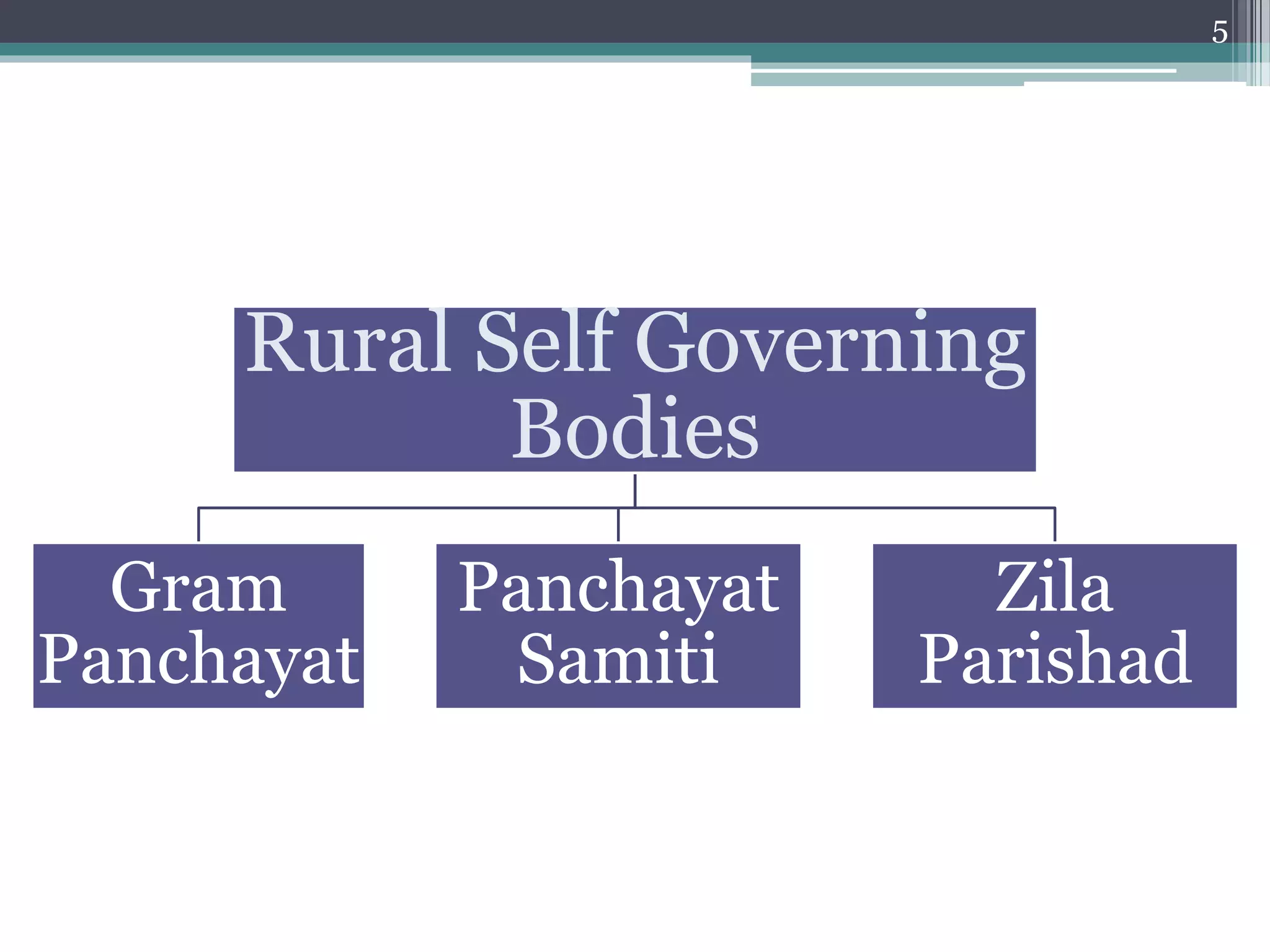
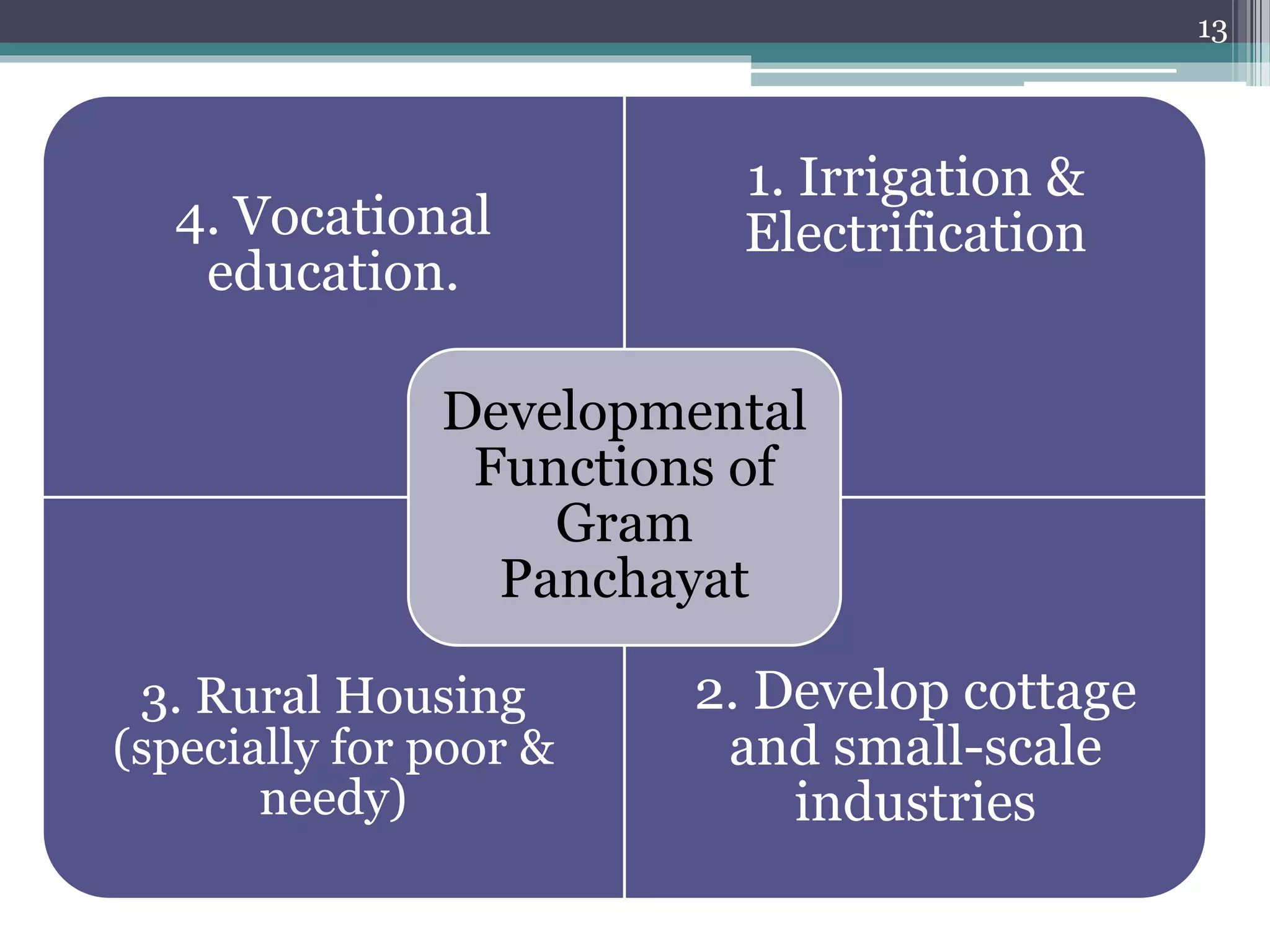
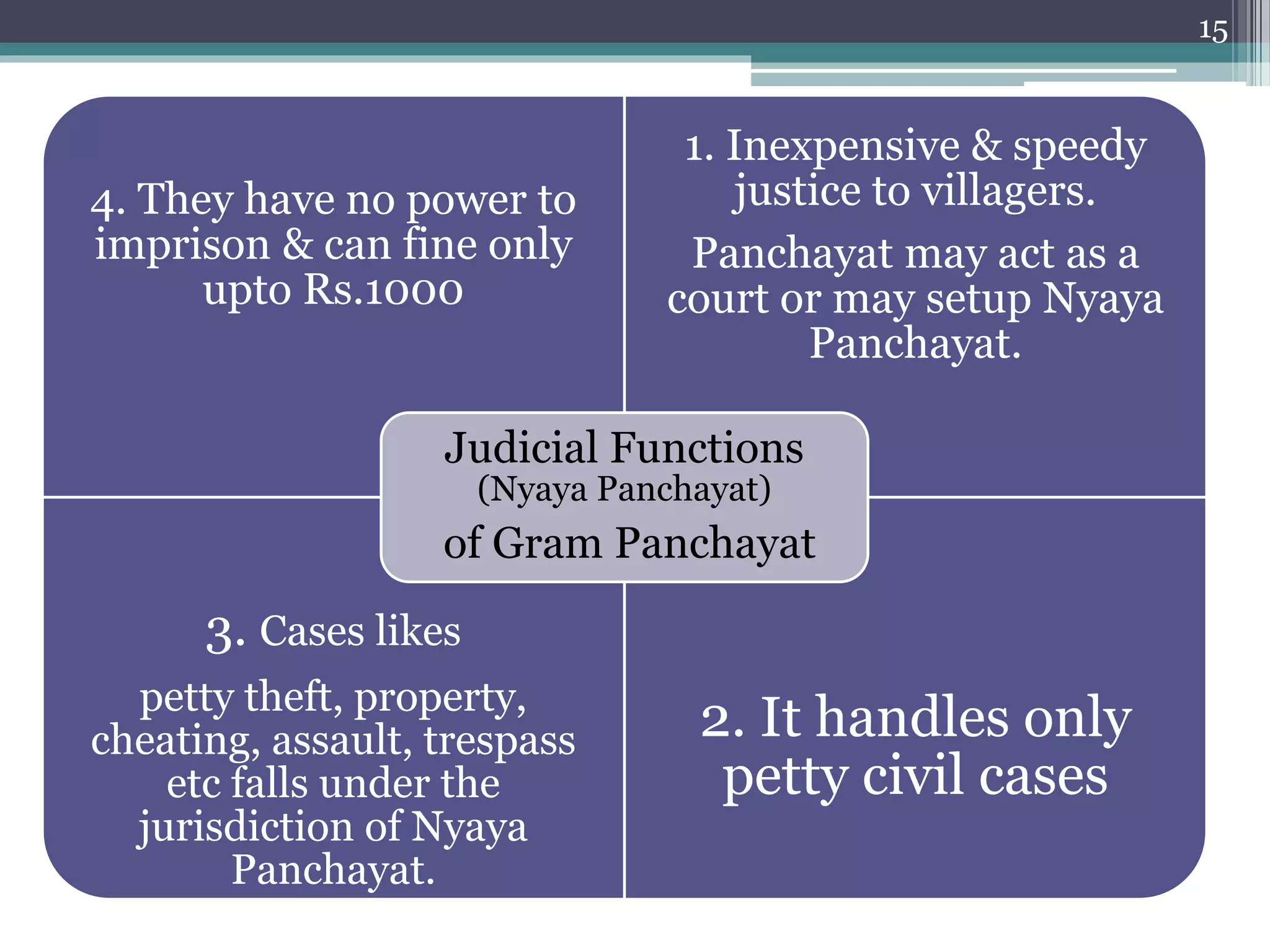
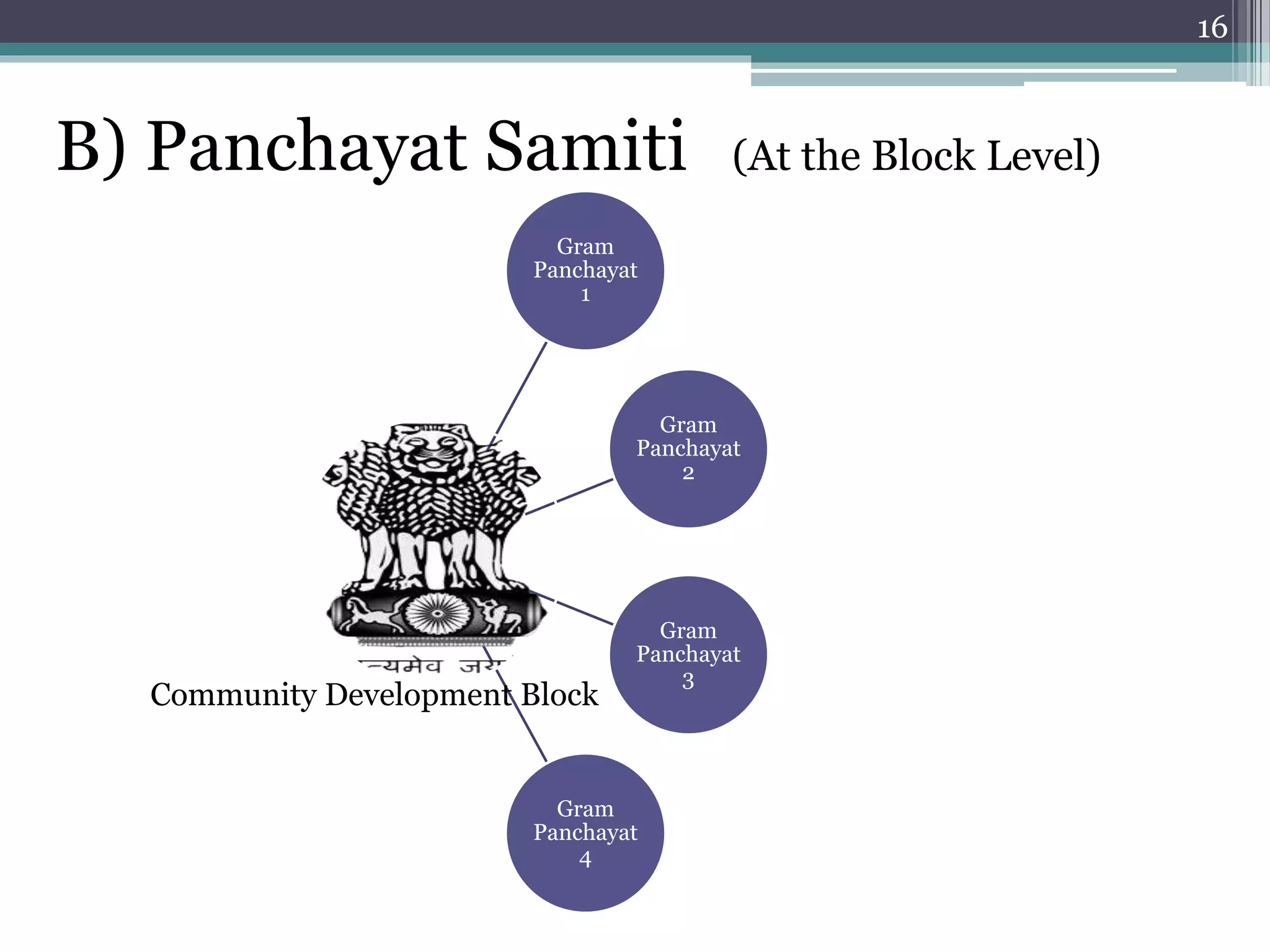
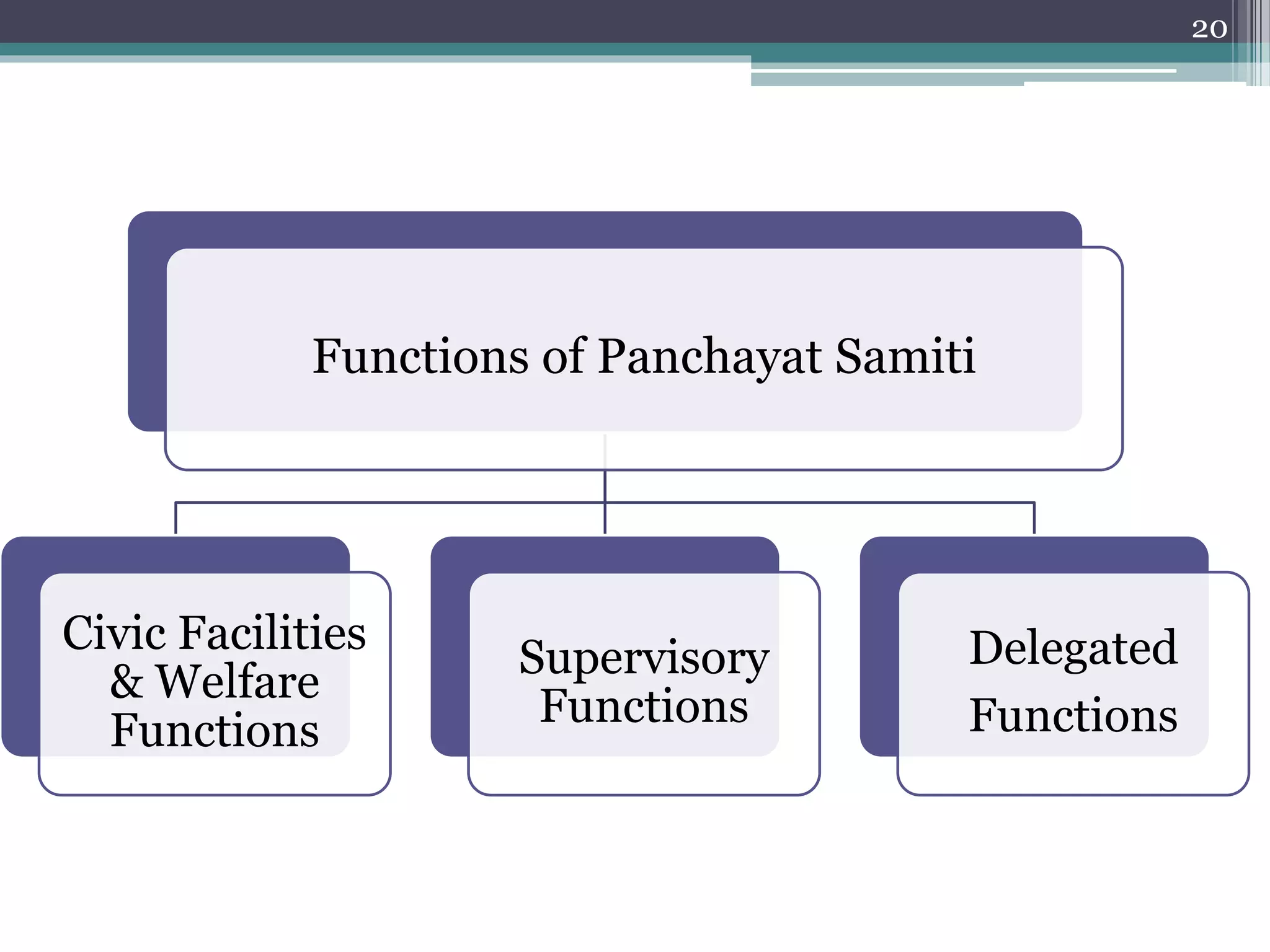
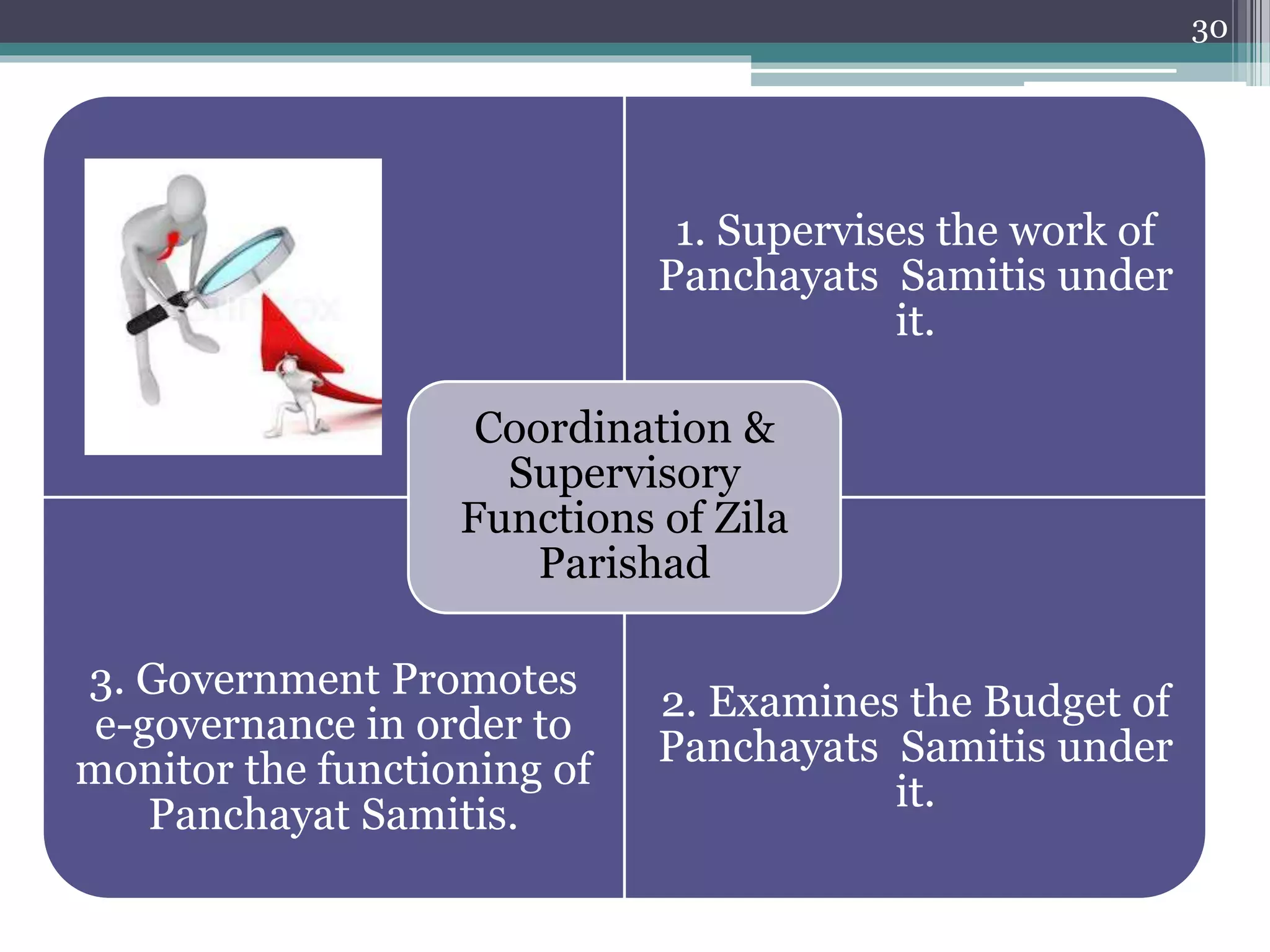
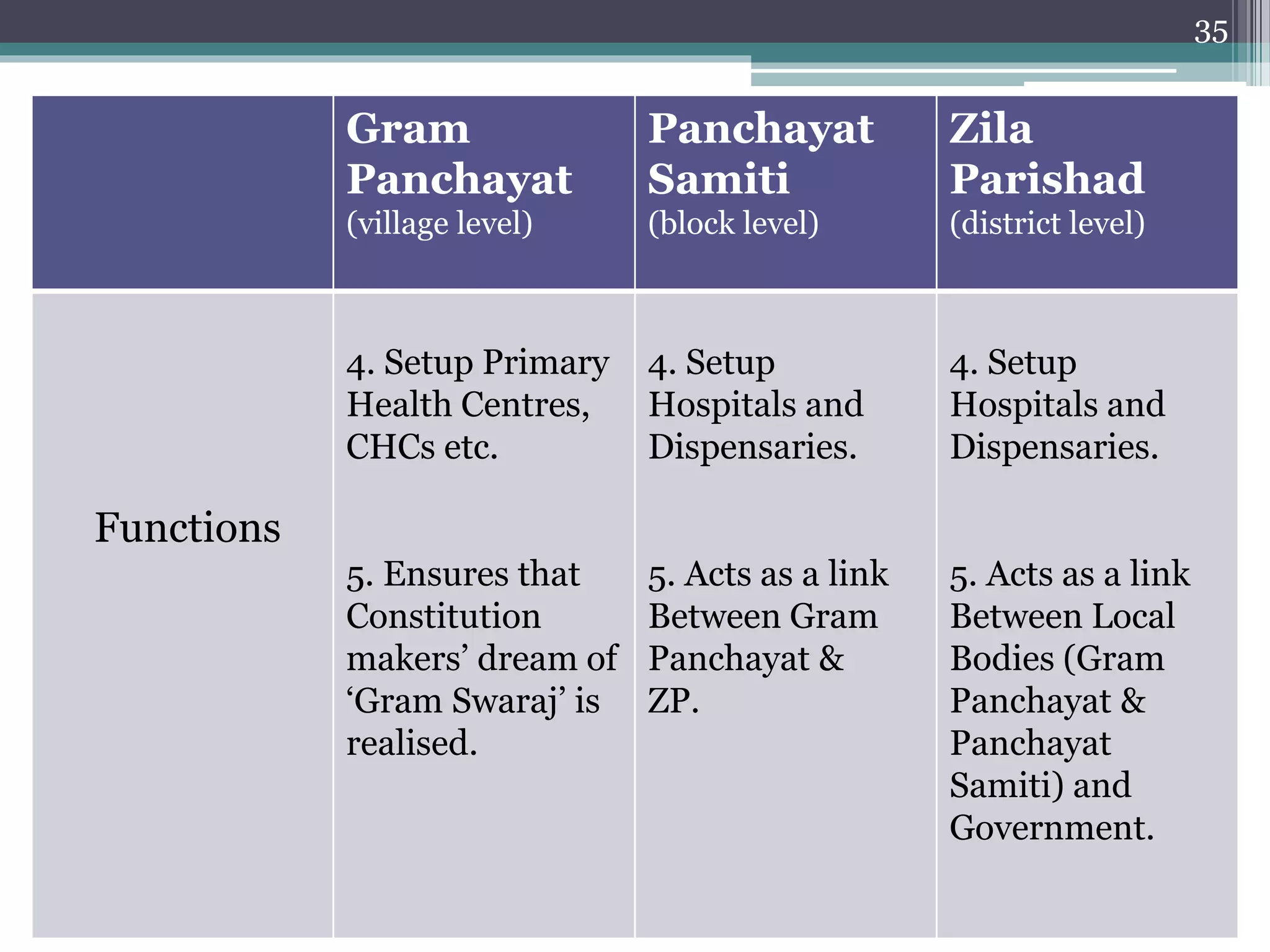
The document summarizes the three-tier system of local self-government in rural India. At the village level is the Gram Panchayat, composed of locally elected representatives who manage civic amenities and provide basic services. Multiple Gram Panchayats fall under a block-level Panchayat Samiti, which coordinates activities and development programs. Finally, at the district level is the Zila Parishad, the apex body that oversees the work of Panchayat Samitis and serves as a link between local governments and the state. The system aims to promote direct democracy and ensure communities can effectively govern local affairs.