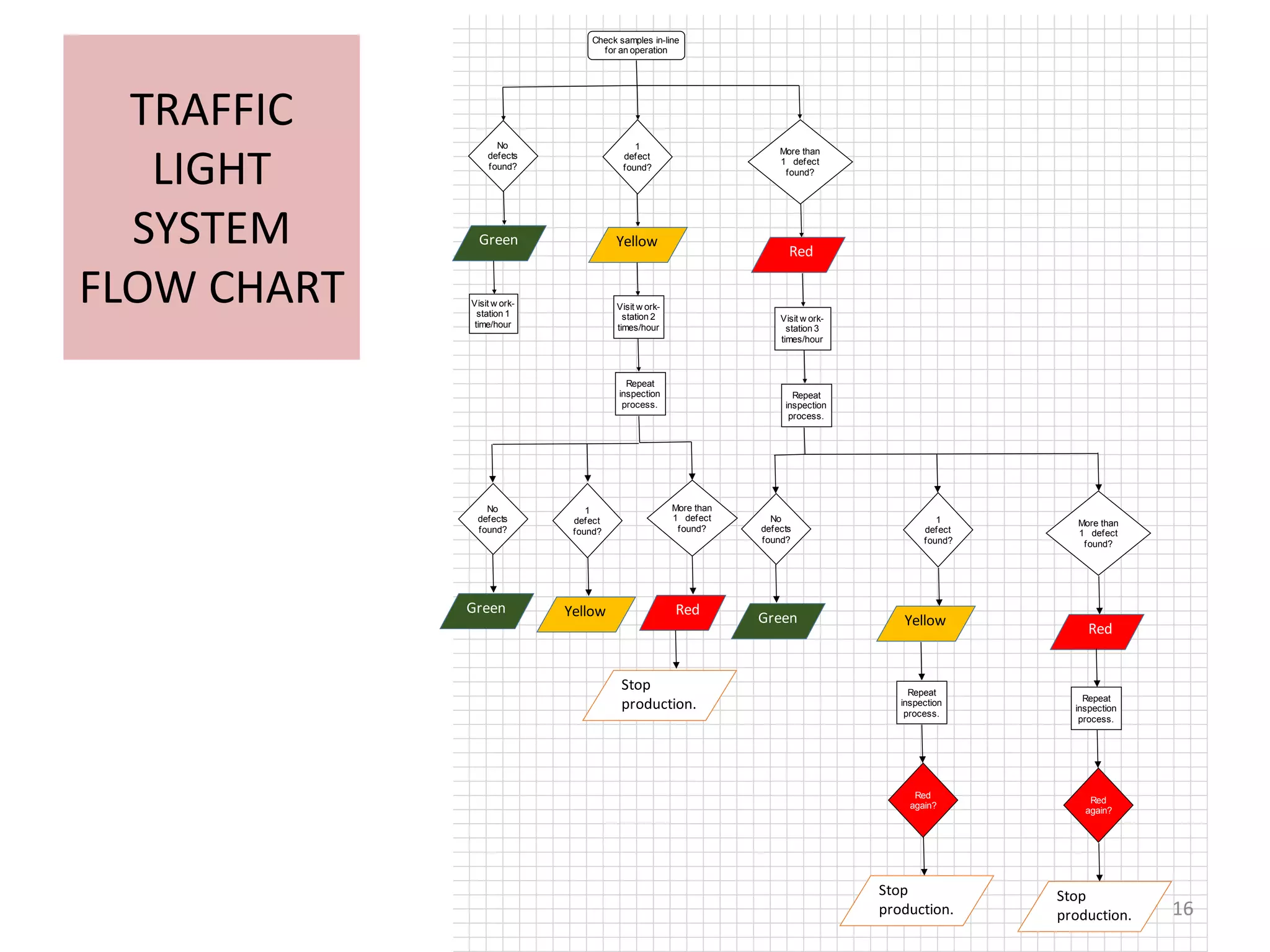
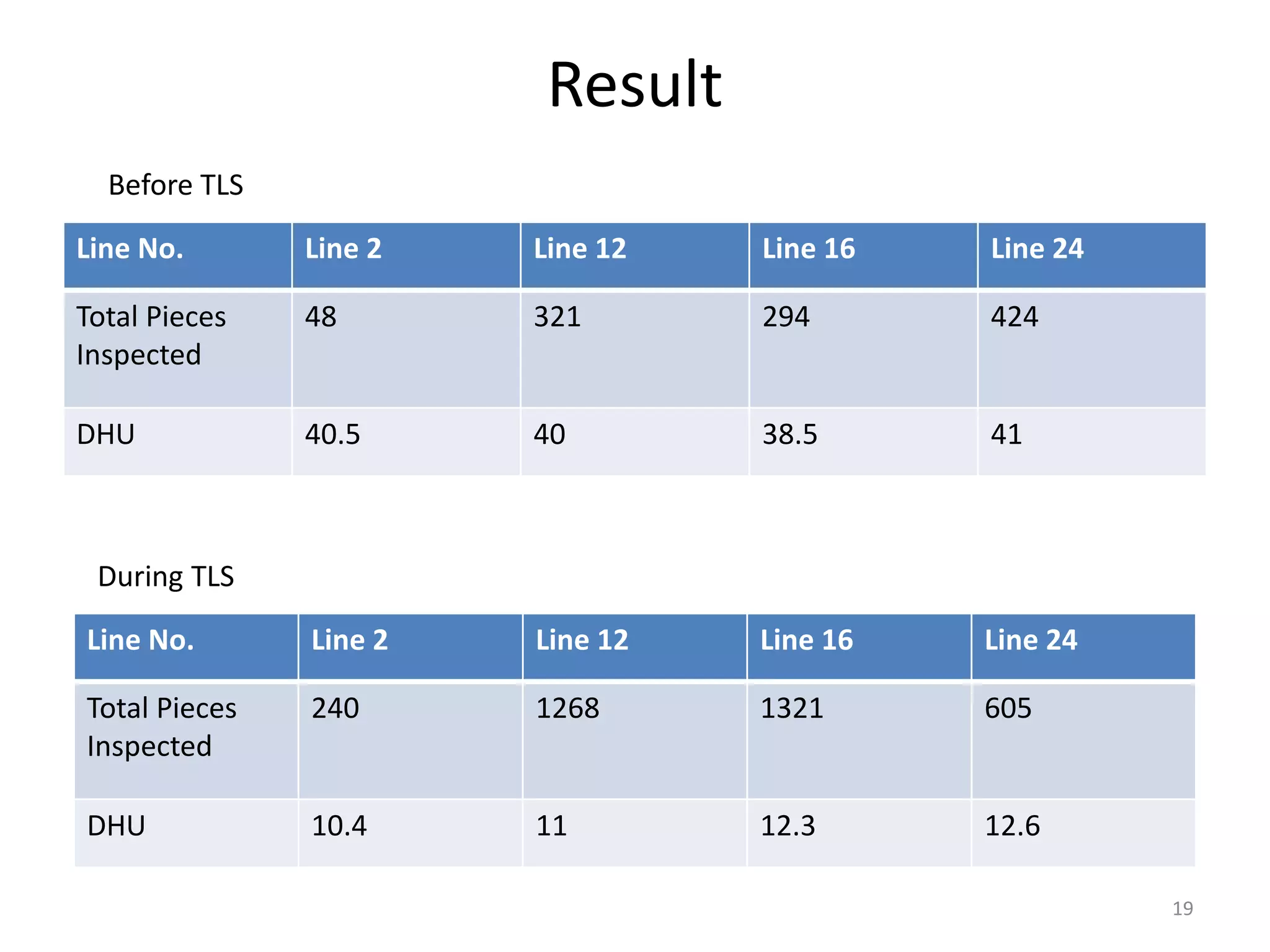
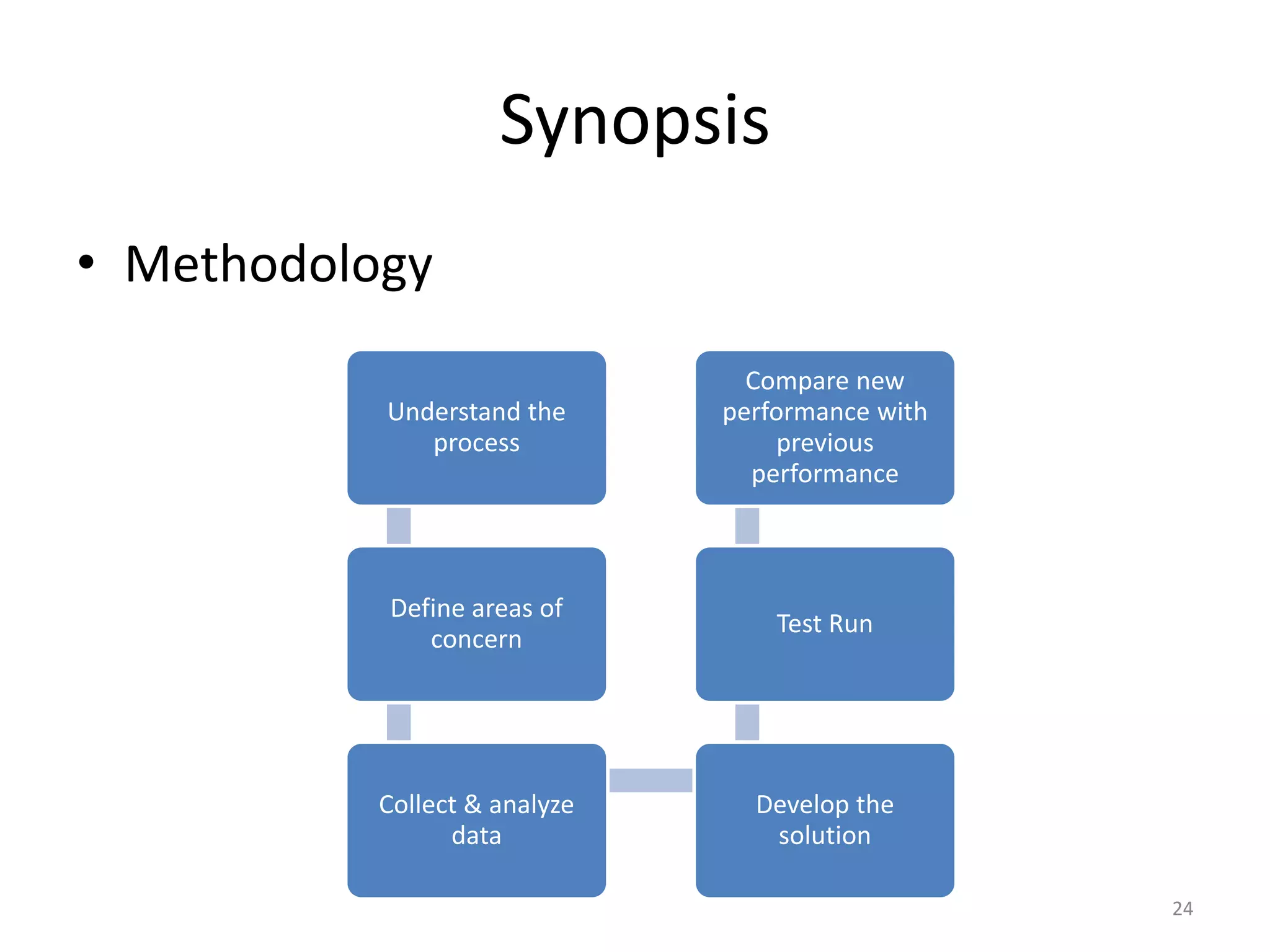
The document describes a Traffic Light System (TLS) implemented at a garment factory to monitor quality and identify problems at production lines. The TLS involves:
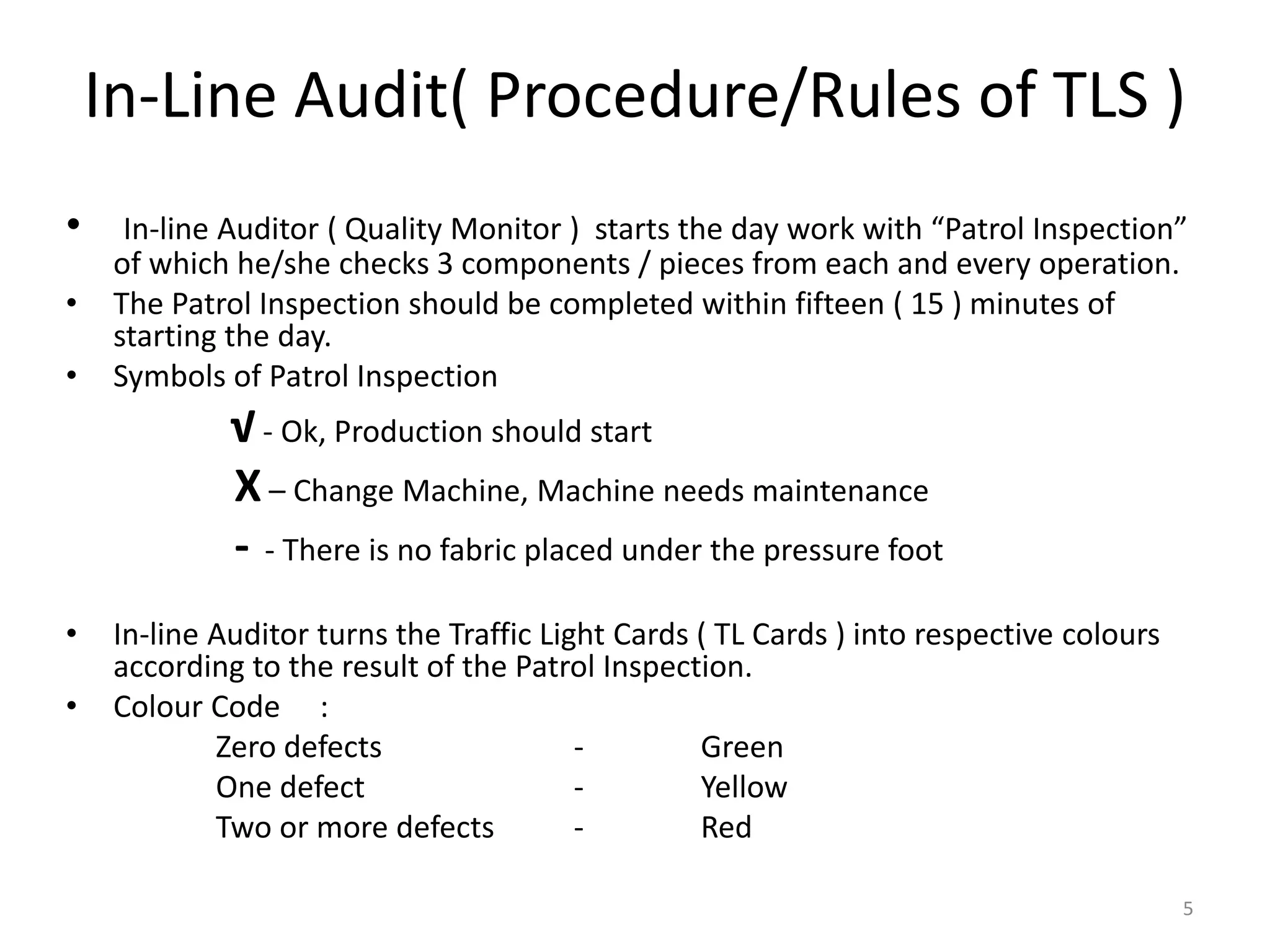
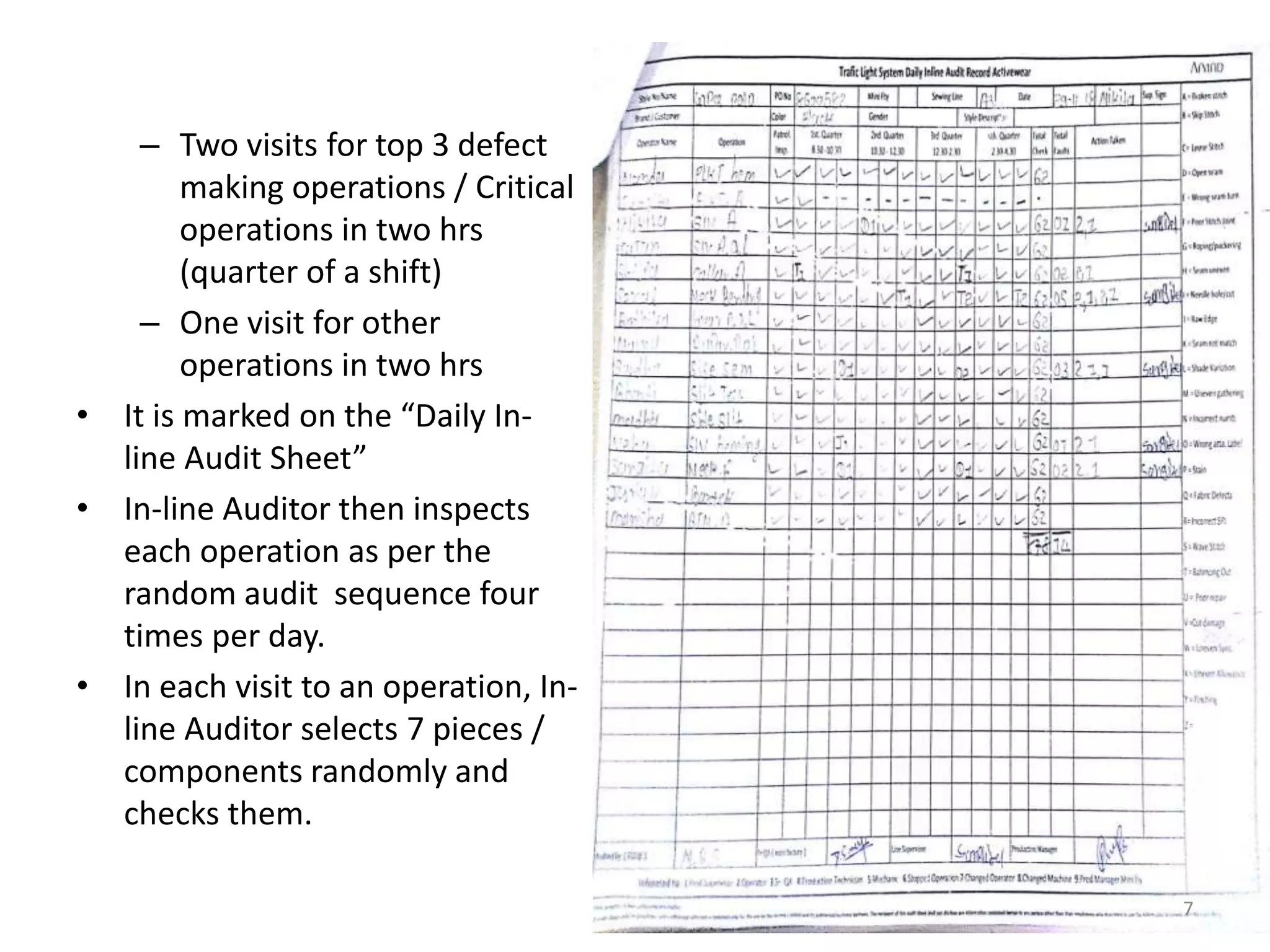
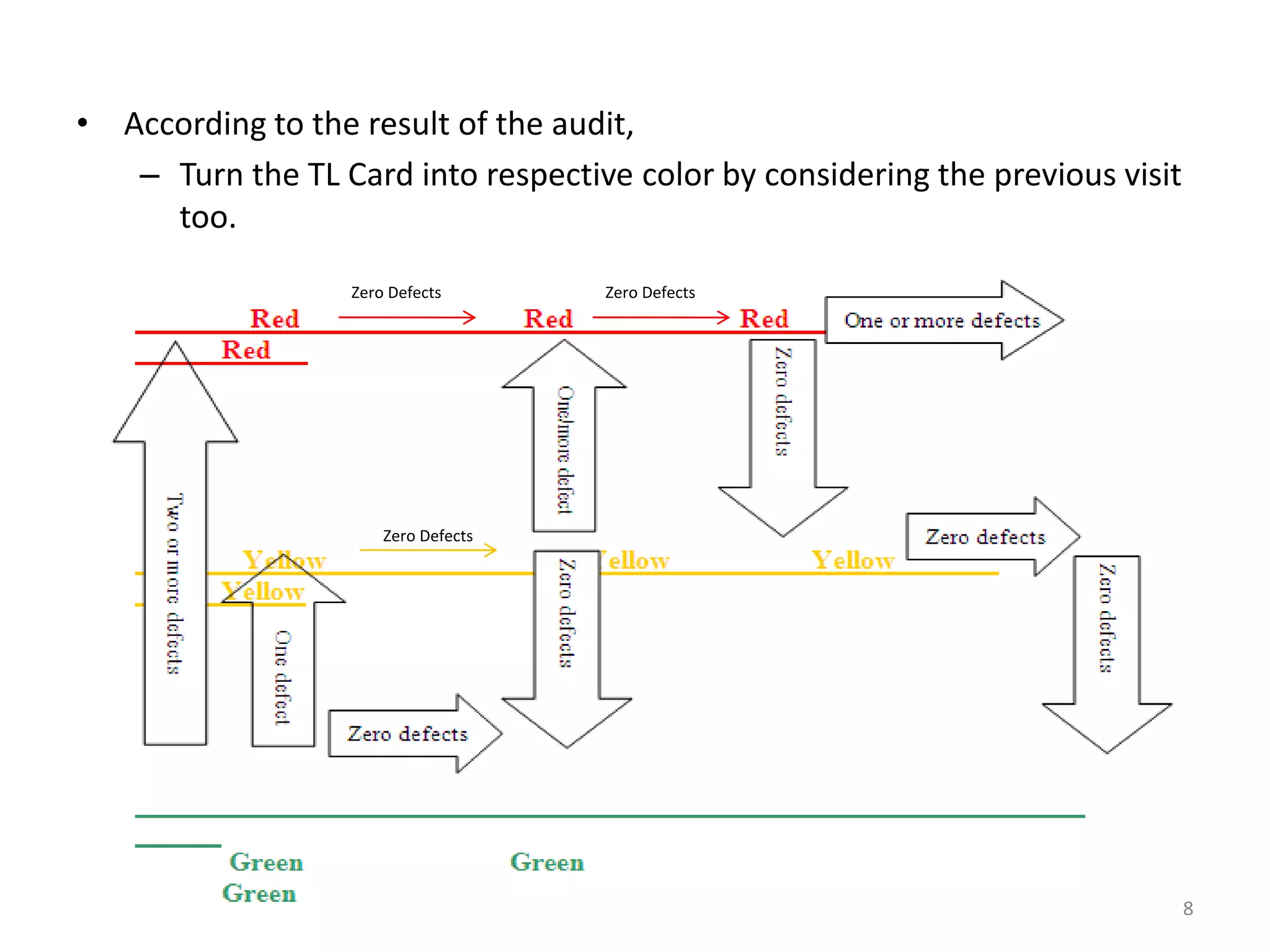
1. An in-line auditor inspecting random samples from each operation daily and assigning color codes (green, yellow, red) based on defects found.
2. Actions like stopping production for red lights to address issues. Top defect-making operations are discussed at meetings.
3. End-line inspection also identifies defect-making operations. Data is captured on forms and charts to track performance over time, with the goal of reducing defects and achieving Right First Time production.