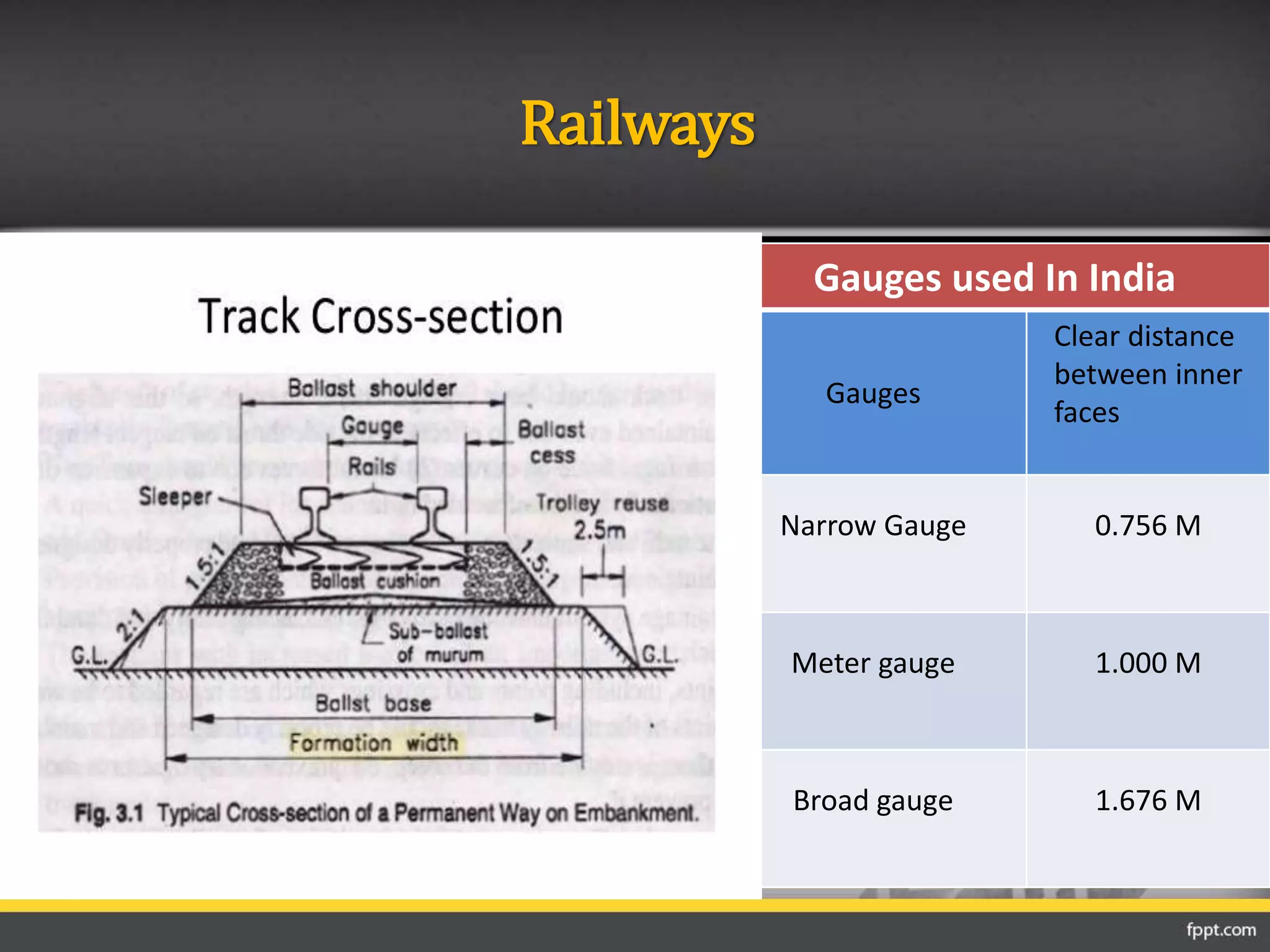
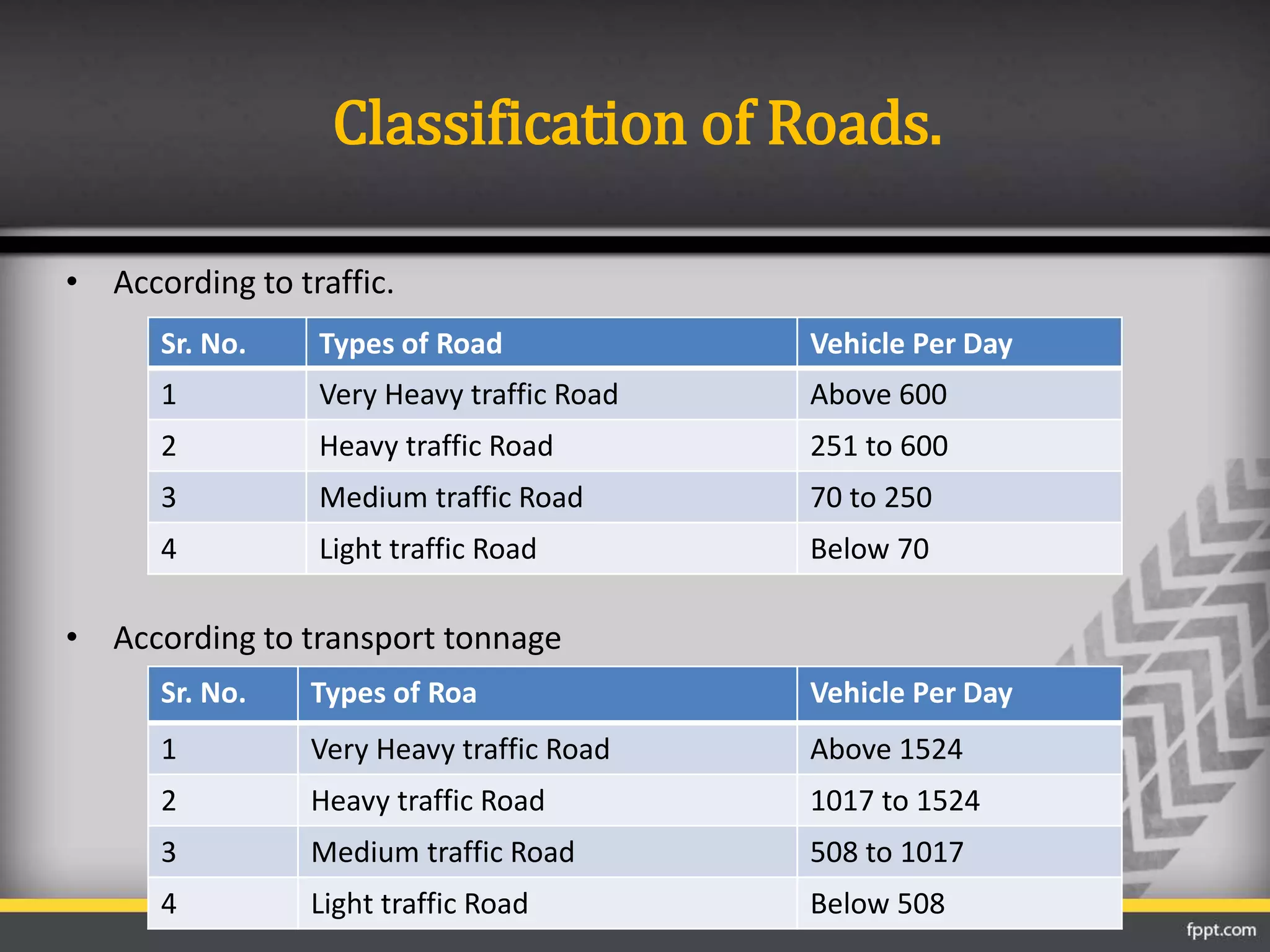
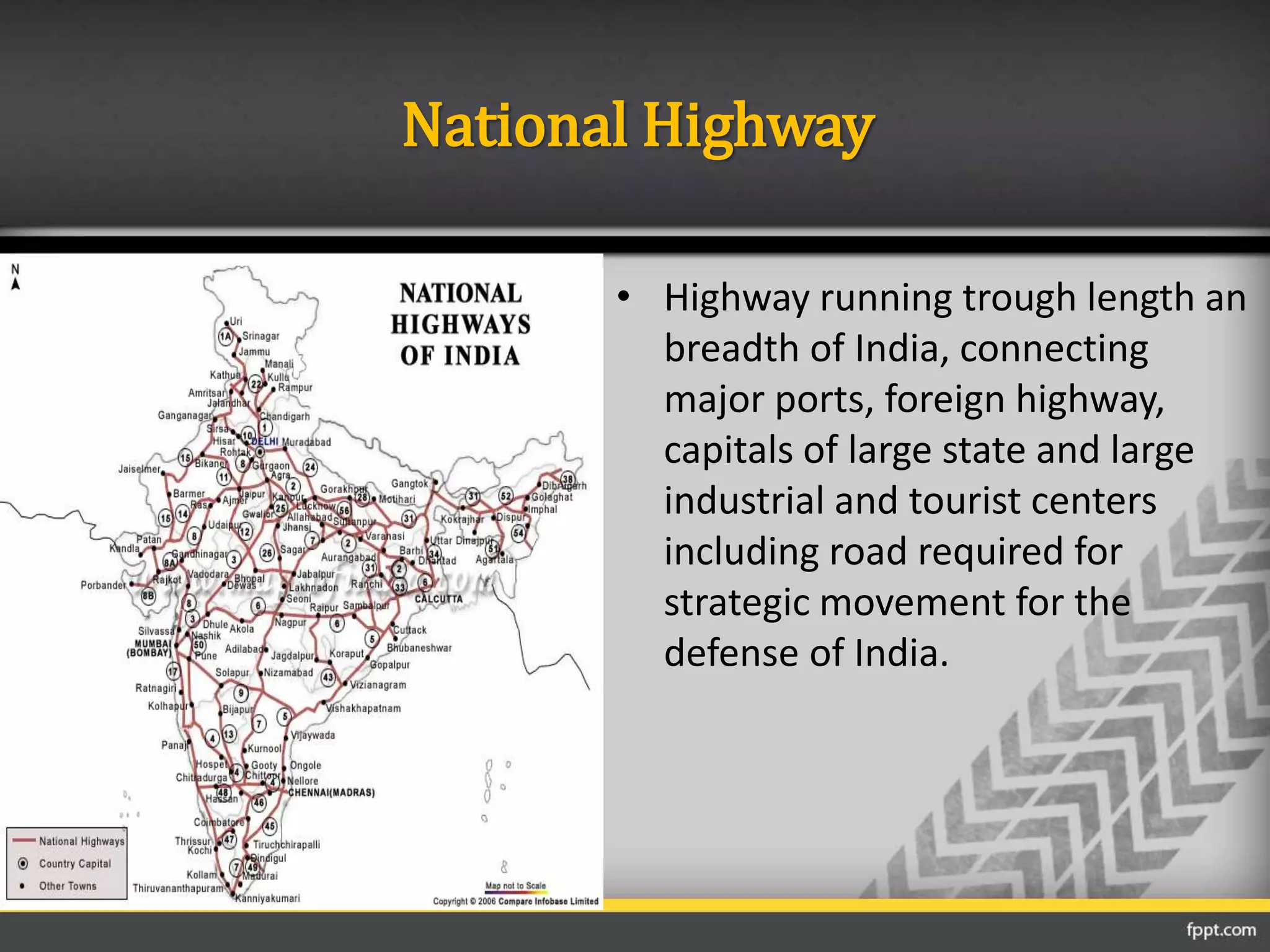
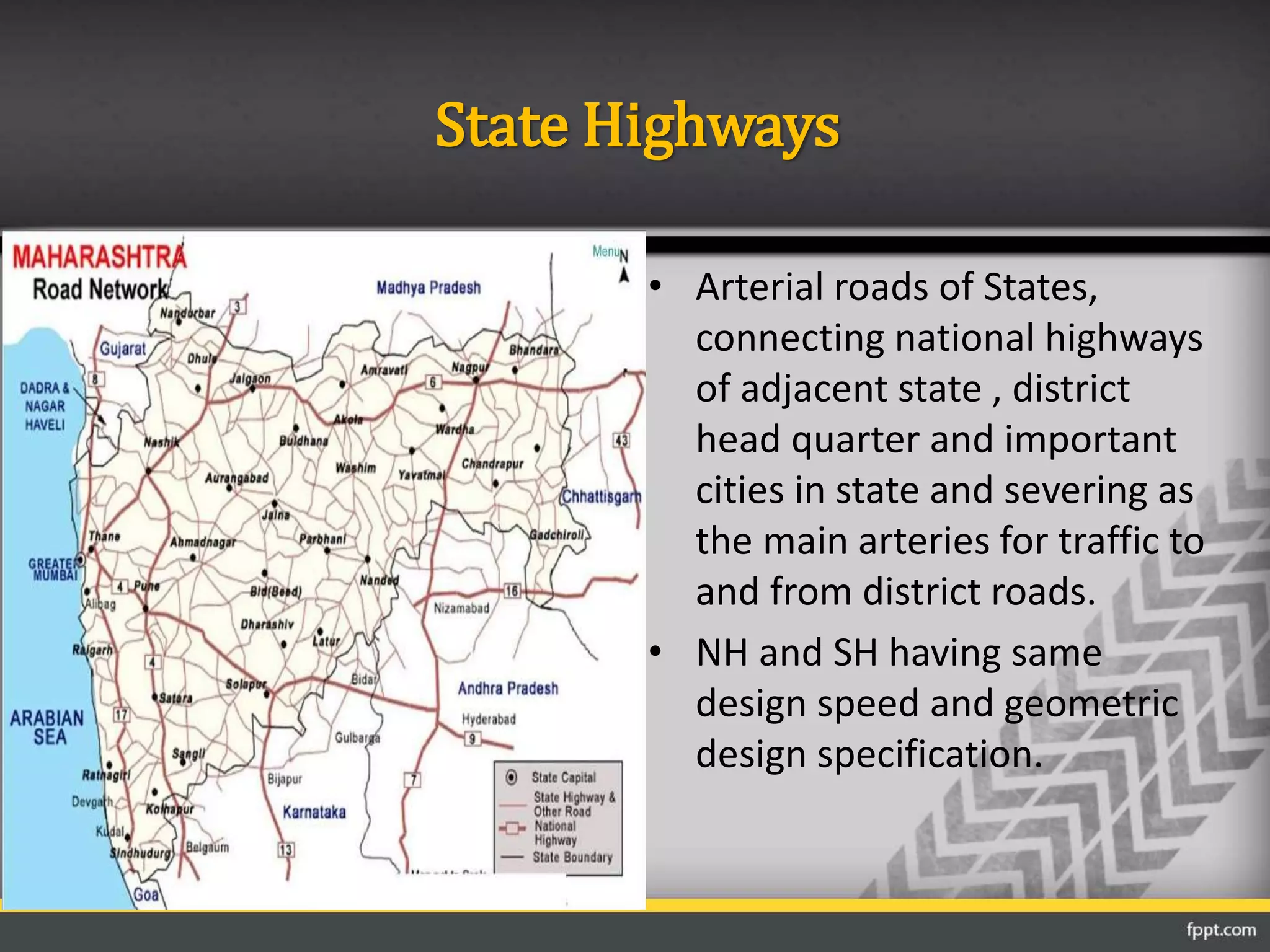
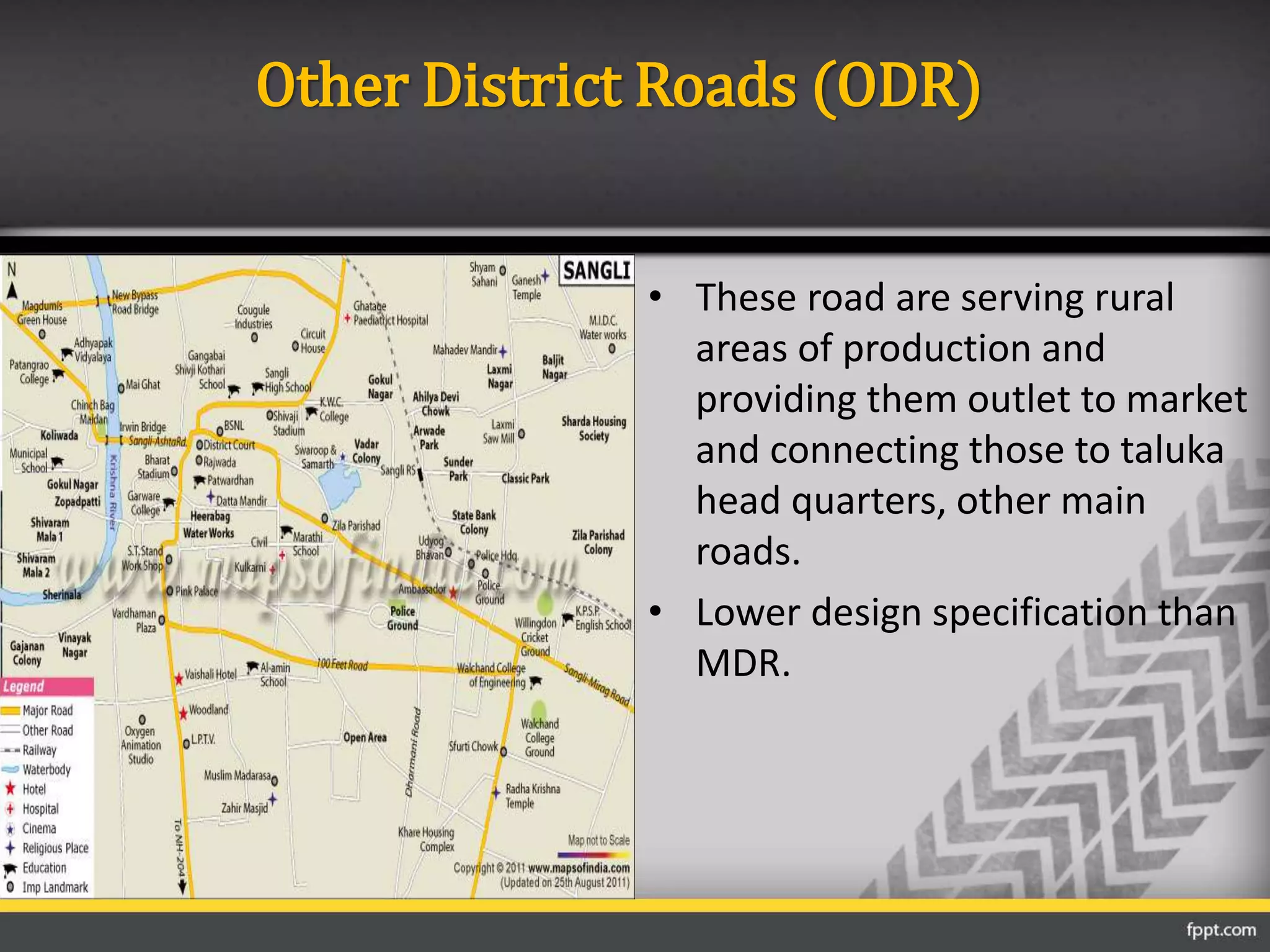
This document discusses the importance of transportation and different modes of transportation including roadways, railways, waterways, and airways. It then focuses on roadways, describing their classification based on location and function. The main classifications of roads in India are national highways, state highways, major district roads, other district roads, and village roads. The document provides details on the characteristics of each type of road, including their intended uses, design specifications, and importance within the transportation network.