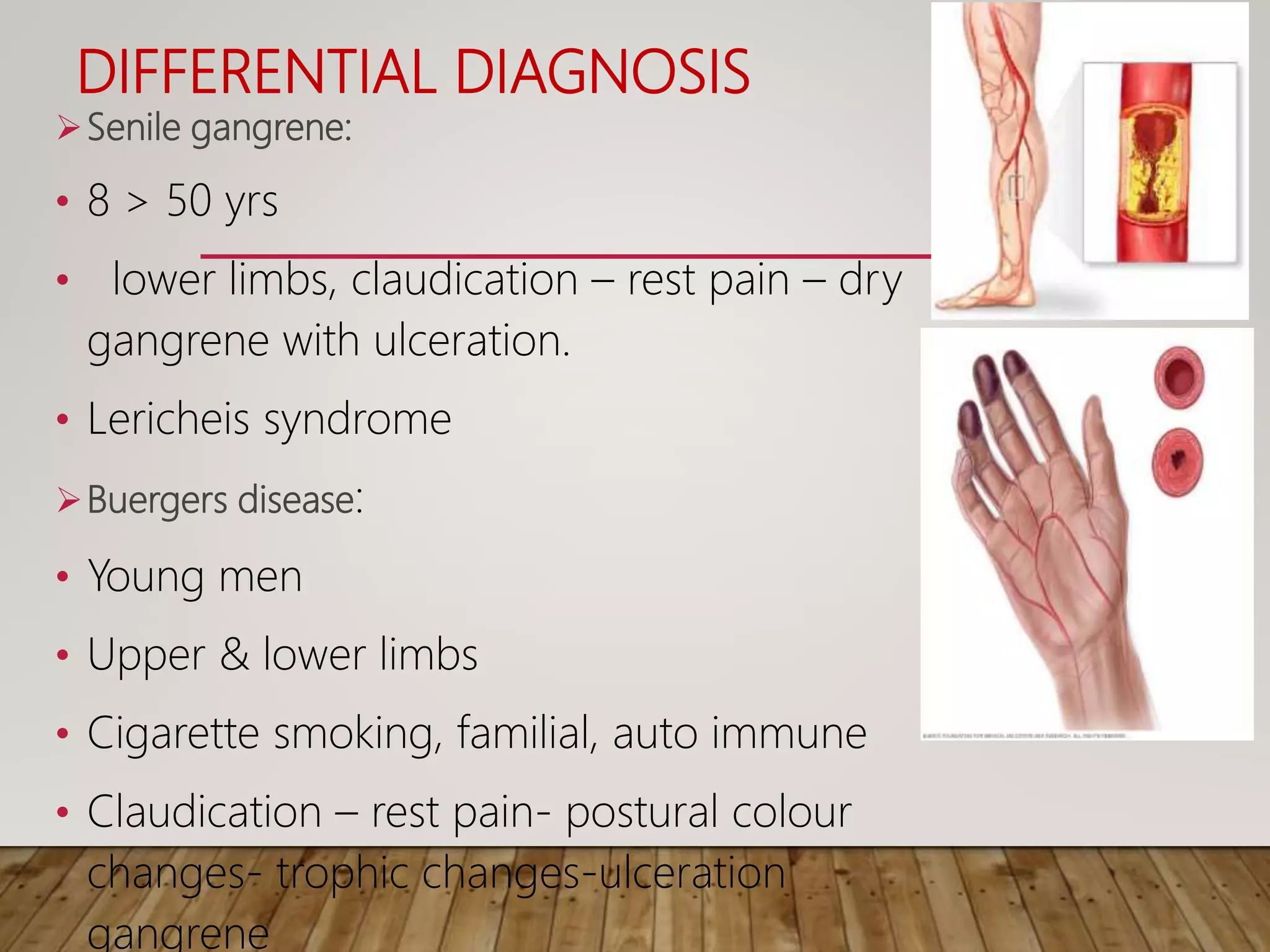
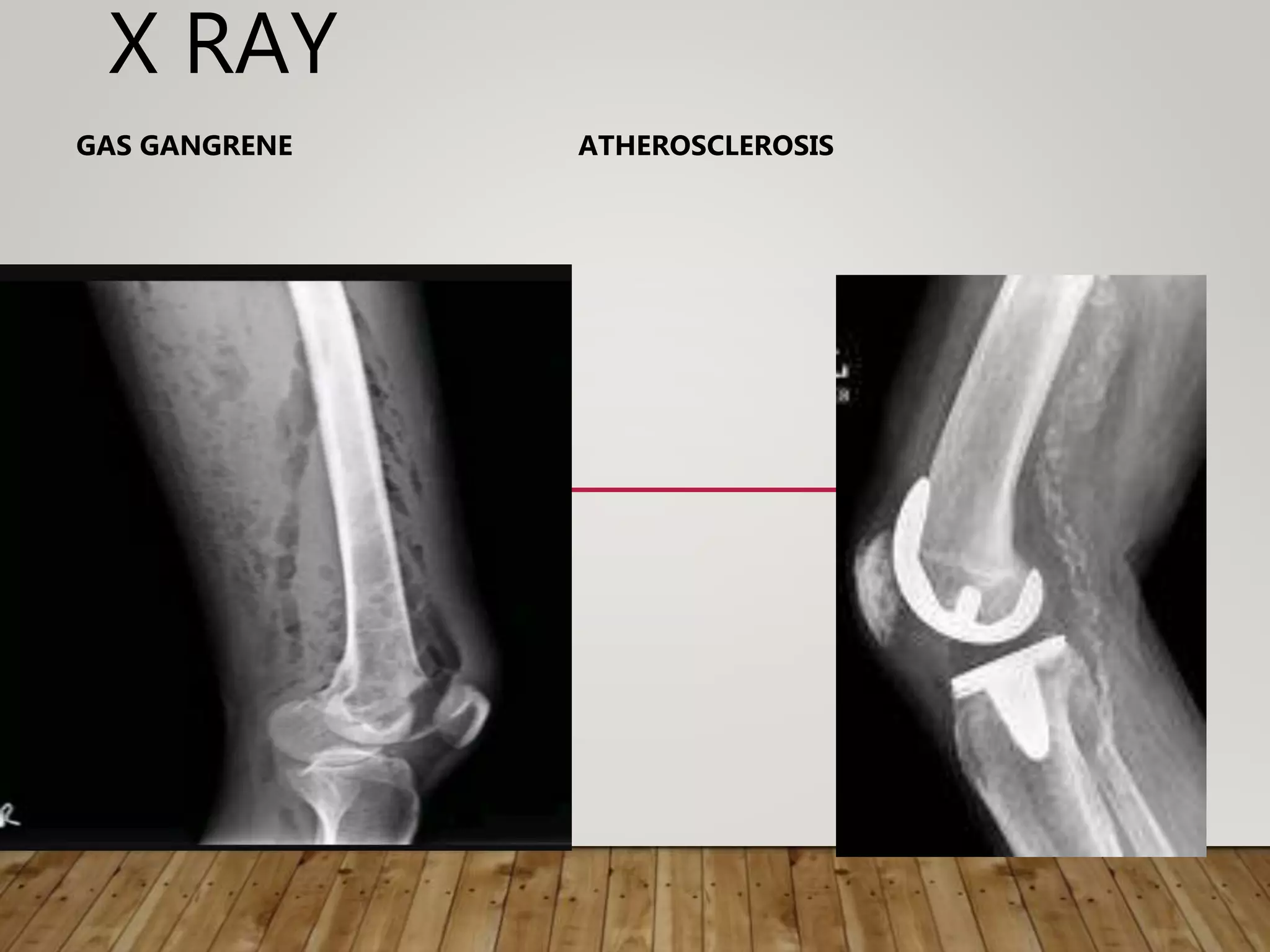
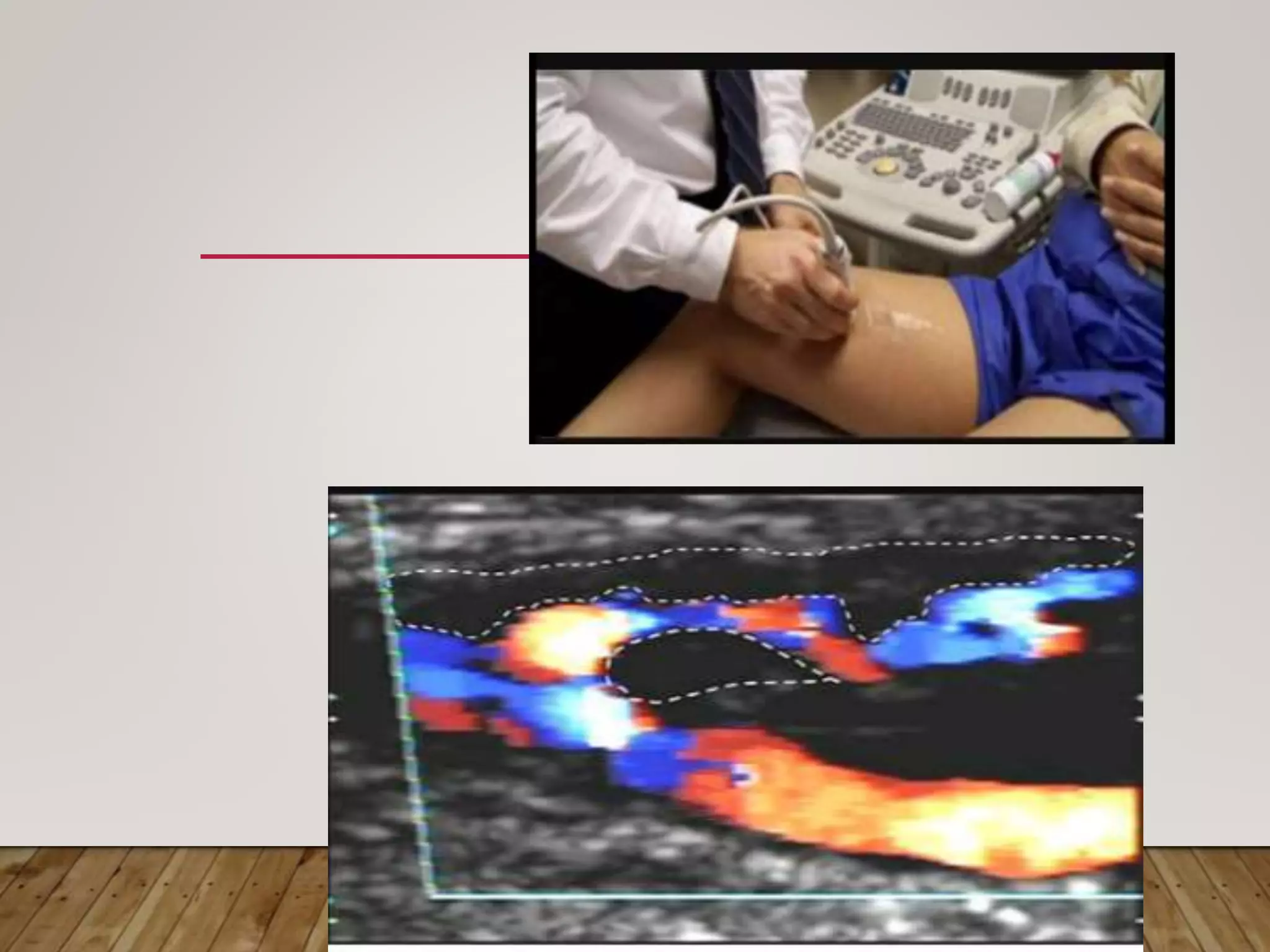
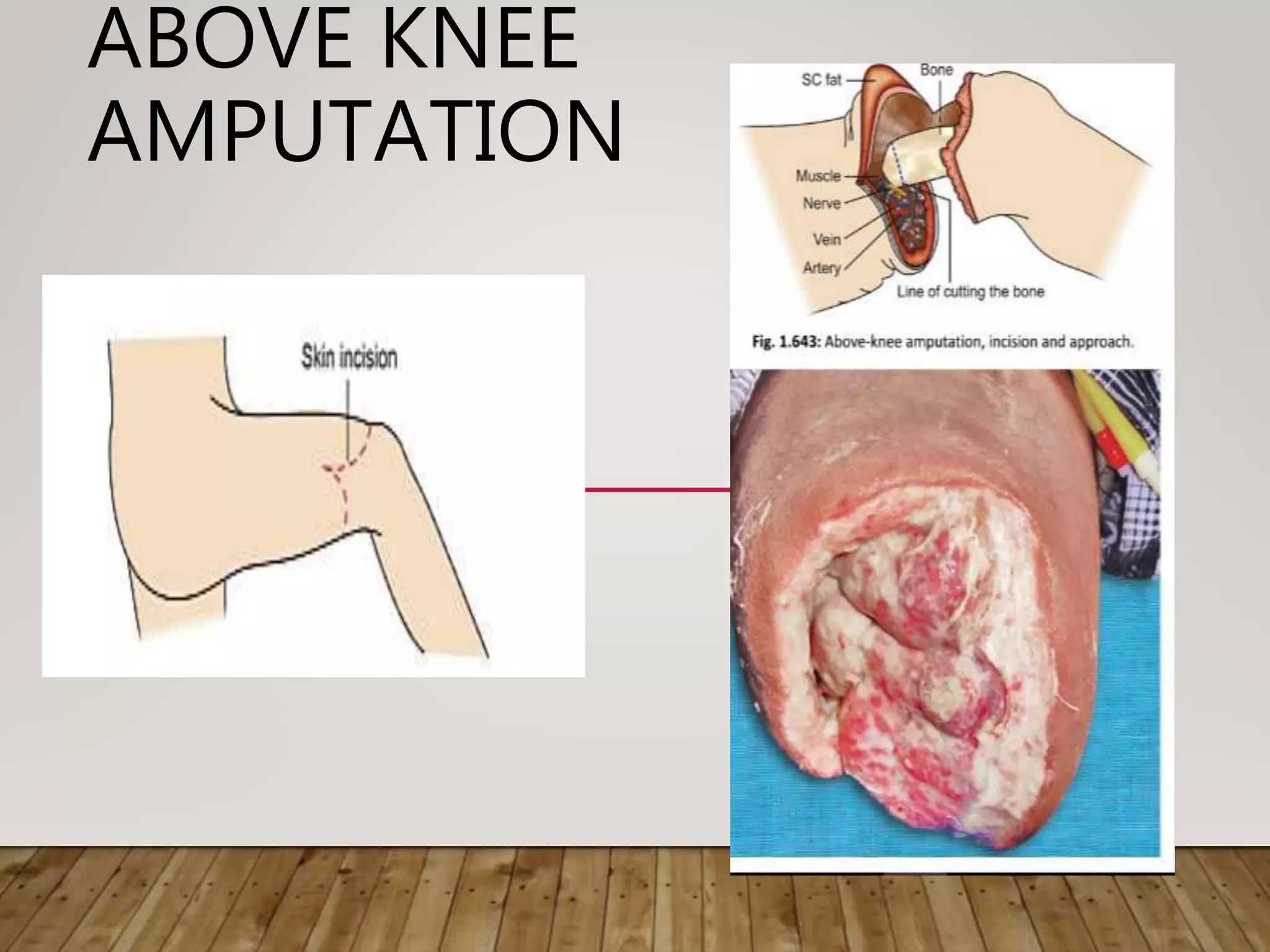
Gangrene is the death of body tissue due to lack of blood supply and oxygenation. There are two main types - dry gangrene caused by arterial blockages, and wet gangrene caused by both arterial and venous blockages along with infection and putrefaction. Gangrene has many potential causes including diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, trauma, frostbite, and infection. Treatment depends on the type and cause but may include antibiotics, debridement, amputation, or in some cases limb salvaging procedures to restore blood flow.