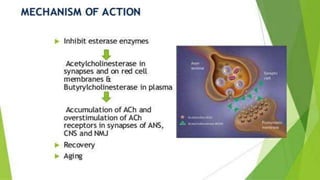
Organophosphorus compounds are widely used as pesticides and some were developed as nerve agents. They work by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, resulting in excess acetylcholine in synapses and stimulation of receptors. Acute poisoning causes cholinergic effects like bronchospasm, vomiting, and bradycardia. Without treatment, respiratory failure can be fatal. Pralidoxime and atropine are used as antidotes to regenerate acetylcholinesterase and block muscarinic effects, respectively. Chronic exposure may cause neuropathies or psychiatric issues.