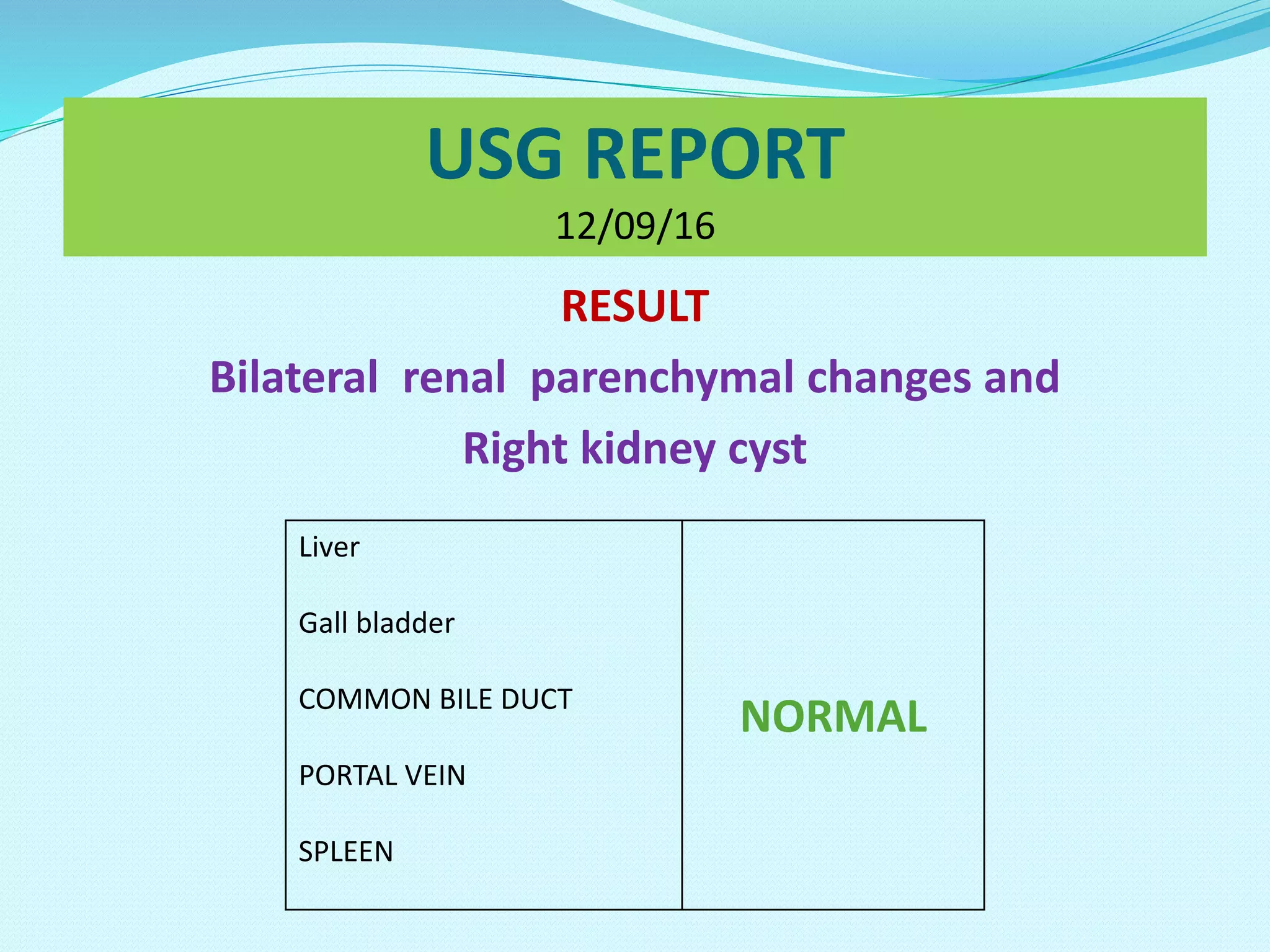
The document summarizes the case of an 82-year-old male patient diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome. It includes details of the patient's medical history, symptoms, lab investigations, biopsy results, medications, and discharge instructions. The patient was started on diuretics, antibiotics, lipid-lowering drugs, thyroid medication, and corticosteroids to treat the condition. The document also provides suggestions to monitor for potential drug interactions and complications related to the patient's treatment and disease.