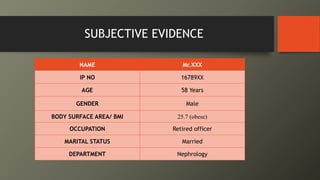
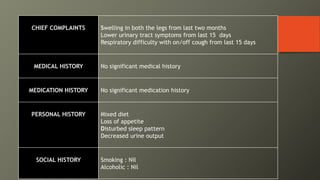
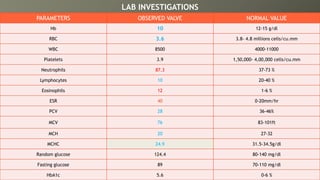
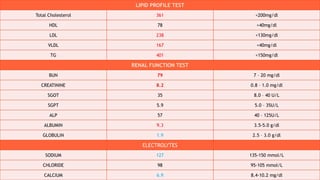
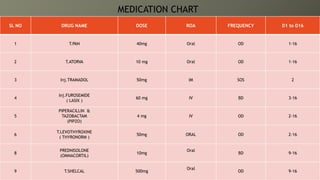
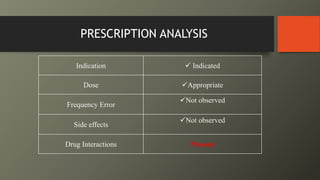
This document presents a case of a 58-year-old male with nephrotic syndrome. The patient presented with leg swelling, lower urinary tract symptoms, and respiratory difficulty. Laboratory tests showed proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and hyperlipidemia. The patient was diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome and stage 1 hypertension. The treatment plan included medications to relieve symptoms, lower cholesterol, improve kidney function, eliminate fluid accumulation, and improve quality of life. The pharmacist provided interventions on monitoring for adverse effects and recommended diet and lifestyle modifications.