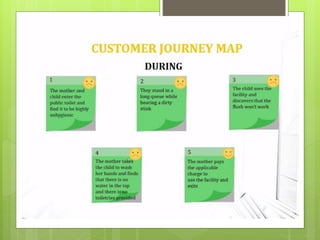
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem solving that involves redefining problems, creating innovative ideas, and testing solutions. It has five phases - empathizing to understand user needs, defining the problem, ideating solutions, prototyping concepts, and testing. Key aspects include customer journey mapping to gain insights, root cause analysis using techniques like 5 whys, and addressing conflicts of interest between stakeholders. The process is iterative, with testing prototypes and getting feedback to refine solutions. Design thinking provides a creative, efficient approach to solving problems and gaining a competitive edge.