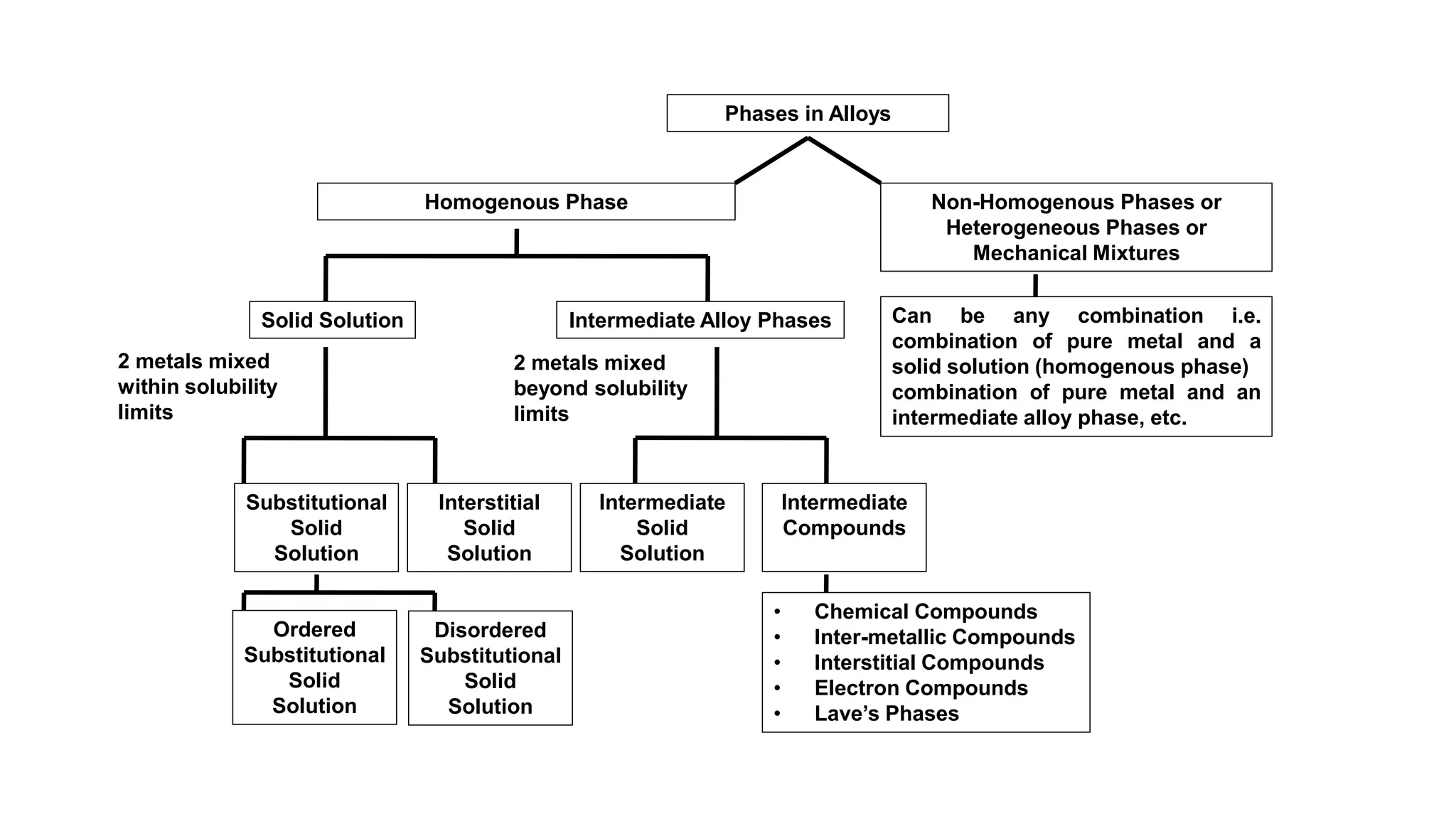
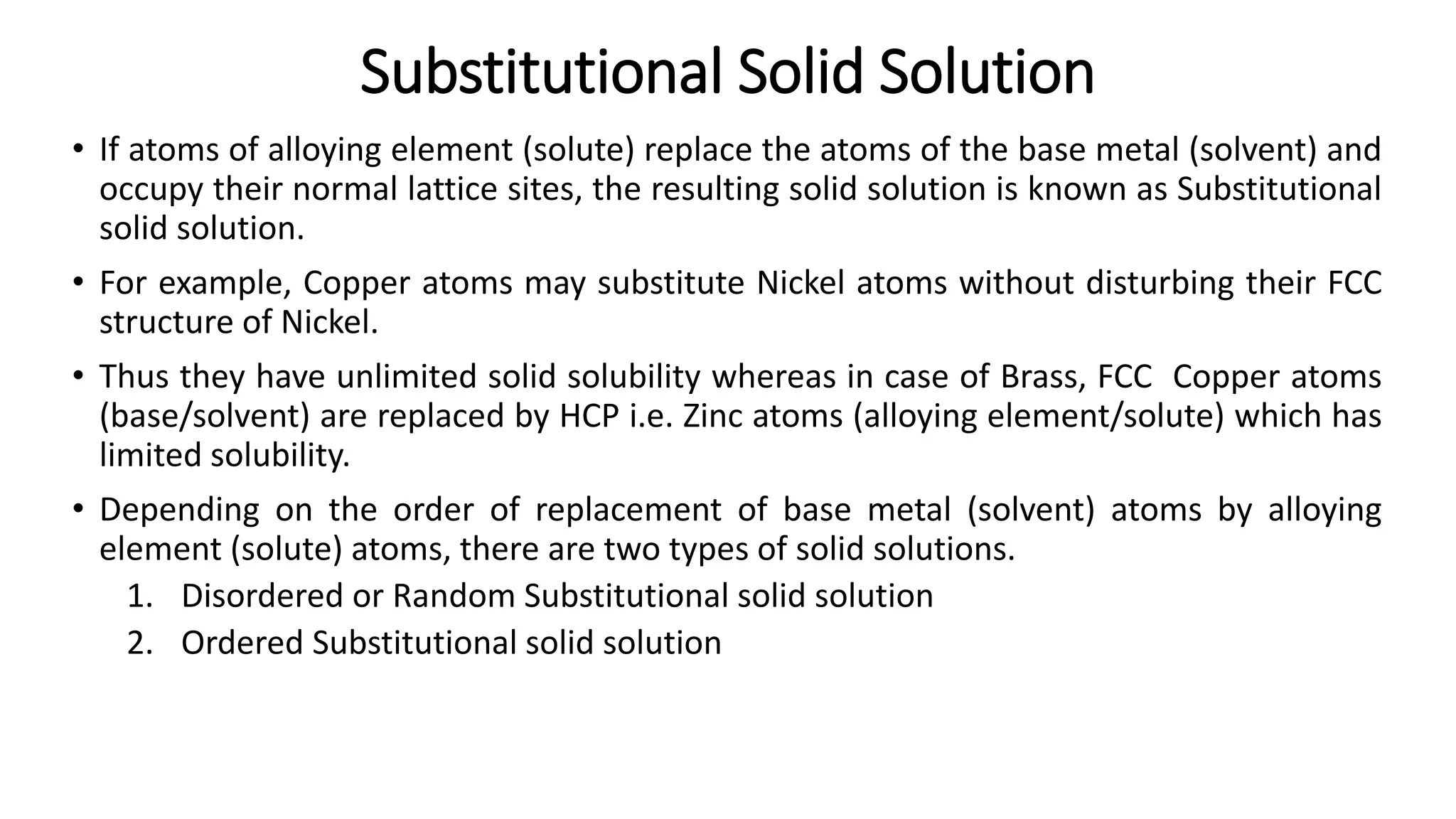
The document discusses the formation of solid solutions, which occur when two metals mix within their solubility limits, leading to either substitutional or interstitial solid solutions. It outlines Hume-Rothery's rules for creating substitutional solid solutions, emphasizing the importance of crystal structure, atomic size, chemical affinity, and valency. Additionally, the document describes intermediate phases and compounds that arise when solubility limits are exceeded, including various types of intermediate compounds and their properties.