This document discusses the different types of conditional sentences in English:
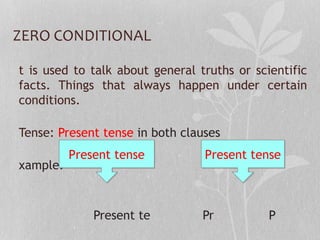
- Zero conditional refers to general truths using present tense in both clauses.
- First conditional refers to possible or real situations using present tense in the if-clause and future tense in the main clause.
- Second conditional refers to unlikely or improbable situations using past tense in the if-clause and "would" in the main clause.
- Third conditional refers to hypothetical or imaginary past situations using past perfect in the if-clause and "would have" in the main clause.
It also covers using time clauses like "when", "as soon as", "until", "before", and "after" with future tenses.