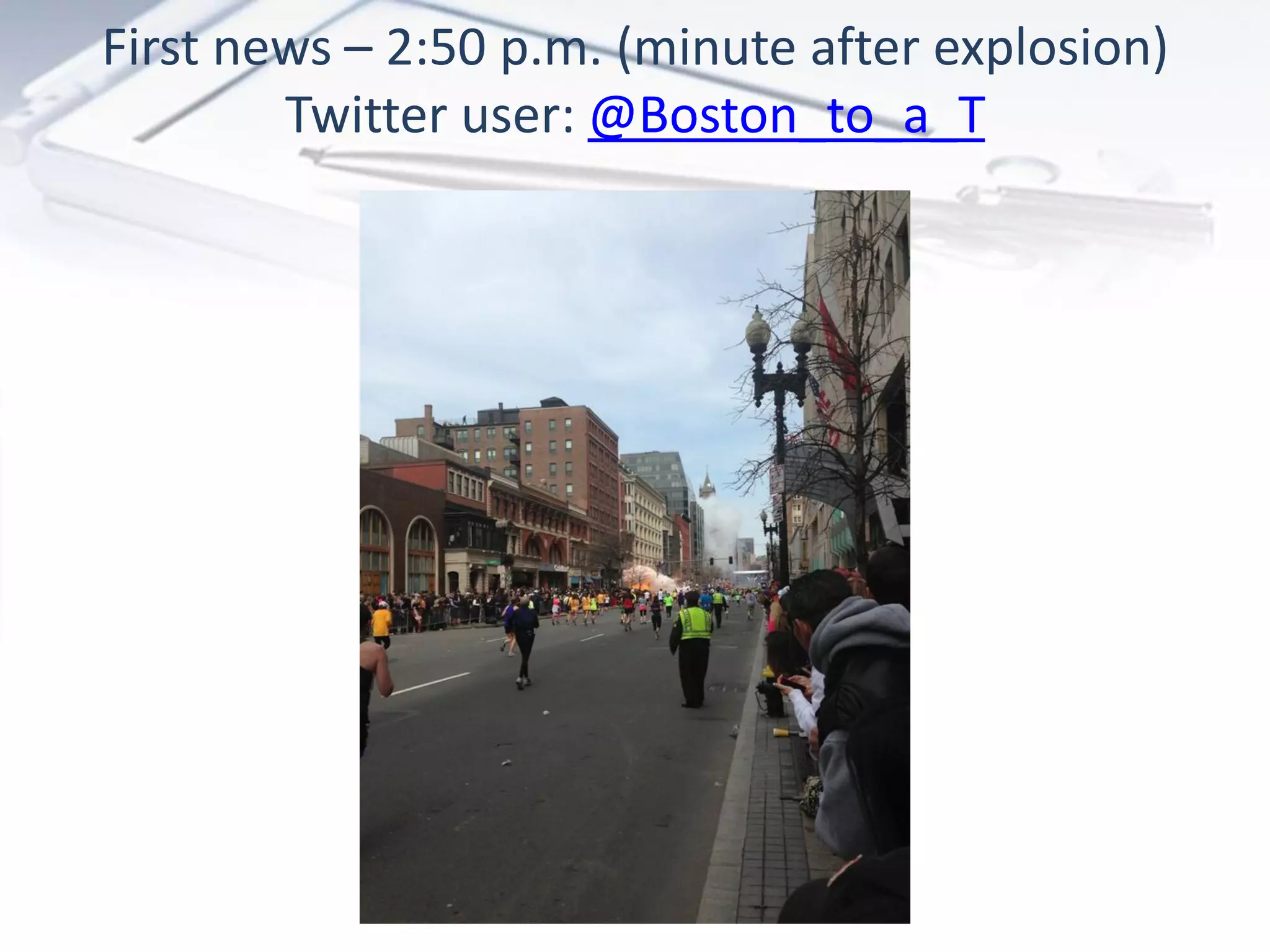
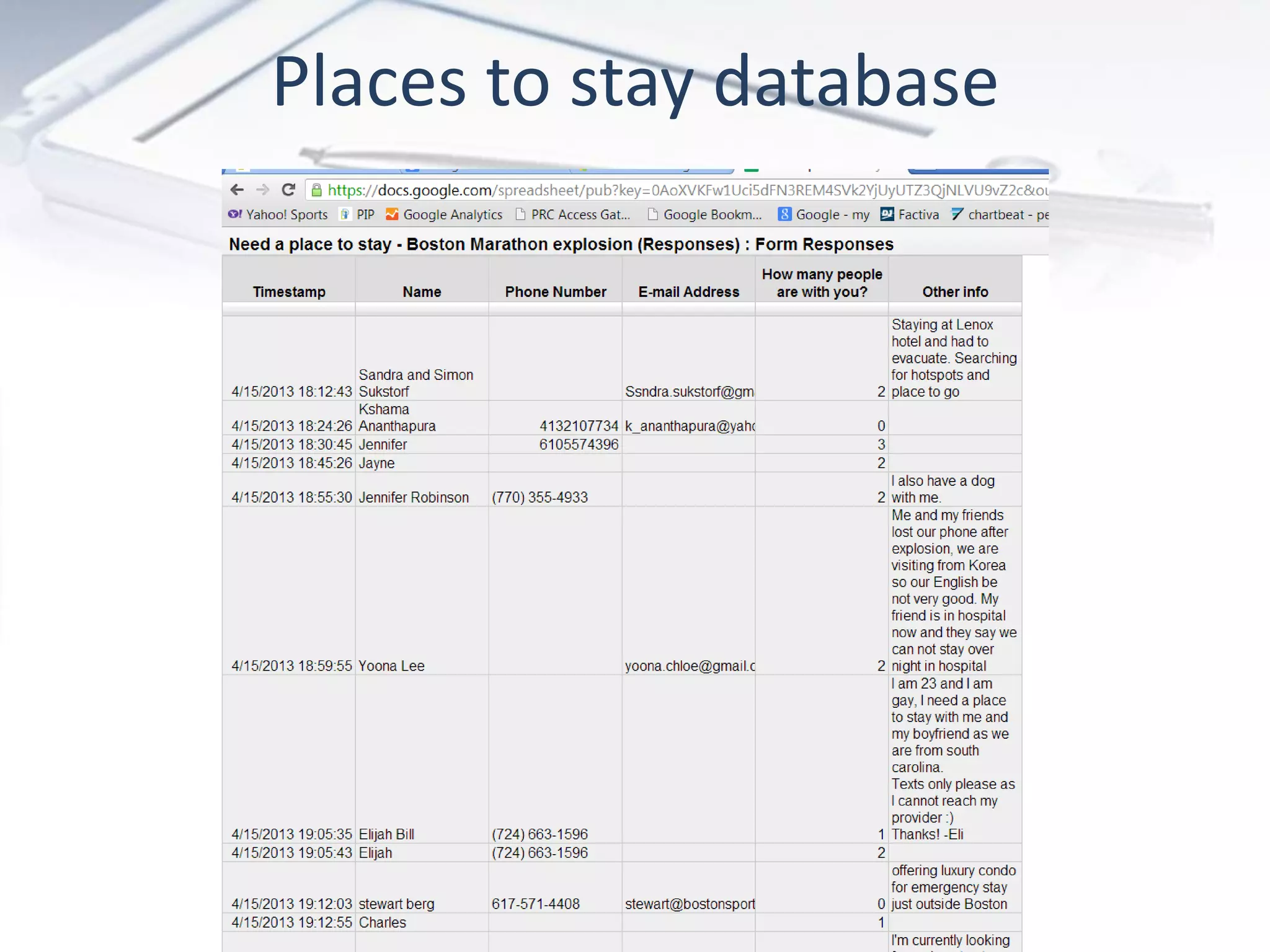
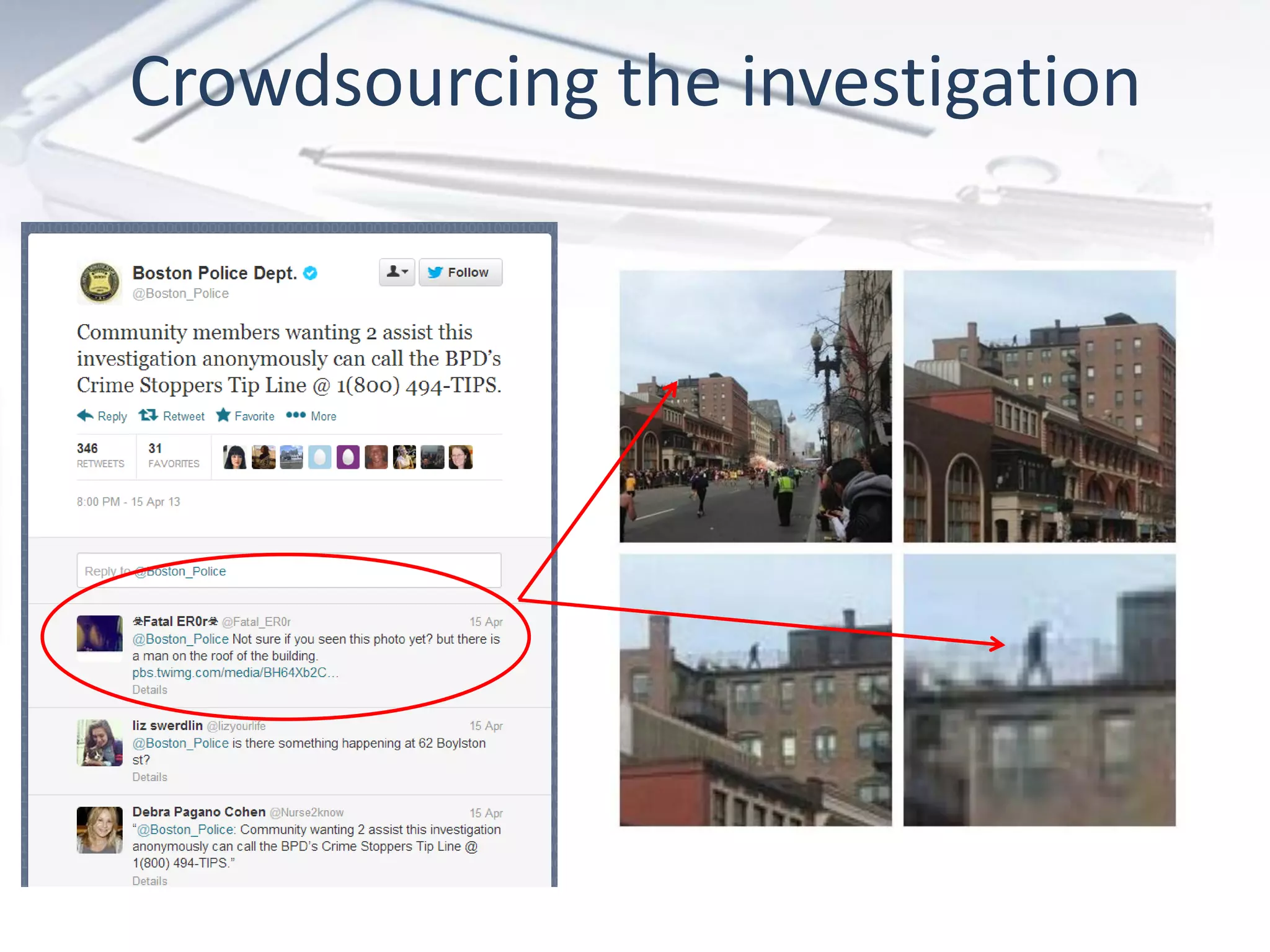
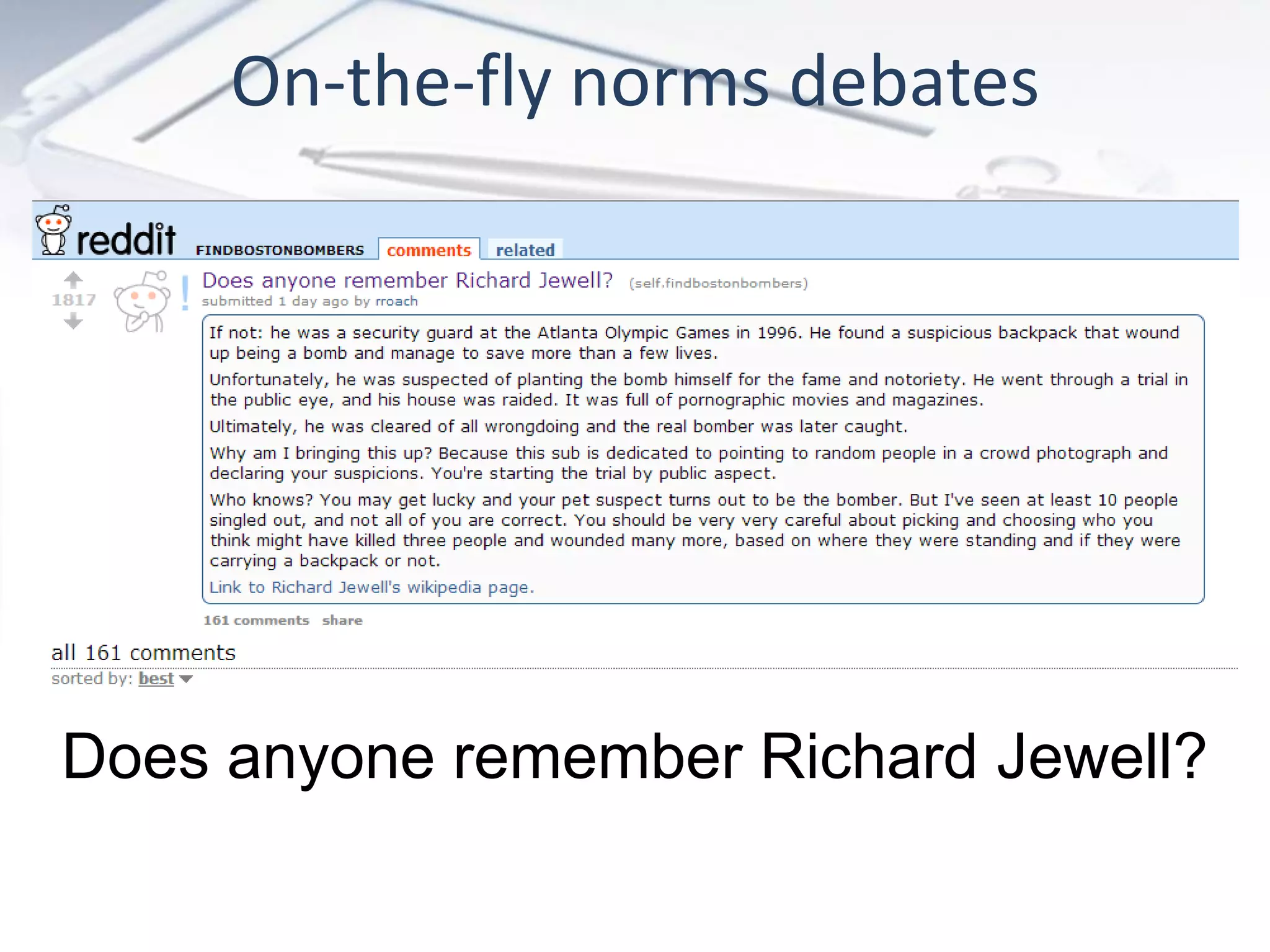
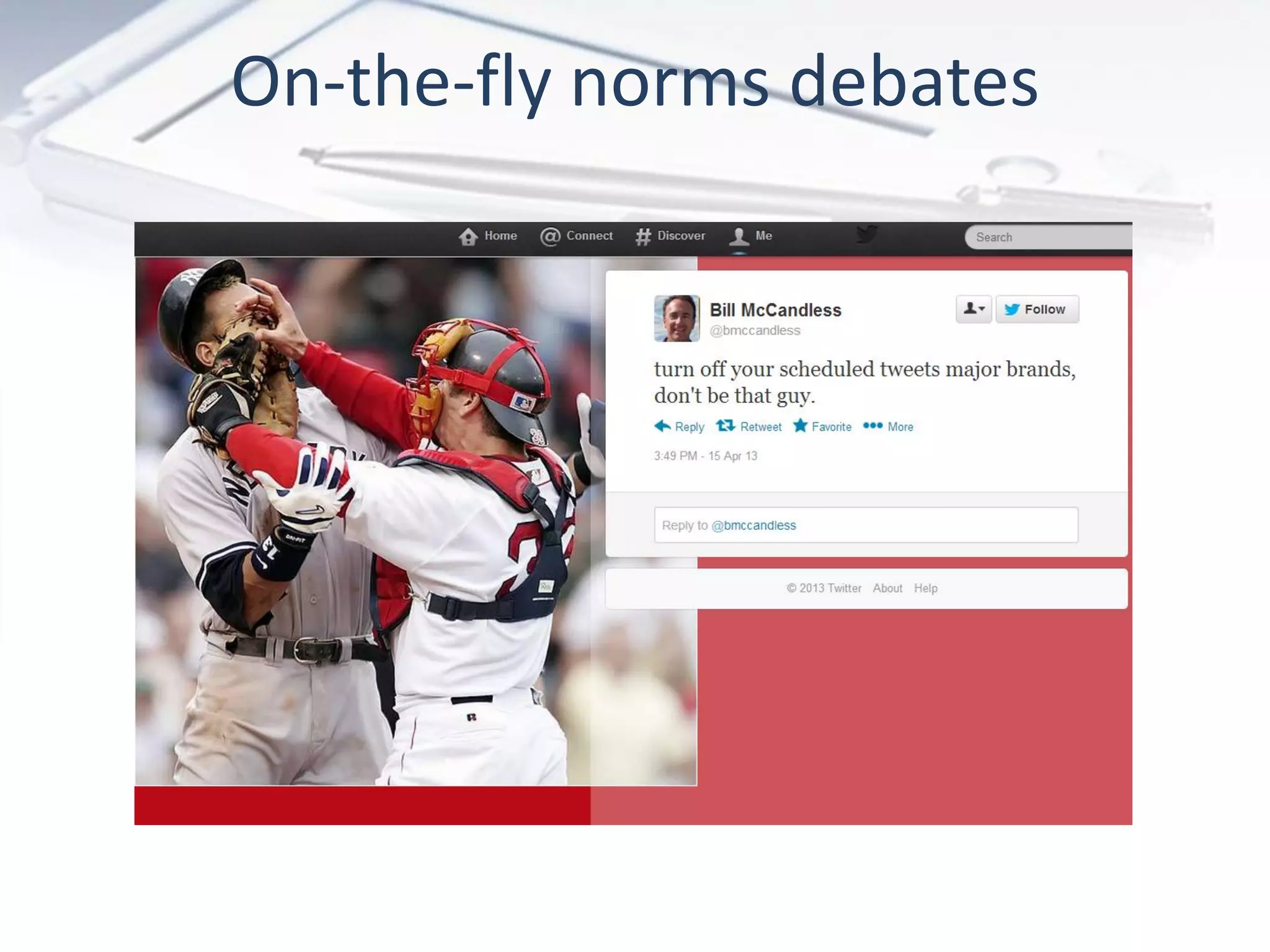
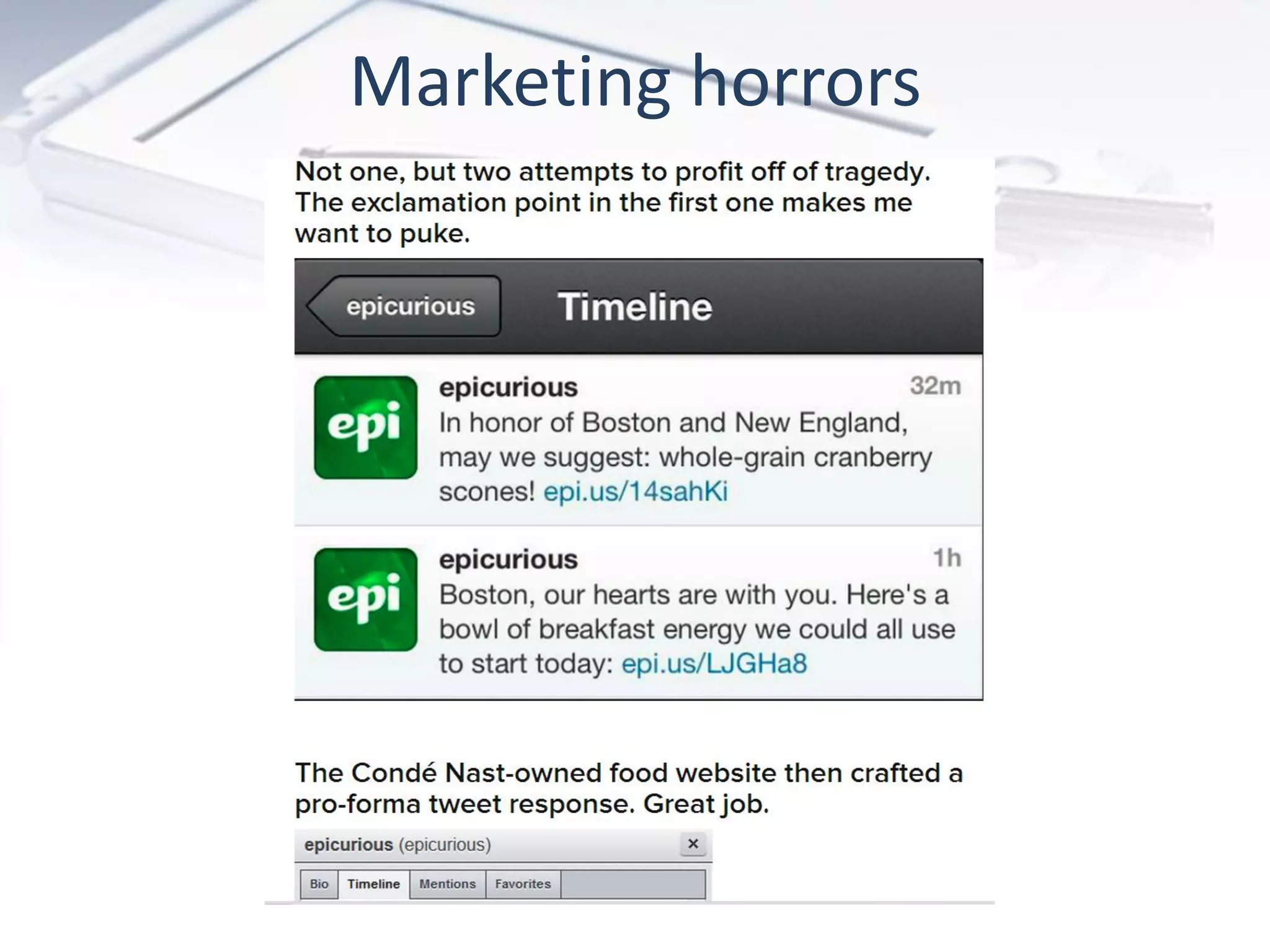
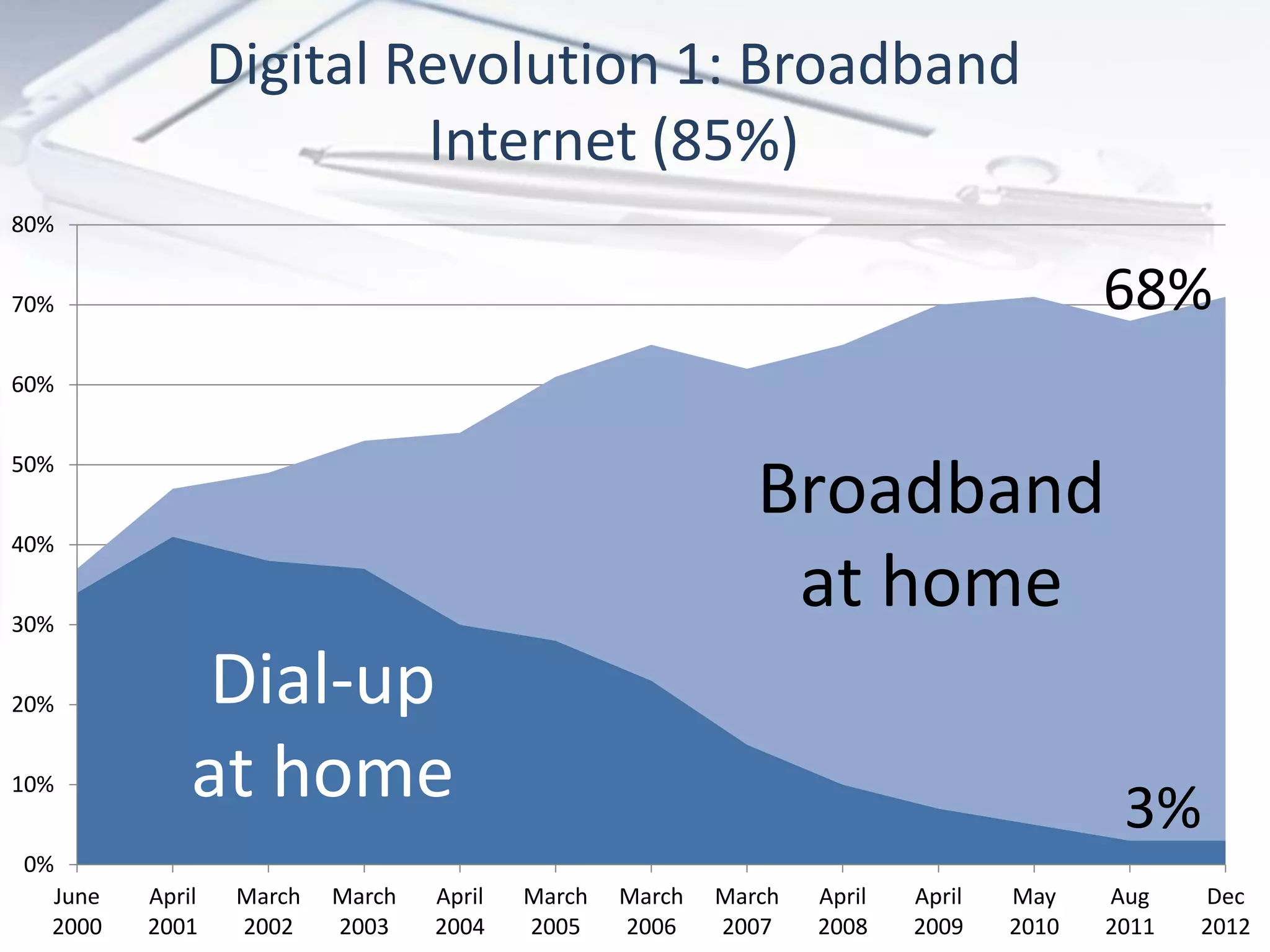
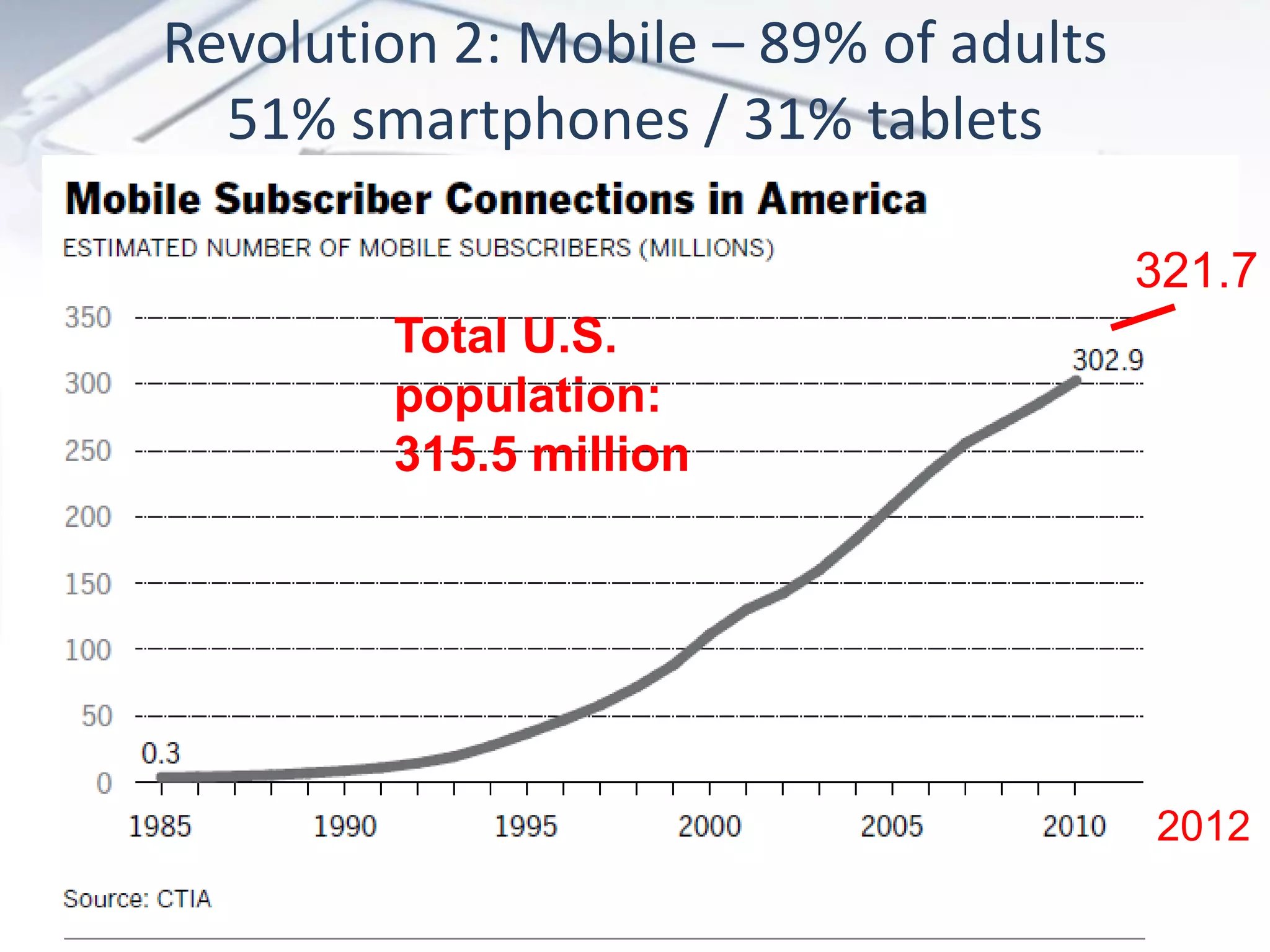
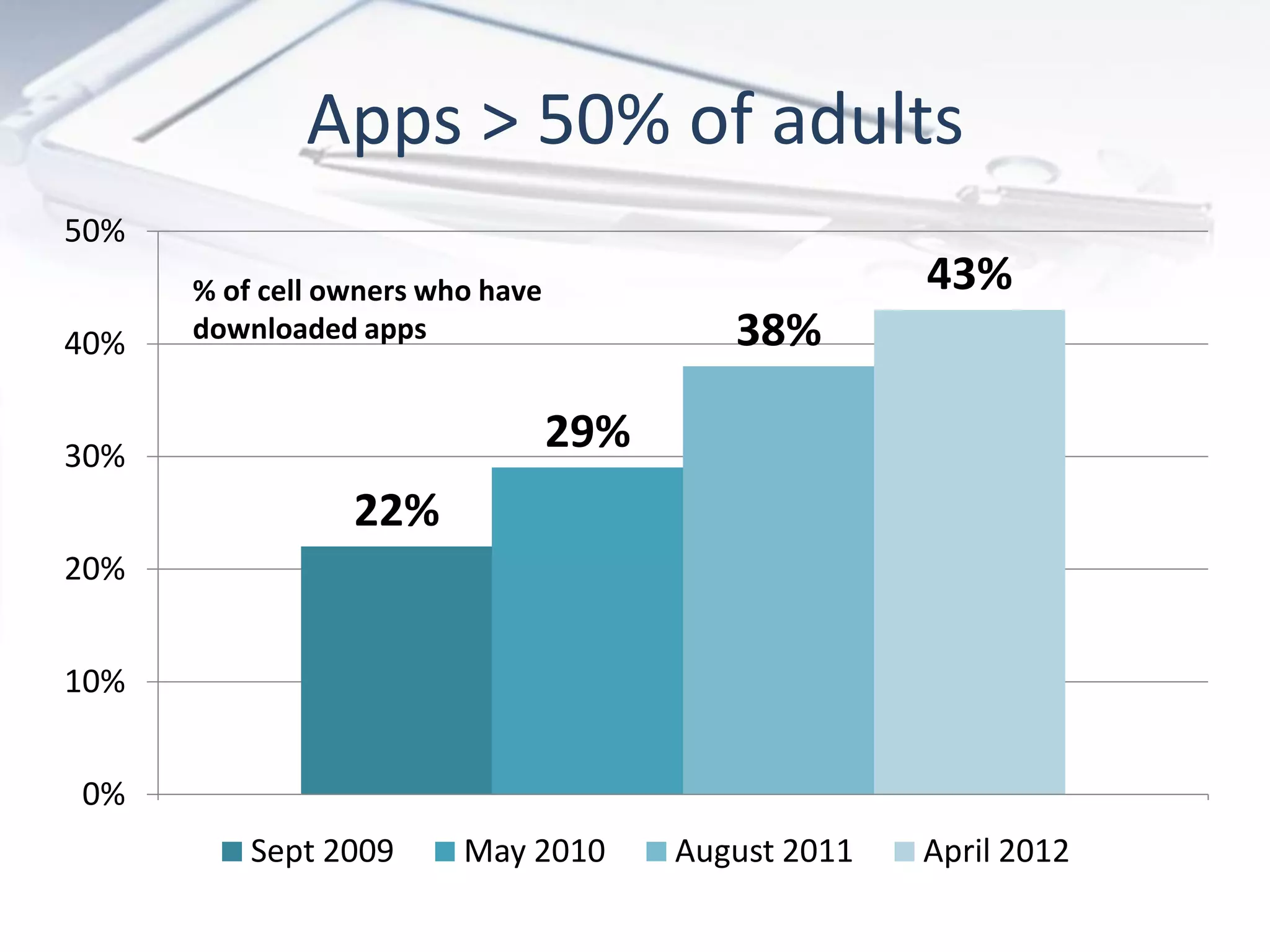
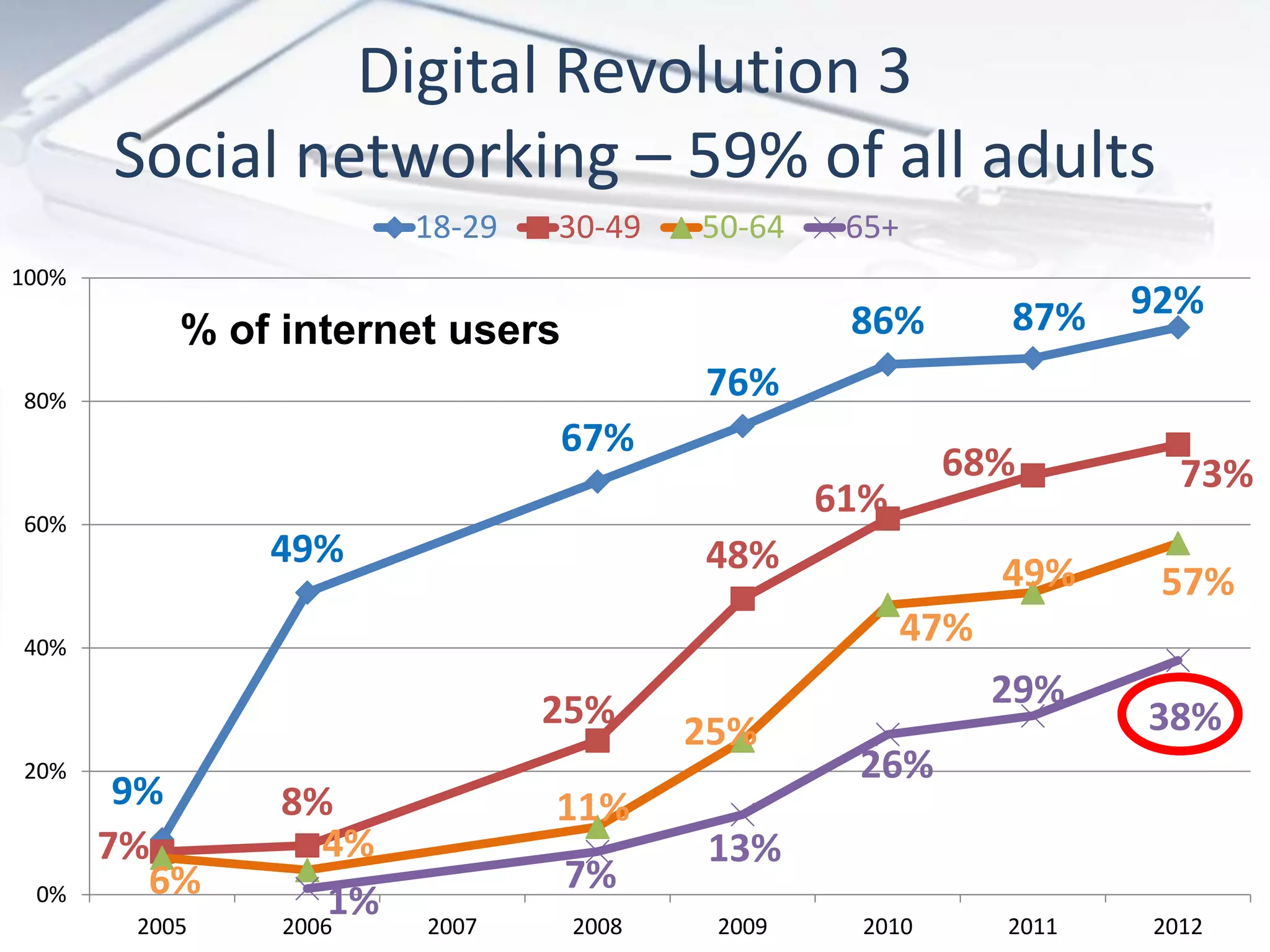
The document discusses the evolution of digital marketing through new media ecosystems, particularly in relation to real-time events like the Boston bombing. Key themes include the rise of mobile and social networking, which have transformed information consumption and marketing strategies. It highlights the complexities of communication in the digital age, including the impact of networked individualism and the challenges marketers face in controlling their messages.