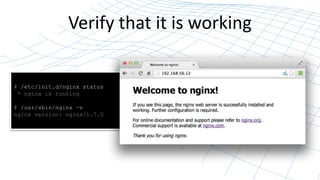
This document outlines a webinar on nginx installation and tuning, detailing the installation process, system and software tuning, and benchmarking techniques. It highlights the functionalities of nginx, compares its open-source version with nginx plus, and provides practical commands for installation and tuning. The final emphasis is on installing from the official nginx repository and the importance of benchmarking for optimal performance.











![The Backlog Queue
• What happens when a connection is received?
– SYN / SYNACK [syn_backlog queue] or syncookie
– ACK [listen backlog queue] / NGINX:accept()
– net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog
– net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies
– net.core.somaxconn
• NGINX: listen backlog=1024
– net.core.netdev_max_backlog](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginxinstallationandtuning-141120212616-conversion-gate01/85/NGINX-Installation-and-Tuning-20-320.jpg)

![Ephemeral Ports
• What happens when NGINX proxies connections?
Each TCP connection requires a unique 4-tuple:
[src_ip:src_port, dst_ip:dst_port]
Ephemeral port range and lifetime:
– net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range
– net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginxinstallationandtuning-141120212616-conversion-gate01/85/NGINX-Installation-and-Tuning-22-320.jpg)