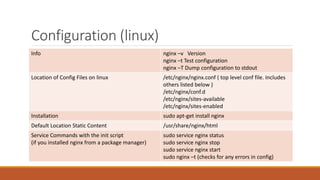
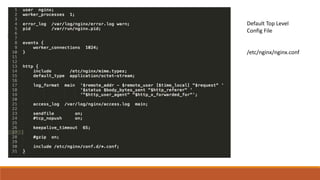
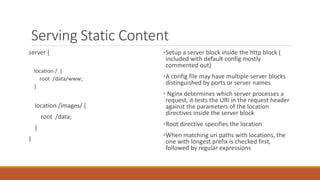
Nginx is a web server and proxy server that is modular, allowing users to specify which modules they want. It has a main configuration file located at /etc/nginx/nginx.conf that includes other configuration files. Nginx uses server blocks and location directives to map URI requests to resources. It can serve static content from a specified root directory or act as a proxy server by forwarding requests to another server. Rewrite rules using the return or rewrite directives allow changing URLs in client requests to redirect users.