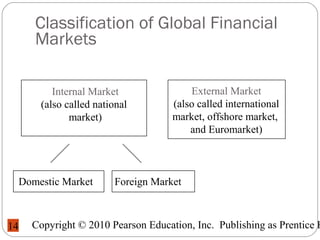
The document outlines the types of assets, distinguishing between tangible and intangible assets, and details various financial instruments including loans and bonds. It explains the role and classification of financial markets, the importance of regulating these markets, and the motivations for integrating and utilizing international markets. Additionally, it addresses the risks associated with financial assets and the functions of derivative instruments in managing those risks.