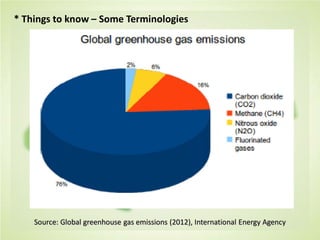
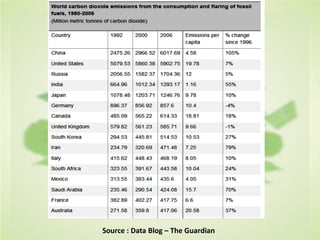
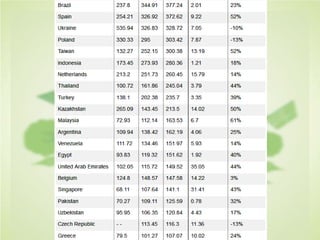
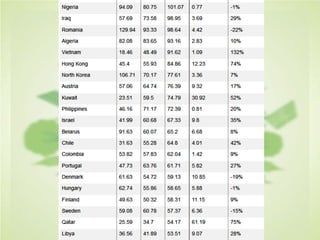
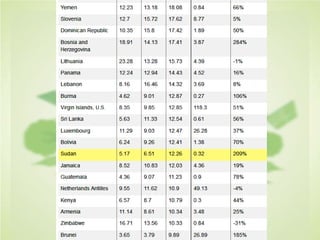
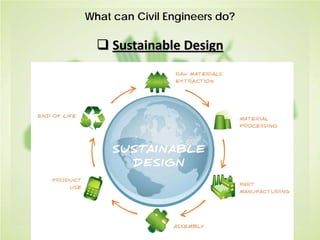
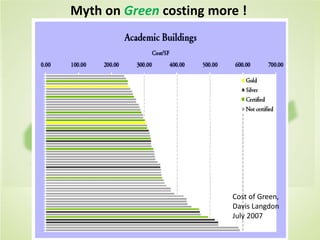
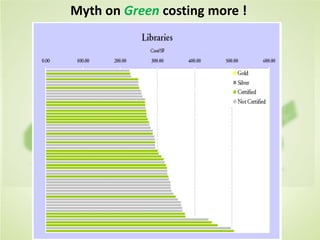
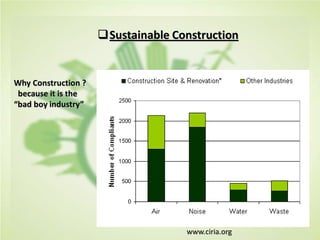
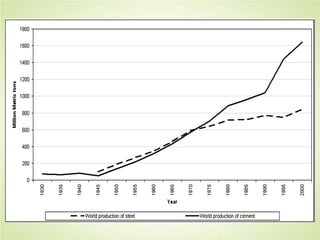
This document summarizes the key concepts of sustainable development and its relationship to civil engineering. It defines sustainability and sustainable development, noting their focus on meeting present needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet their own needs. For civil engineers, sustainability means using natural resources to improve society's quality of life indefinitely. The document outlines 17 sustainable development goals and discusses civil engineers' role in achieving these through sustainable design, green buildings, and sustainable construction practices like reducing waste and using renewable building materials. It provides examples of sustainable buildings from around the world.