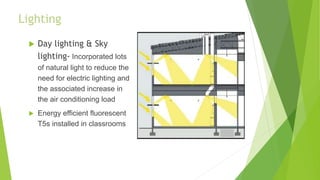
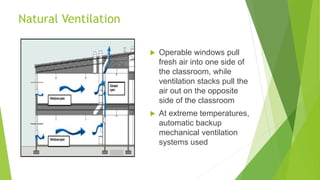
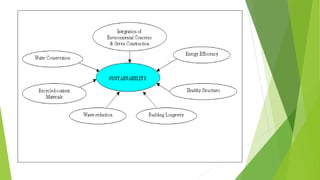
The document discusses green buildings and their benefits. Green buildings are designed to reduce pollution and natural resource consumption through techniques like minimizing toxic materials and maximizing energy efficiency. They aim to be in harmony with surrounding nature, control pollution, and recycle waste on-site. Green buildings provide benefits like reduced operating costs, higher property values, and improved occupant health and productivity compared to traditional buildings.