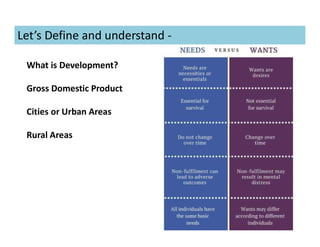
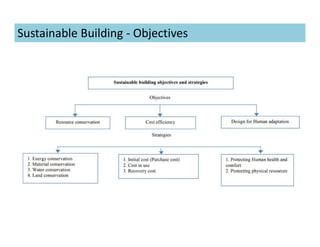
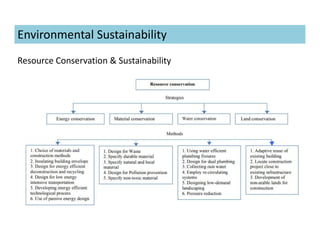
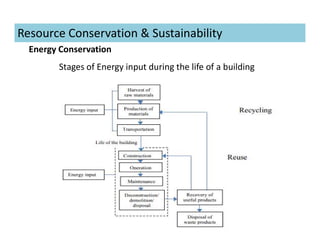
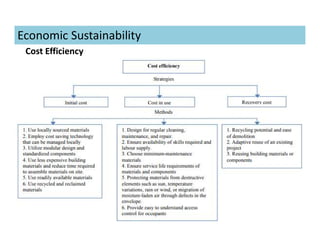
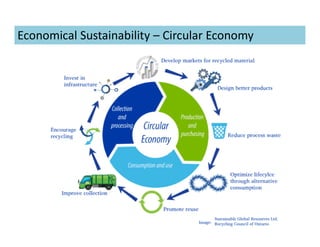
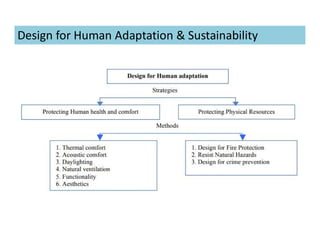
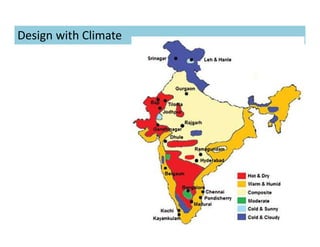
This document discusses concepts of sustainable buildings from social, economic, and environmental perspectives. It provides definitions of sustainable development as meeting present needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet their own needs. Sustainable buildings aim to achieve environmental sustainability through resource conservation, economic sustainability through cost efficiency over the building's lifetime, and social sustainability by considering impacts on communities. The document outlines objectives and strategies for sustainable building design across these three pillars of sustainability.