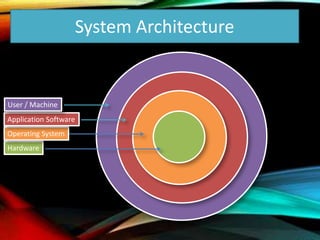
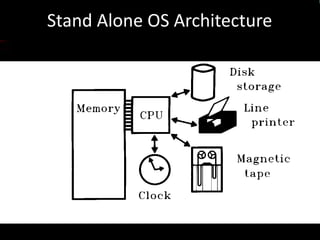
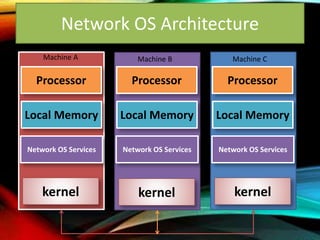
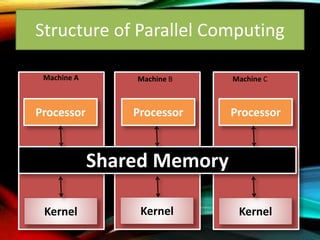
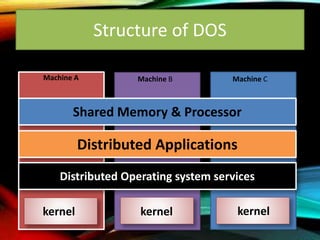
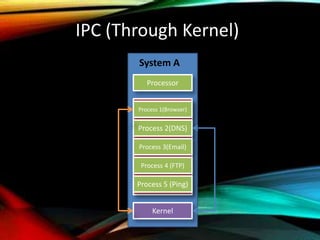
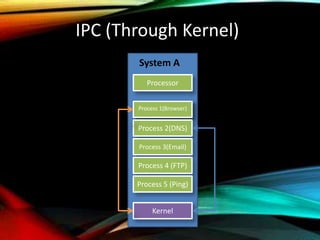
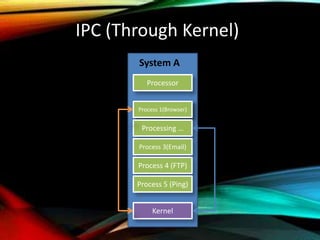
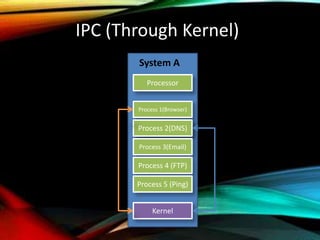
The document provides an overview of distributed operating systems, detailing components such as the kernel, command interpreter, and device drivers, as well as different types of operating systems like standalone, networked, and distributed. It describes distributed applications and parallel processing, highlighting how they operate on multiple computers within a network for efficiency. Additionally, it discusses memory systems, inter-process communication, and procedures for executing operations between systems in a network.