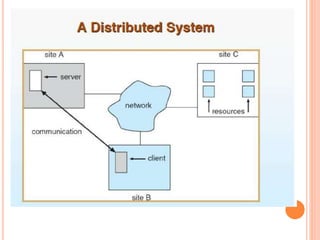
A distributed operating system allows applications to run on multiple interconnected computers. It makes the distributed computers appear as a single centralized system to users. There are two main types - networking operating systems, which allow file and printer sharing on a local network, and distributed operating systems, where users are unaware of the underlying machines. Effective communication between the distributed systems requires addressing issues like naming, routing, connections, and dealing with contention for shared resources. While distributed systems provide benefits like improved performance and reliability, they also face challenges such as security, bandwidth limitations, and reduced performance due to network delays.