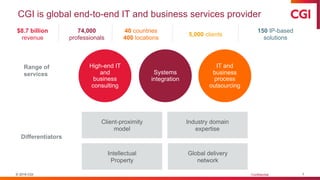
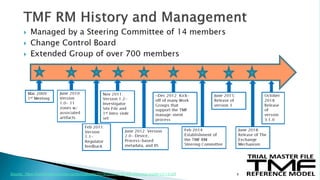
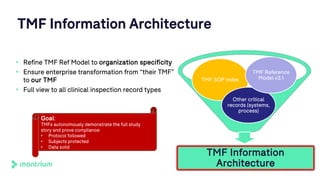
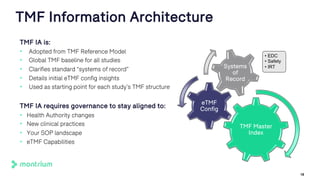
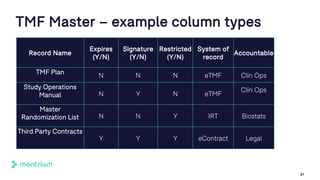
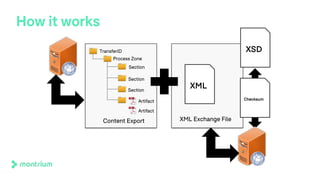
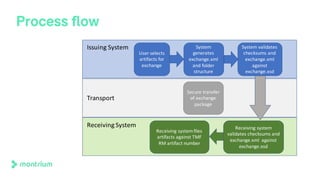
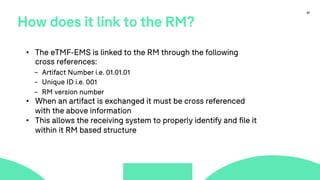
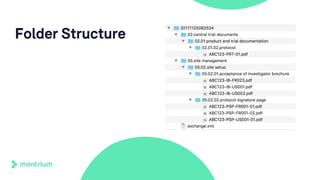
The document outlines a webinar discussing the implementation of the TMF Reference Model and its relevance in managing clinical trial documentation. It covers topics such as adapting the model for trial organizations, electronic TMF systems, and the TMF Exchange Mechanism Standard. The session also features insights from professionals in the life sciences industry and emphasizes the framework's benefits for compliance and efficiency.