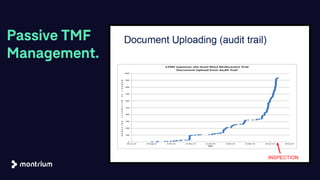
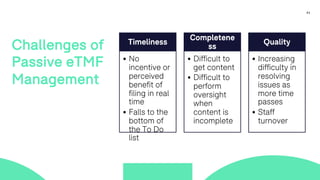
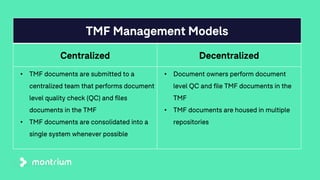
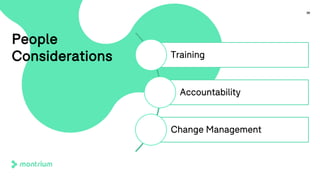
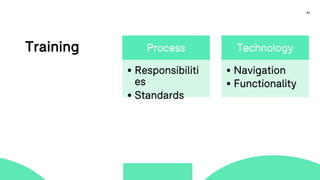
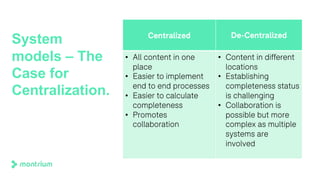
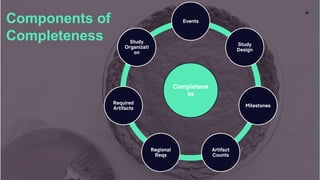
The document outlines a webinar focused on transitioning from passive to active Trial Master File (TMF) management using eTMF systems. It defines passive TMF management as outdated and risky, while highlighting the advantages of active management, including real-time updates and better oversight. Discussions also cover different management models, roles, and technology considerations necessary for successful eTMF implementation.