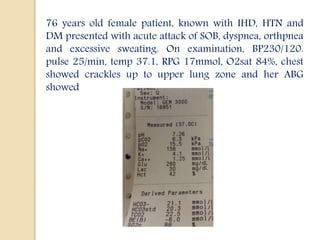
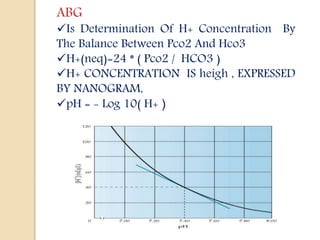
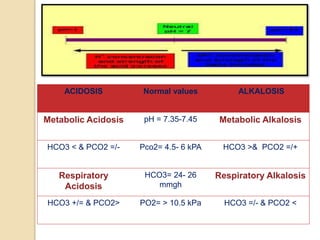
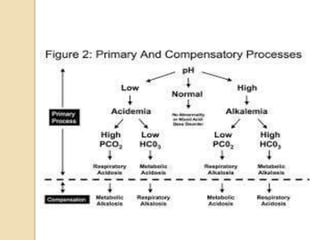
This document discusses arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, including how to interpret ABG results, indications for ABG testing in the emergency room, and examples of ABG readings in different clinical scenarios. ABG analysis determines the concentration of hydrogen ions (pH) and helps identify respiratory and metabolic acid-base disturbances. The primary pathologies can be metabolic, respiratory, or mixed. Compensatory mechanisms aim to return the pH to normal range. Anion gap should be considered in metabolic insults.



![Degree Of Compensation
In respiratory causes:
oIf acute acidosis: pH falls by 0.08 and HCO3 rises by
1 mmol/L for each 1.5 kPa above 5.5.
oIf chronic acidosis: pH falls by 0.03 and HCO3 rises
by 2-4 mmol/L for each each 1.5 kPa above 5.5 kPa.
oFor respiratory alkalosis, the opposite directions are
present for all changes.
In metabolic causes
oIf metabolic acidosis: Expected PaCO2 = (1.5 x
[HCO3] + 8) +/- 2.
oIn metabolic alkalosis: Expected PaCO2 = (0.9 x
[HCO3] + 9) +/- 2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abg-151030153734-lva1-app6892/85/ABG-FOR-EMERGENCY-DEPARTMENT-7-320.jpg)



![Mixed Acid Base Disorder
Mixed metabolic respiratory disorder
When the PCO2 is elevated and the [HCO3-] reduced,
respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis coexist. And vice
vecra
oChronic Respiratory Acidosis and Anion Gap Metabolic
Acidosis
Example:
COPD patient who develops shock and lactic acidosis
oChronic Respiratory Acidosis and Metabolic Alkalosis
Example:
Pulmonary insufficiency and diuretic therapy
oRespiratory Alkalosis and Metabolic Acidosis
Example:
Salicylate intoxication](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abg-151030153734-lva1-app6892/85/ABG-FOR-EMERGENCY-DEPARTMENT-12-320.jpg)