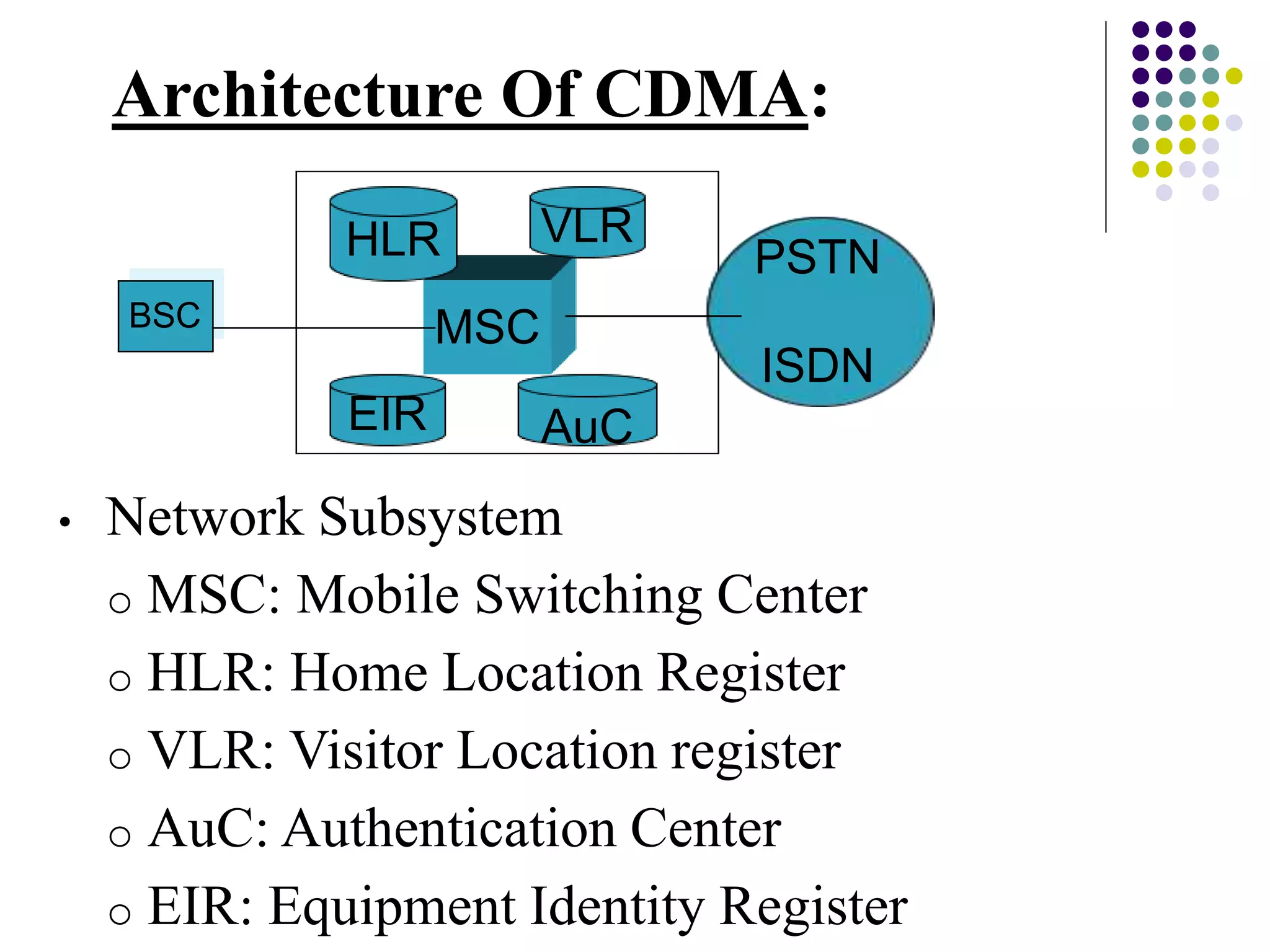
This document discusses Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) cellular radio networks. It describes the key components of a CDMA network including the mobile station, base station subsystem, and network subsystem. It explains how CDMA works by allocating different codes to users allowing multiple users to transmit over the same radio channel simultaneously. The advantages of CDMA include spread spectrum communication, soft handoff, and high quality voice. Disadvantages include the near-far problem and lower network capacity compared to GSM initially. The document concludes that CDMA is superior to other multiple access techniques and is an important technique in radio communications.