Embed presentation
Downloaded 262 times



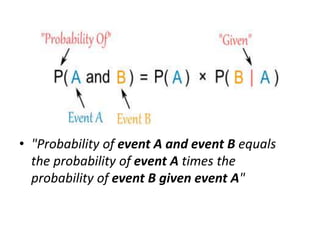





Conditional probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has occurred. It is calculated as the probability of both events occurring divided by the probability of the first event. An example is given of calculating the probability of drawing two white balls in succession from an urn without replacement. The formula for conditional probability is derived as the probability of events A and B occurring divided by the probability of A. This is demonstrated using an example of finding the percentage of friends who like chocolate that also like strawberry.







