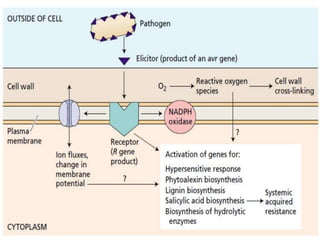
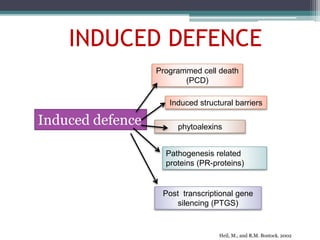
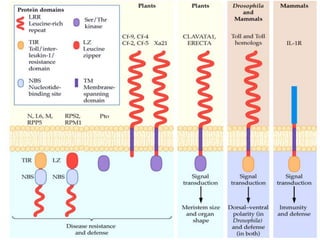
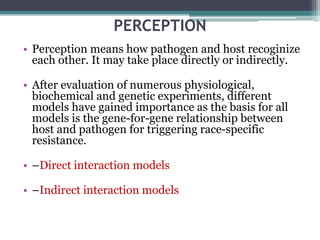
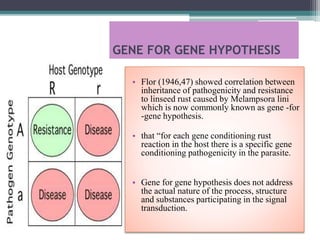
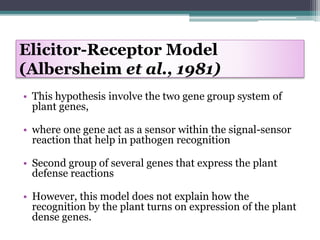
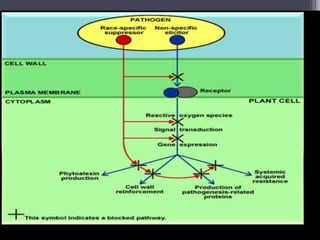
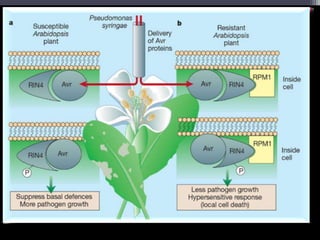
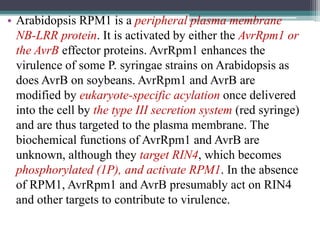
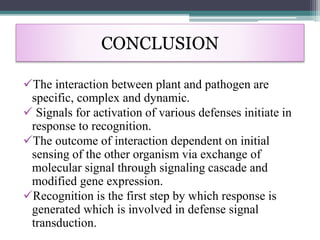
The document discusses the complex interactions between plants and pathogens, detailing types of pathogens, their effects, and plant immune responses. It outlines models of recognition and defense mechanisms, including the gene-for-gene hypothesis and various interaction models such as the elicitor-receptor and guard hypotheses. The conclusion emphasizes the specificity and dynamism of plant-pathogen interactions, with defense signaling initiated by pathogen recognition.