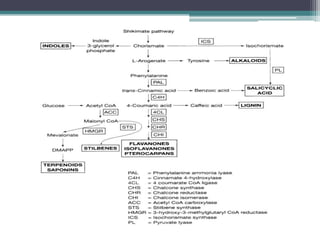
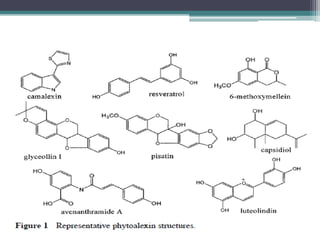
- Phytoalexins are antimicrobial compounds produced by plants after exposure to microorganisms or abiotic stress. They are chemically diverse and fall into classes like terpenoids and alkaloids.
- The concept of phytoalexins was formalized in 1941 after observing that bean tissue produced inhibitory compounds when exposed to a fungal pathogen. Phytoalexins restrict pathogen growth at infection sites.
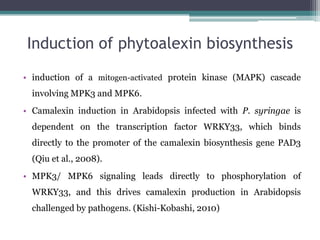
- Induction of phytoalexins involves MAP kinase signaling cascades and transcription factors like WRKY33 regulating genes in biosynthesis pathways. Camalexin production in Arabidopsis in response to pathogens depends on WRKY33 phosphorylation by MPK3/MPK6.