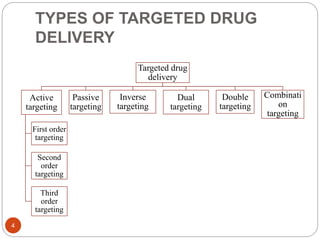
Targeted drug delivery aims to maximize the concentration of drugs at their intended sites of action to improve efficacy and reduce side effects. It involves using drug carriers like liposomes, nanoparticles, and monoclonal antibodies to transport drugs. These carriers can actively or passively target drugs to specific organs, tissues, or cells. Ideal carriers for targeted delivery are non-toxic, stable, and can control drug release rates. Research focuses on developing various carrier types and targeting strategies like passive accumulation, ligand-receptor interactions, and saturation of the reticuloendothelial system. Targeted delivery holds promise for overcoming drug resistance and improving treatment of cancer, diabetes, and other diseases.