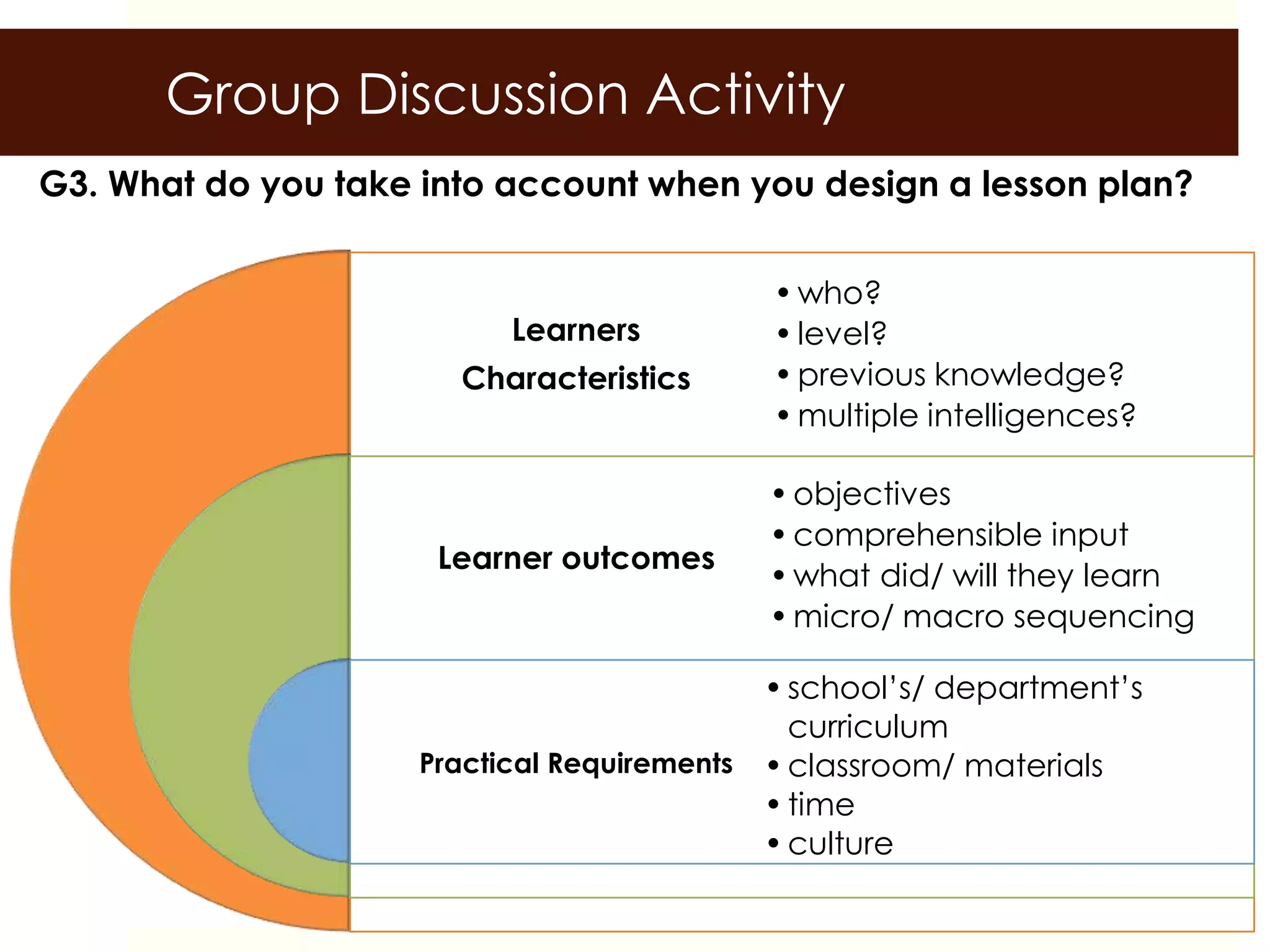
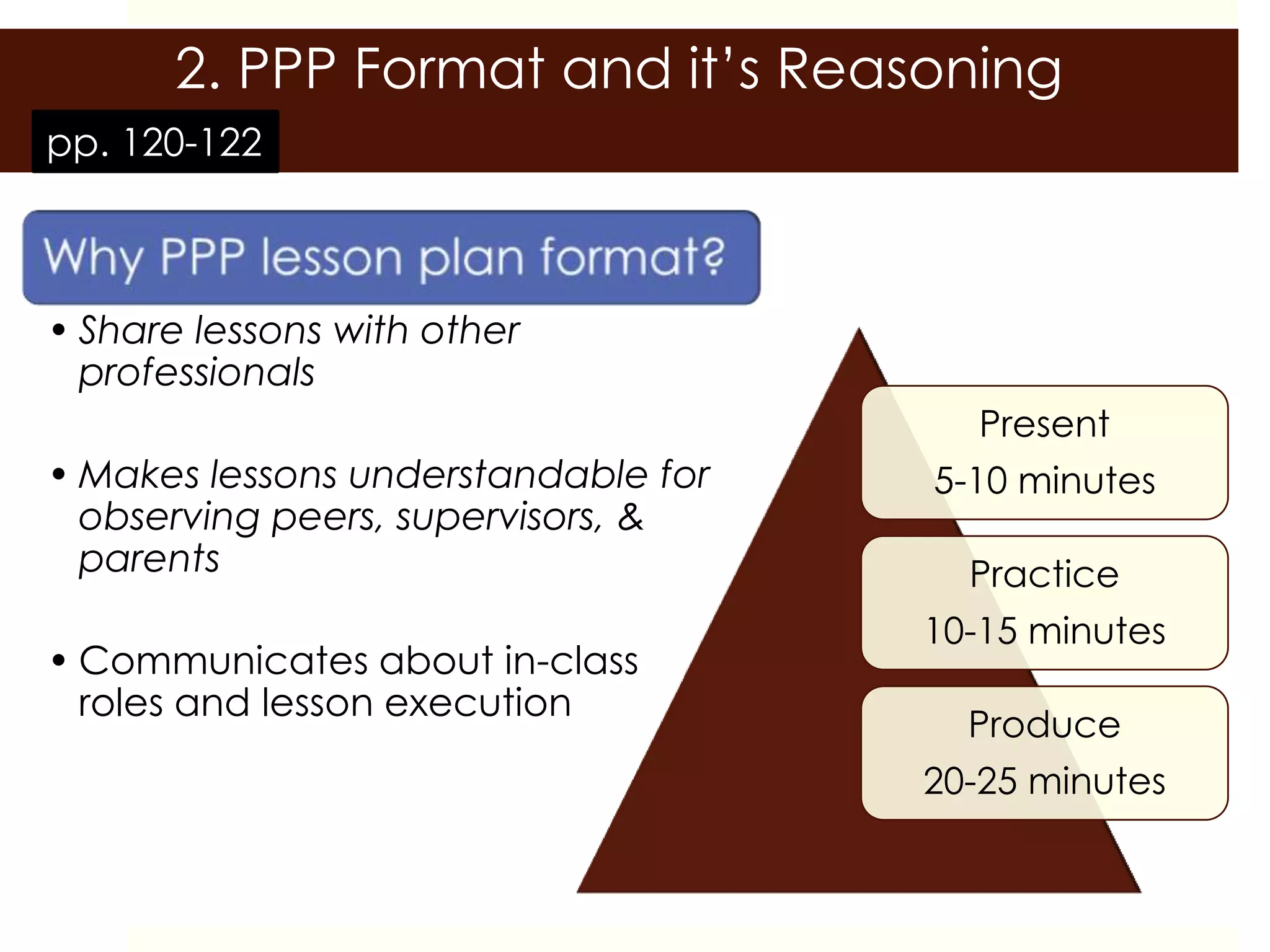
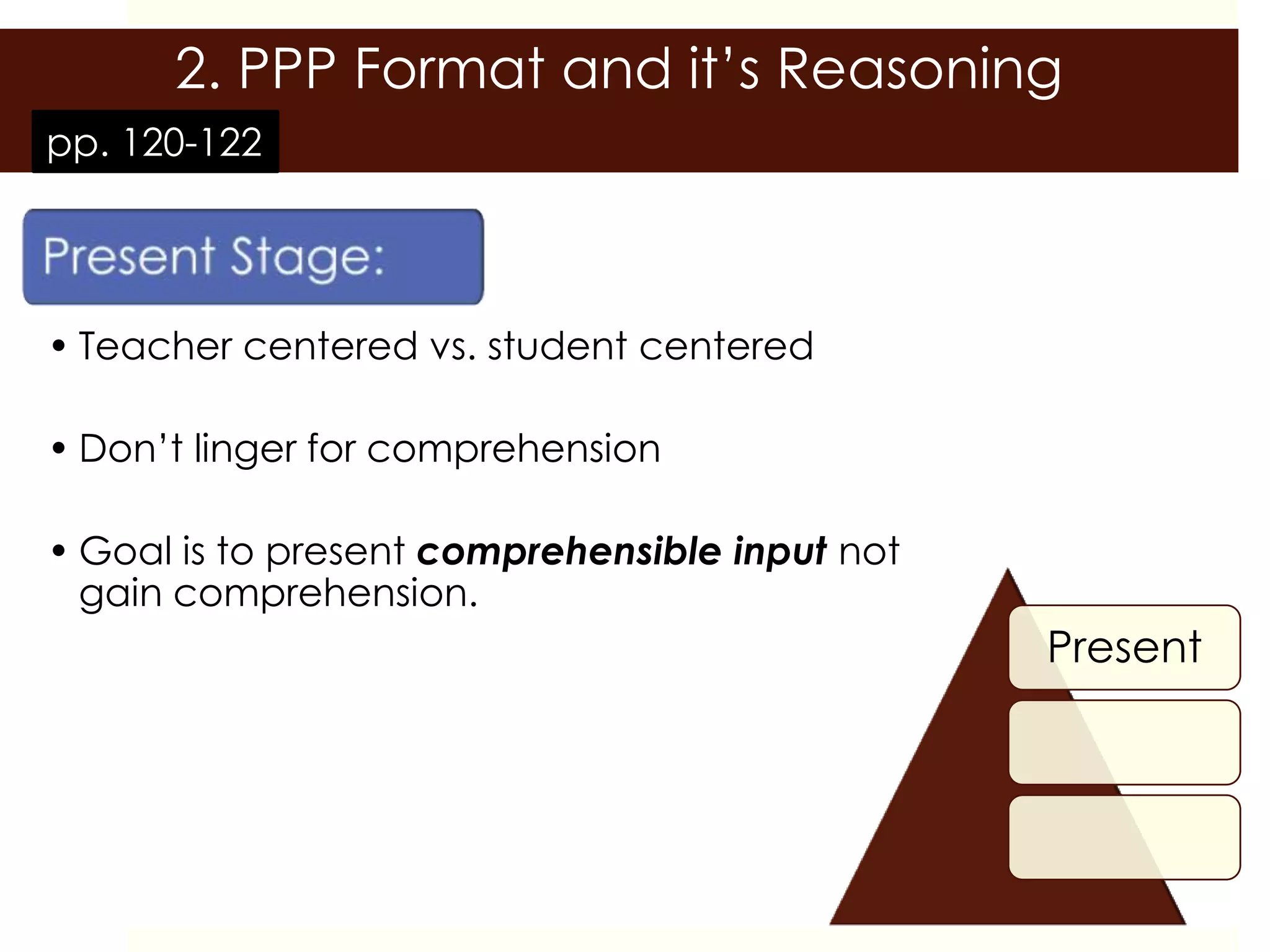
This document outlines a training session on lesson planning using the PPP (Present, Practice, Produce) format. It includes an introduction, group discussion on lesson planning, a lecture covering language skills and methodology, the PPP format and its reasoning, key lesson plan elements, and a lesson planning activity where participants create and peer review lesson plans. The goal is to prepare participants to create effective lesson plans using the PPP format and consider important elements like objectives, materials, and assessments.