Embed presentation
Downloaded 31 times


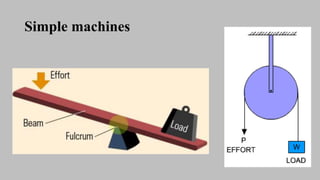
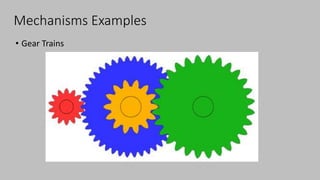



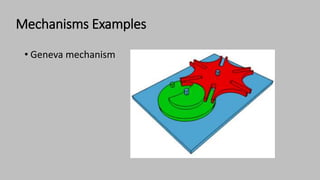
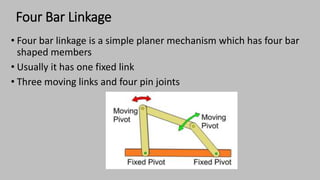
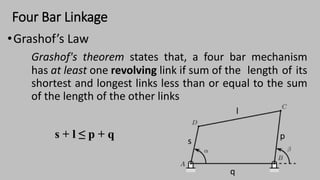

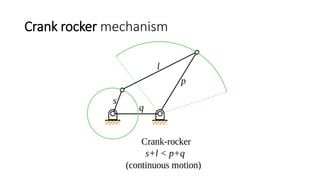
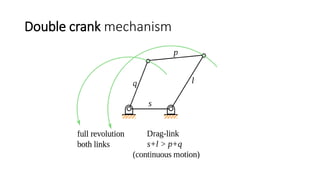
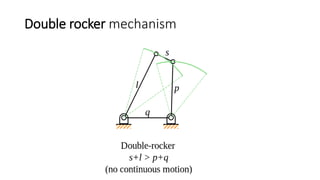
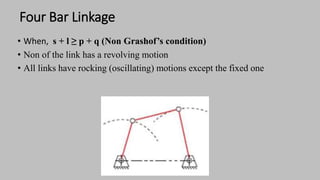
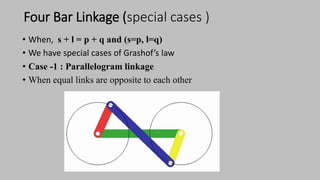




The document introduces mechanisms, defining them as assemblies of machine components designed to create desired motion from available motion while transmitting forces. It explains the four bar linkage mechanism, including Grashof's law, which determines the motion types based on the lengths of links, and describes various crank mechanisms. Additionally, it covers special cases of the four bar linkage such as parallelogram and deltoid linkages.


















