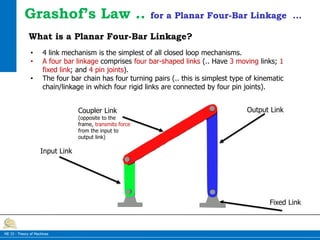
The document discusses Grashof's law for planar four-bar linkages. Grashof's law states that for continuous relative rotation between links, the sum of the shortest and longest link lengths must be less than or equal to the sum of the other two link lengths. The document describes the different types of four-bar linkages that satisfy or do not satisfy Grashof's law and their motion characteristics. It also discusses the significance of Grashof's law in mechanisms driven by motors to ensure the input crank can rotate fully.