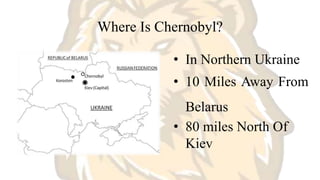
The Chernobyl disaster was the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. In 1986, Reactor 4 of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine exploded and caught fire during a safety test, releasing massive amounts of radiation into the atmosphere. Over 100,000 people were evacuated and hundreds of square miles of land were severely contaminated, with higher rates of cancer and other illnesses reported among those exposed. The cleanup required thousands of liquidators and cost billions. While a sarcophagus was constructed to contain the reactor, the effects of the radiation release continue to impact the region for decades to come.