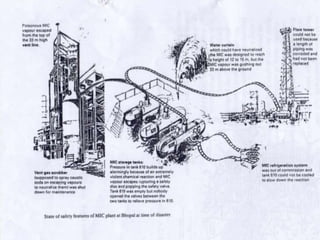
The Bhopal gas tragedy occurred on December 3rd, 1984 when a leak of methyl isocyanate and other toxic gases from a pesticide plant owned and operated by Union Carbide India Limited caused over 500,000 injuries and thousands of deaths. Poor maintenance of the plant, reduced and untrained staff, and inadequate safety systems led to water entering a tank containing tons of methyl isocyanate and initiating a chemical reaction that released large volumes of toxic gases. The gases rapidly spread over nearby slums and caused immense suffering through damage to eyes, lungs, and other organs among both those exposed and their descendants. The disaster highlighted the need for stricter international safety standards in industrial plants.