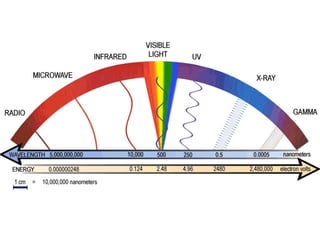
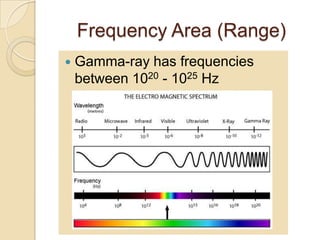
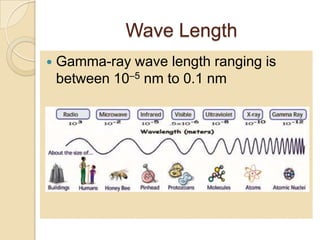
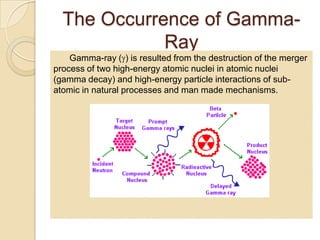
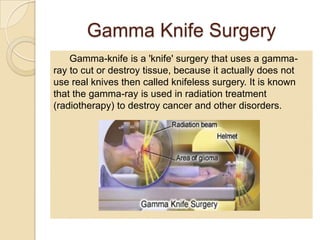
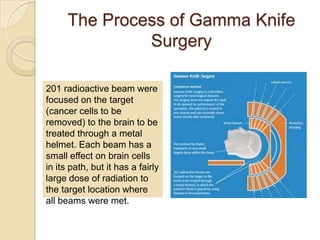
Gamma rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation emitted from radioactive decay processes. They have short wavelengths between 10-5 to 0.1 nm and high frequencies between 1020-1025 Hz. Gamma rays were discovered in 1900 by Paul Ulrich Villard and occur naturally from processes like nuclear fusion and electron-positron annihilation. They are used in medicine for radiography, CT scans, and gamma knife surgery. Gamma knife surgery uses over 200 concentrated gamma rays to destroy targeted tumor tissue without damaging surrounding brain areas. Gamma rays can also have negative effects if overexposed, like cell damage and infertility.