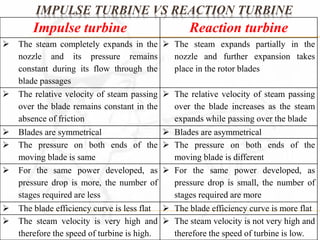
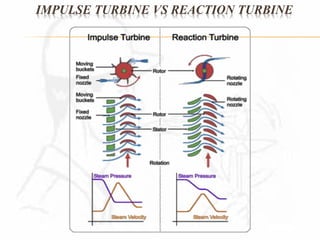
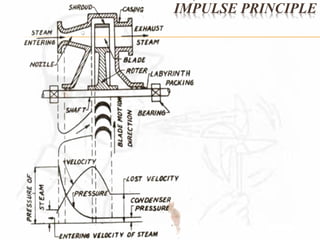
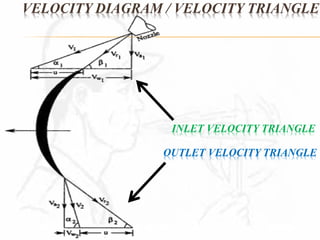
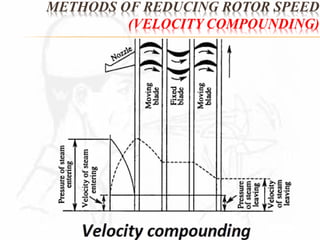
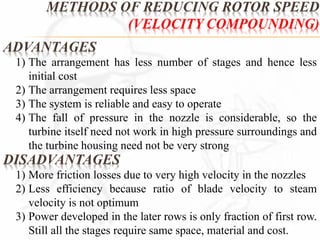
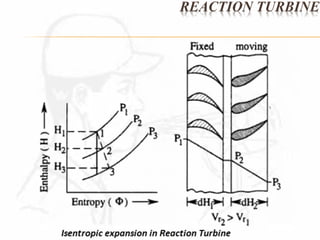
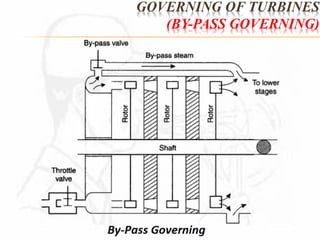
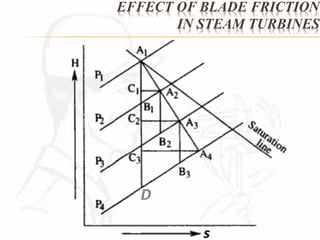
A steam turbine works by transforming the potential energy of steam into kinetic energy and then into rotational mechanical energy. Steam turbines are commonly used for power generation and transport. There are two main types: impulse turbines, where steam pressure remains constant as it strikes and spins turbine blades, and reaction turbines, where steam expands and loses pressure both in nozzles and on moving blades. Impulse turbines generally have higher speeds but reaction turbines are more efficient.