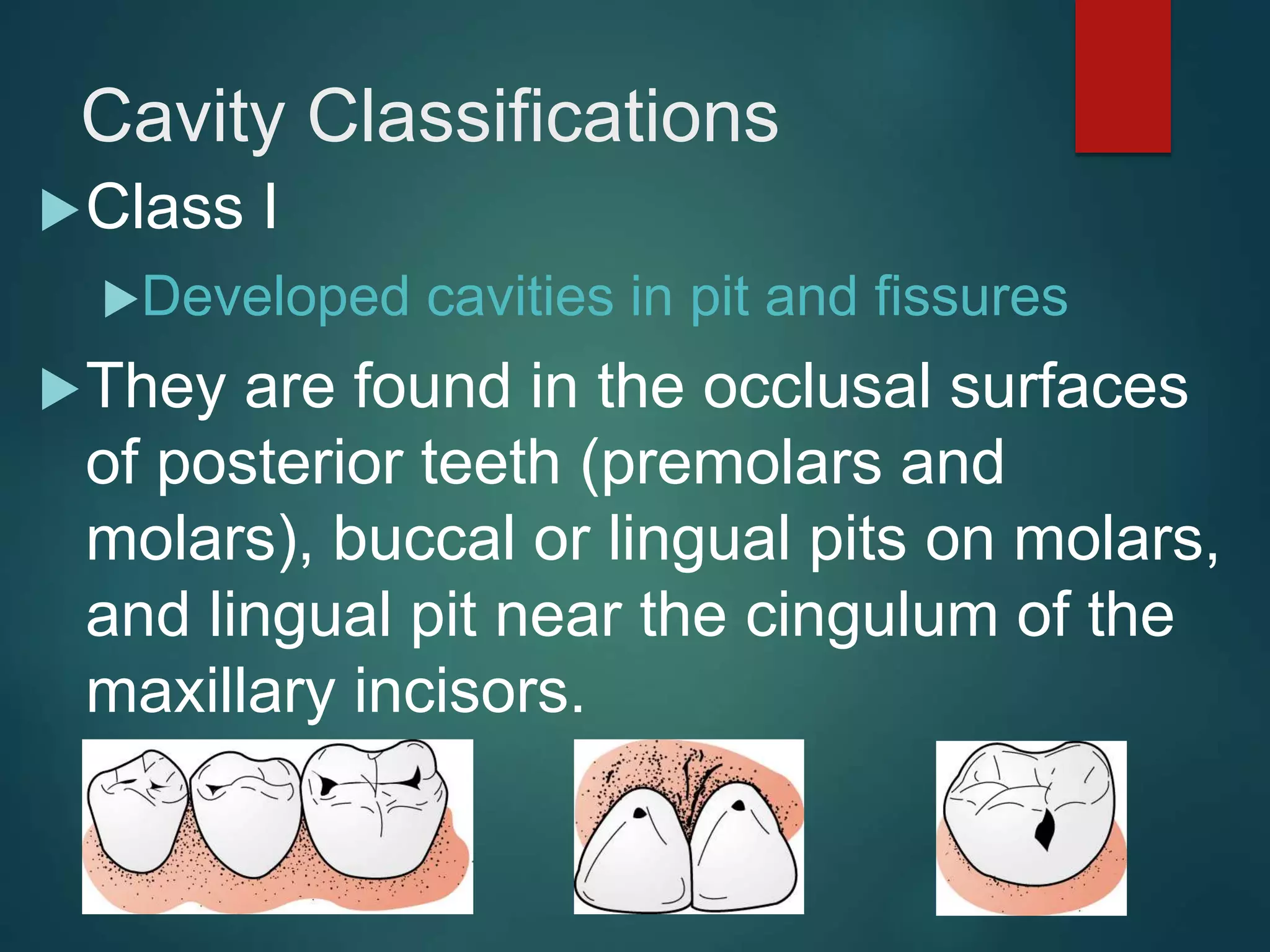
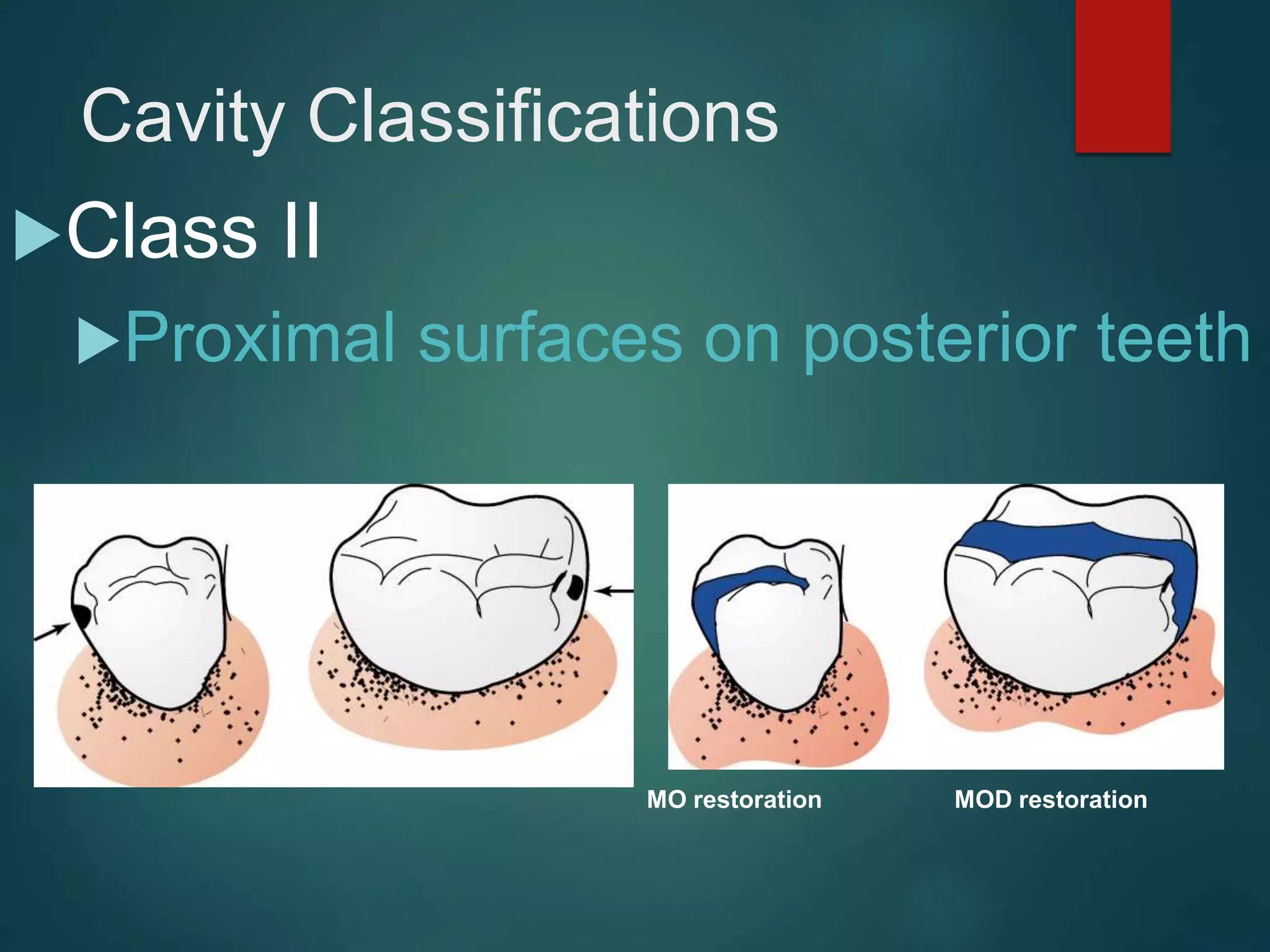
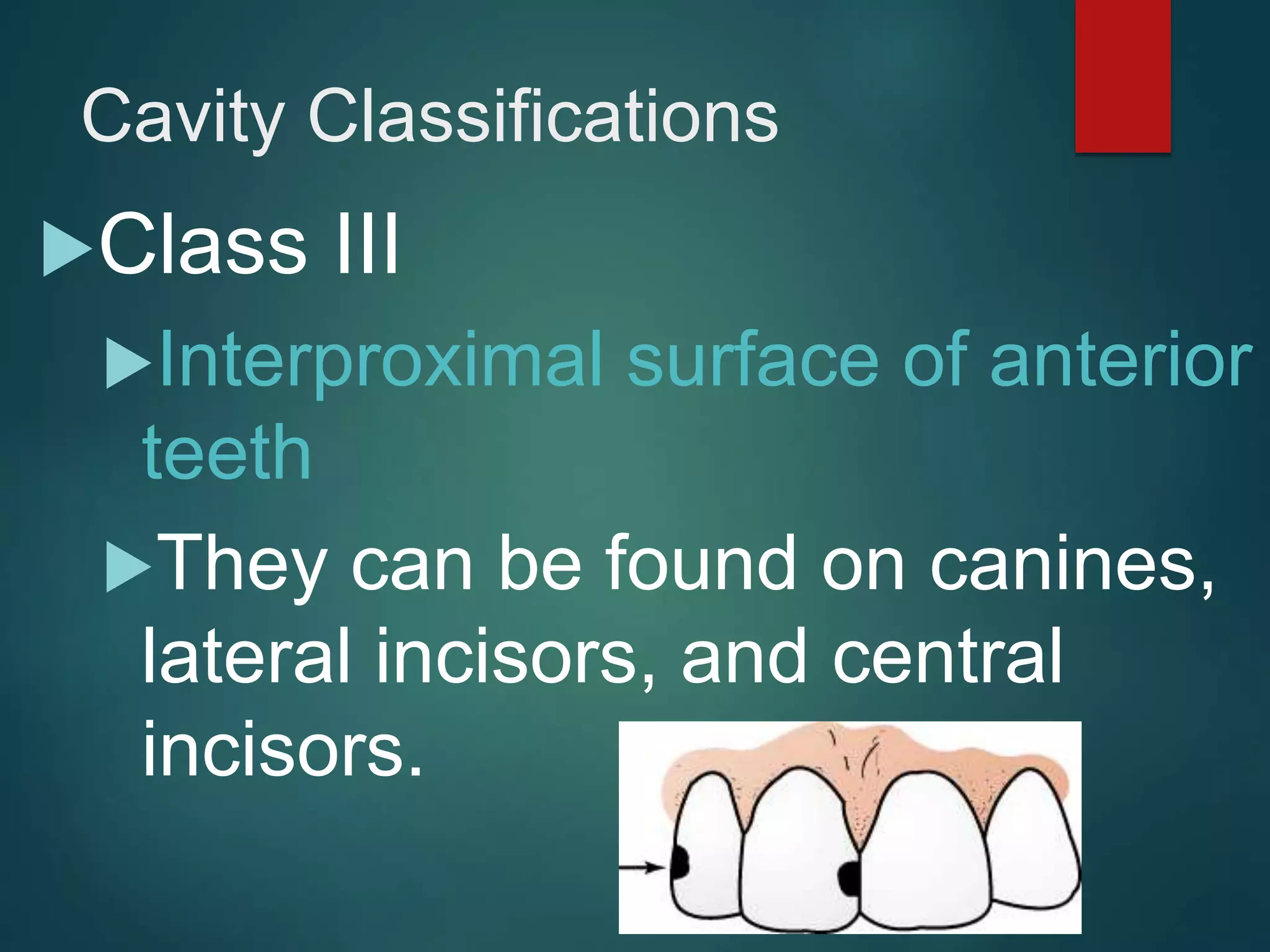
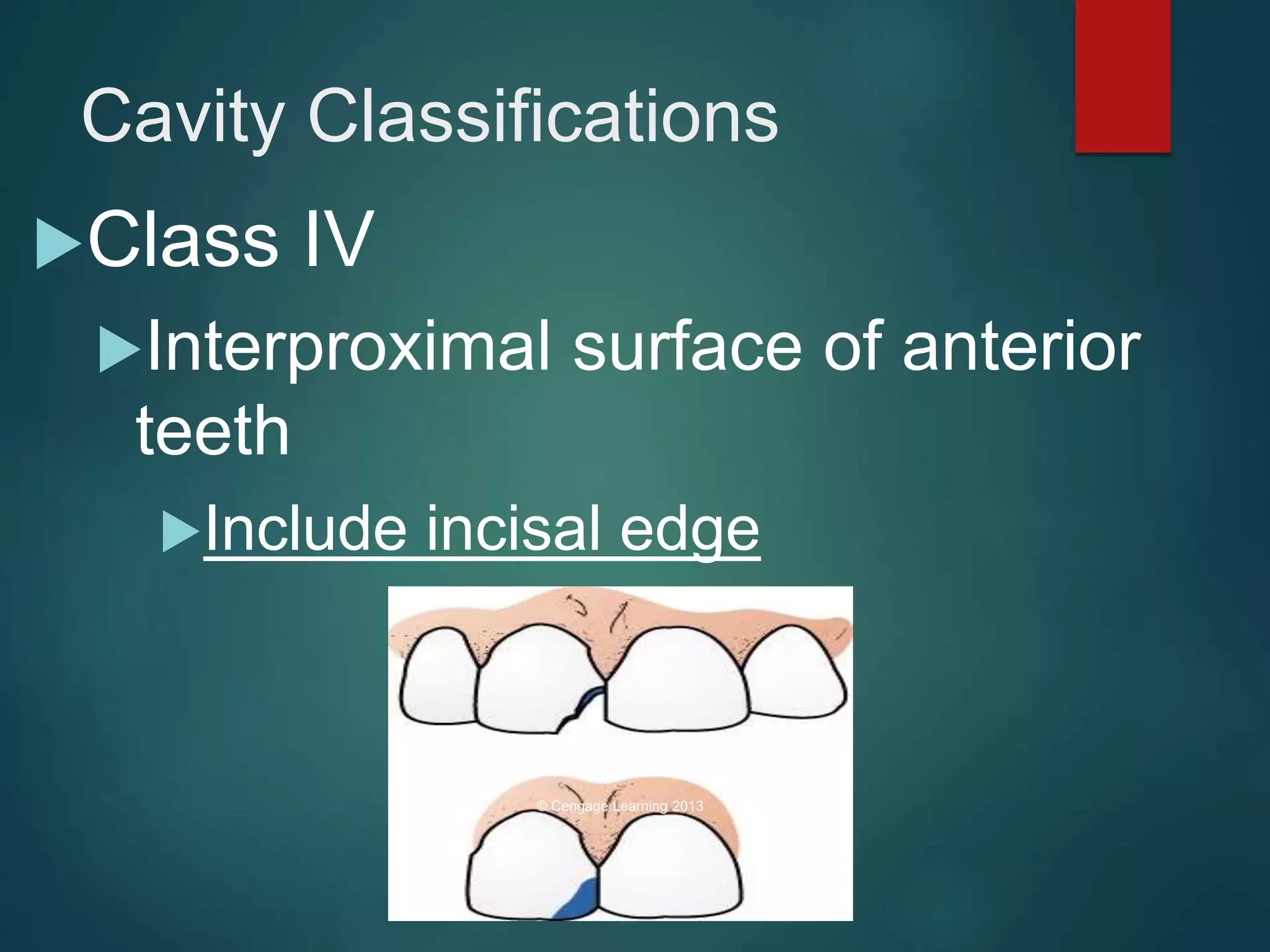
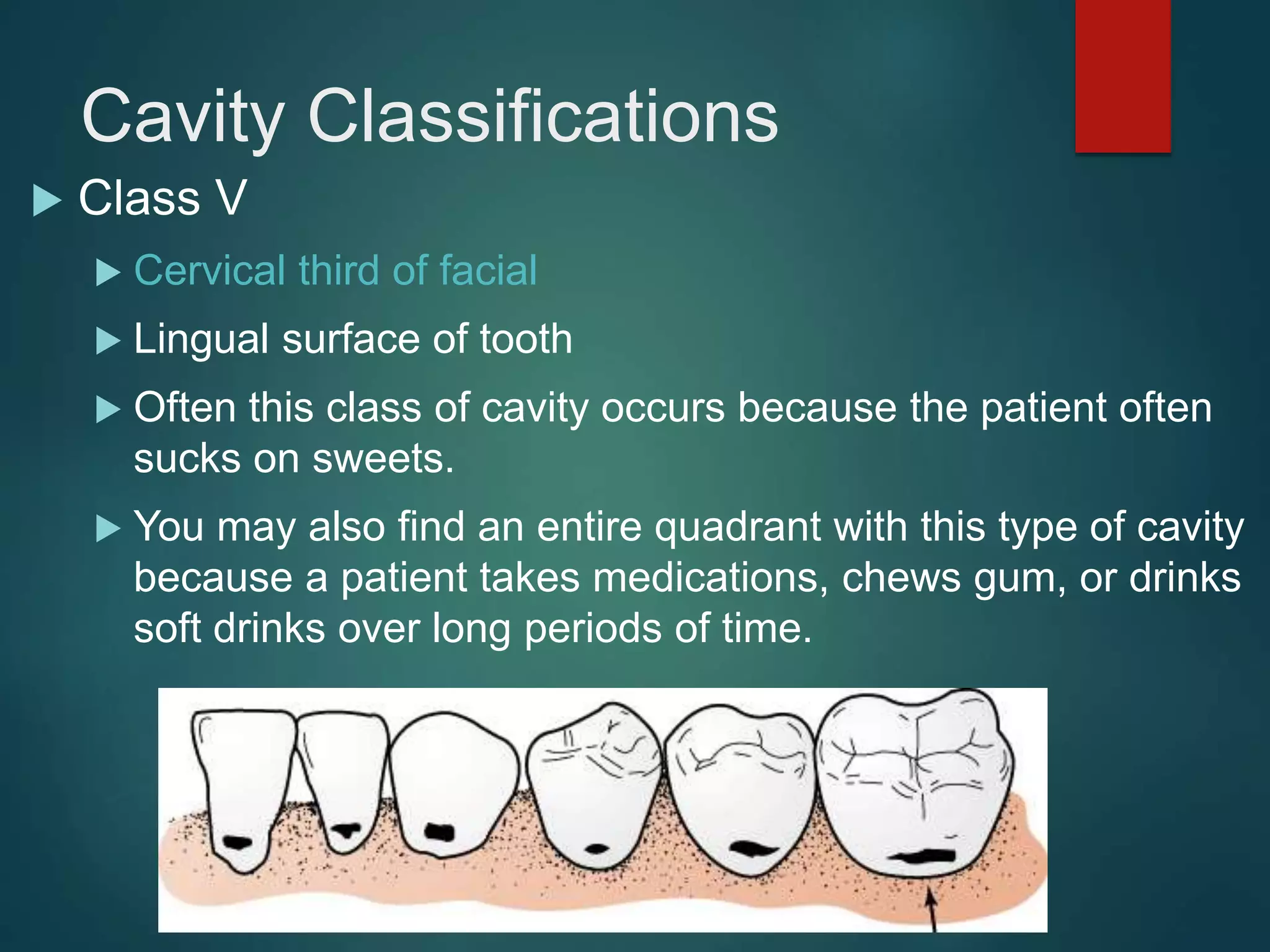
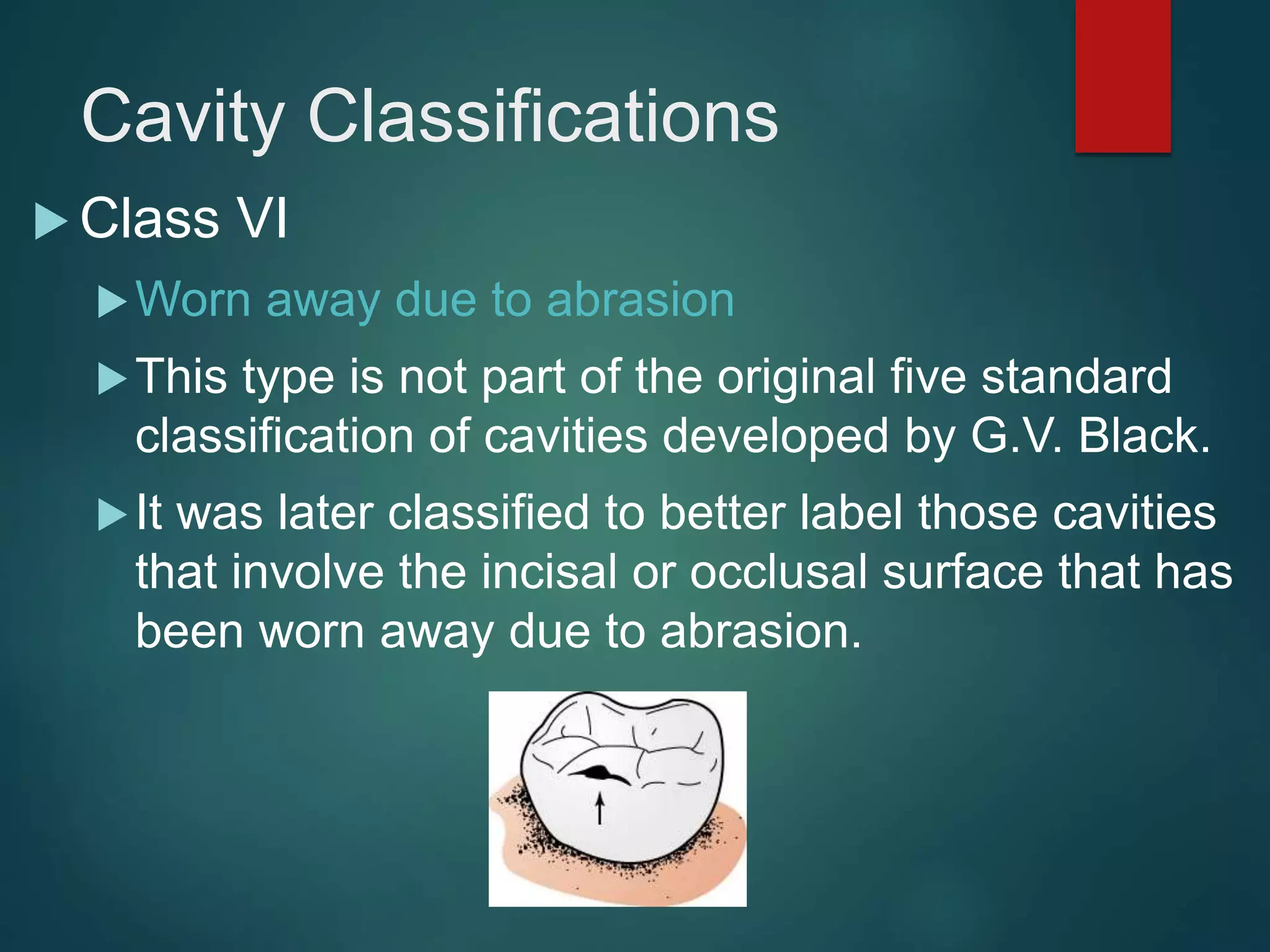
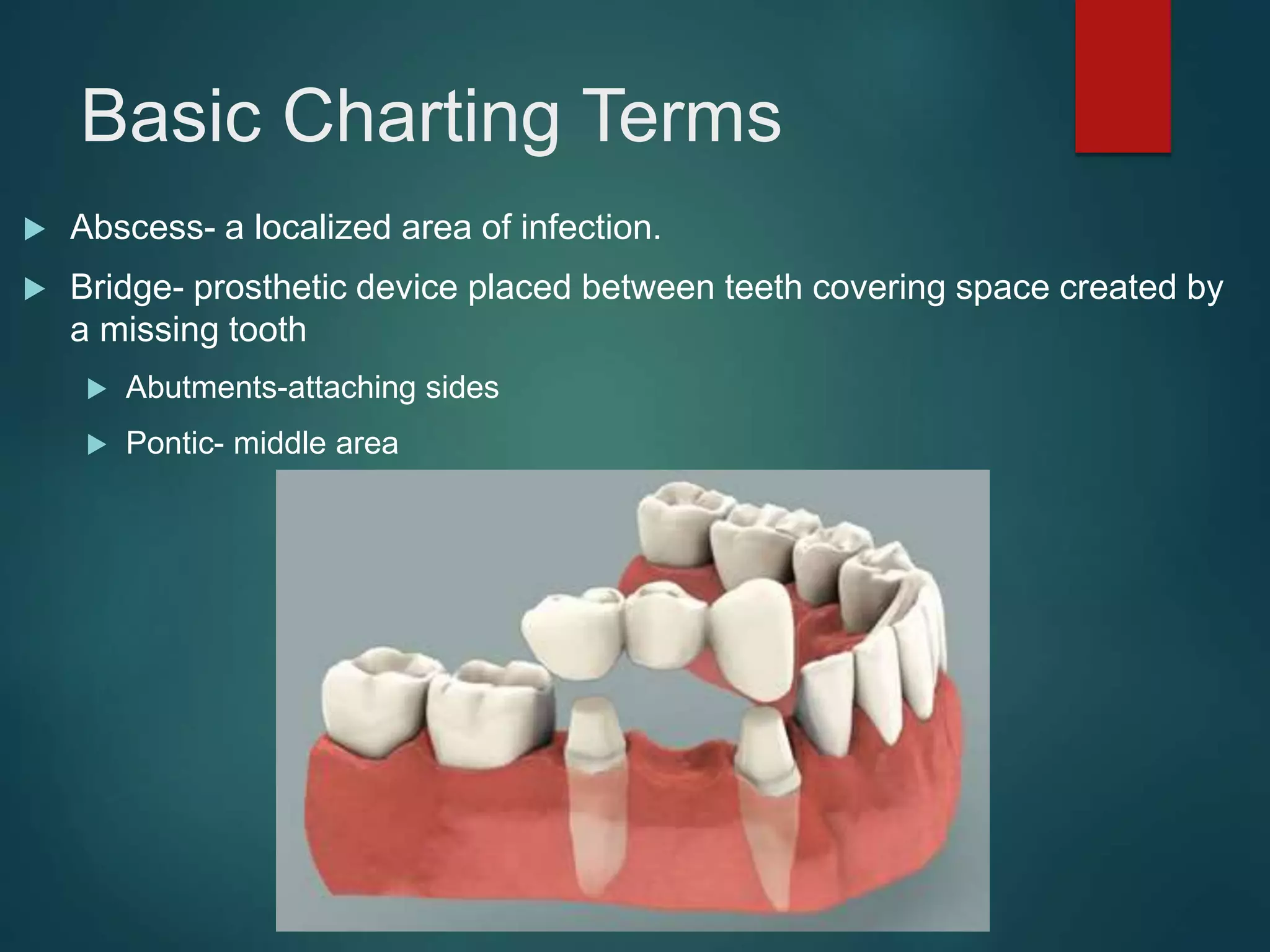
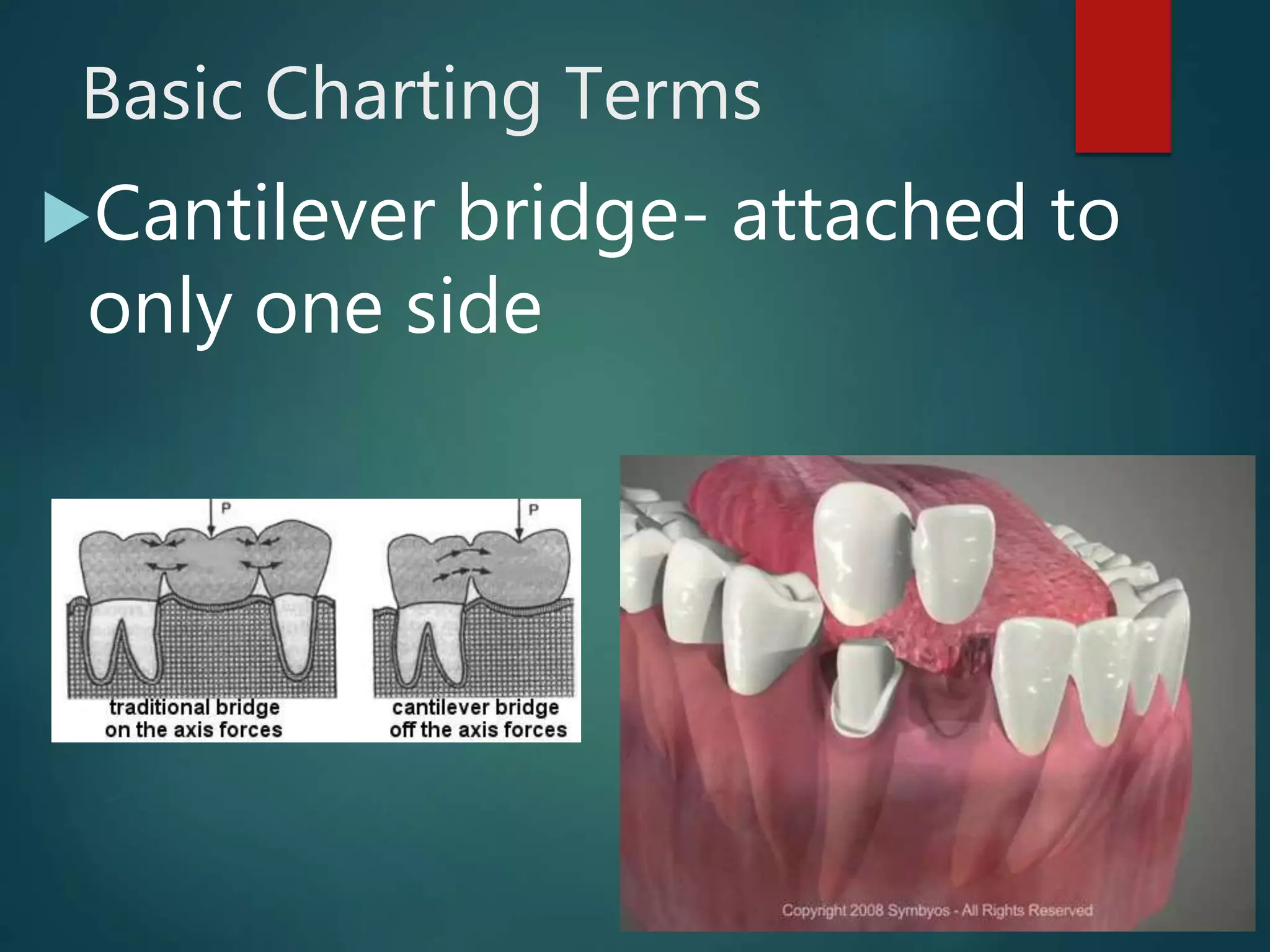
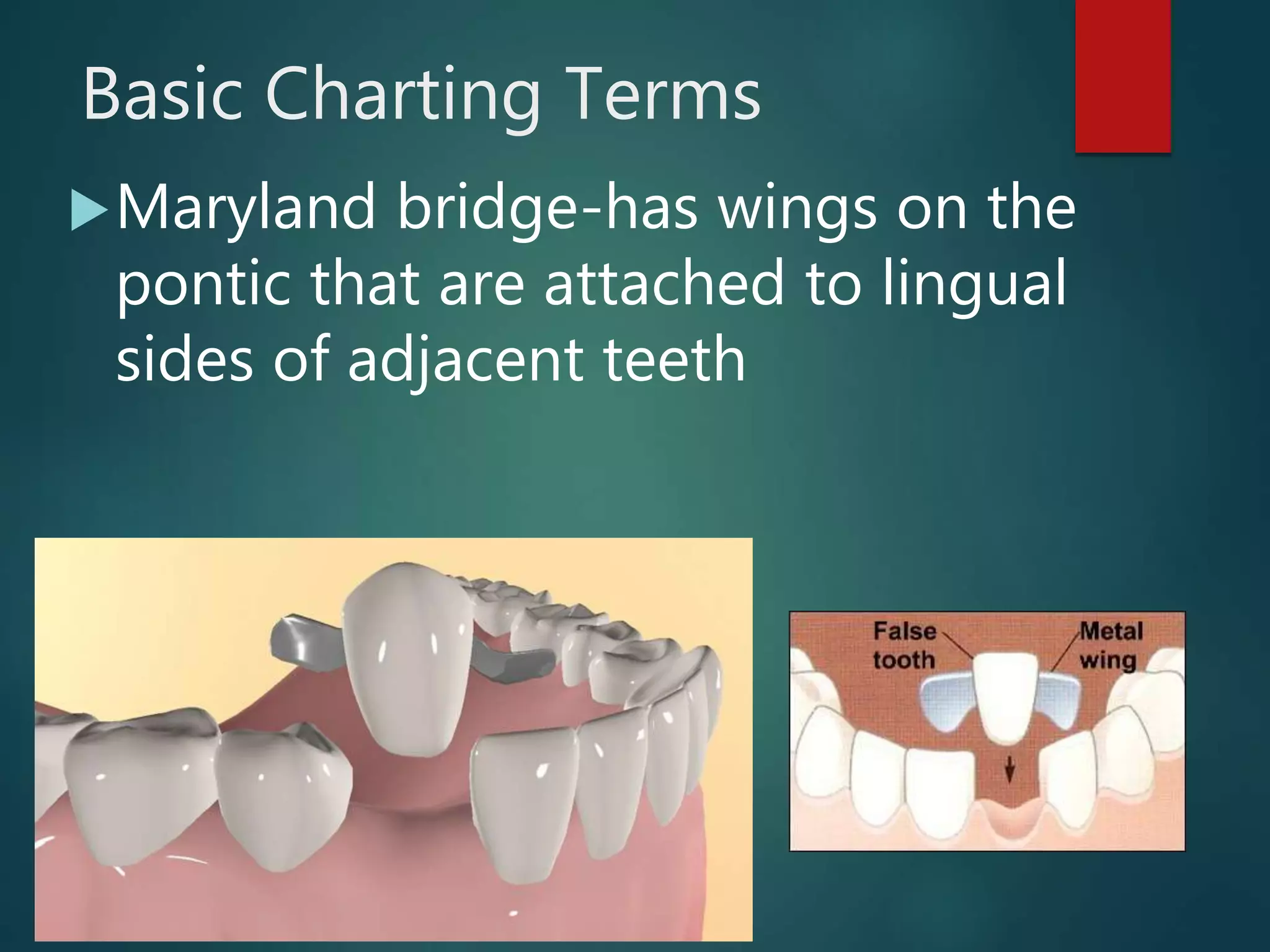
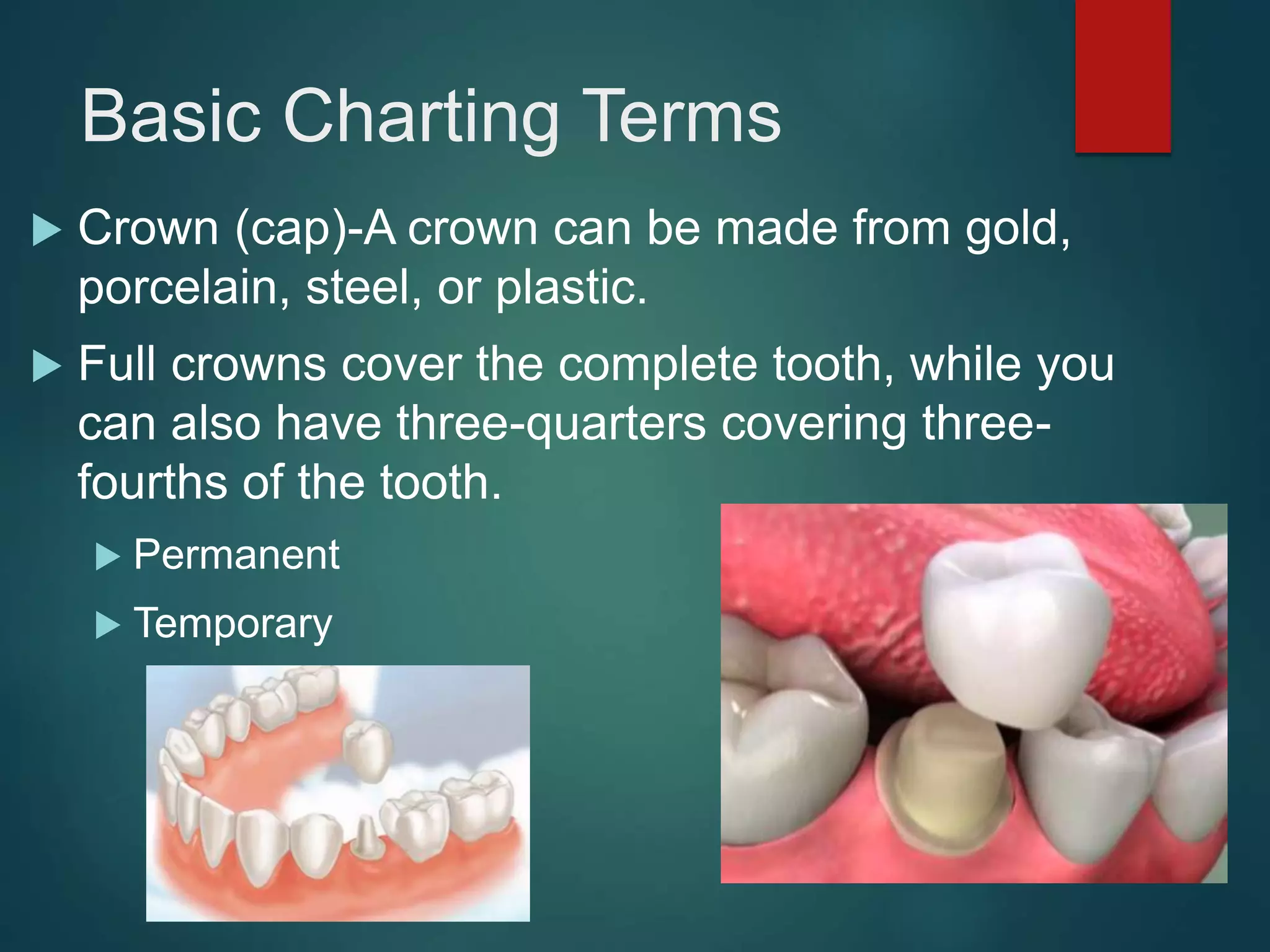
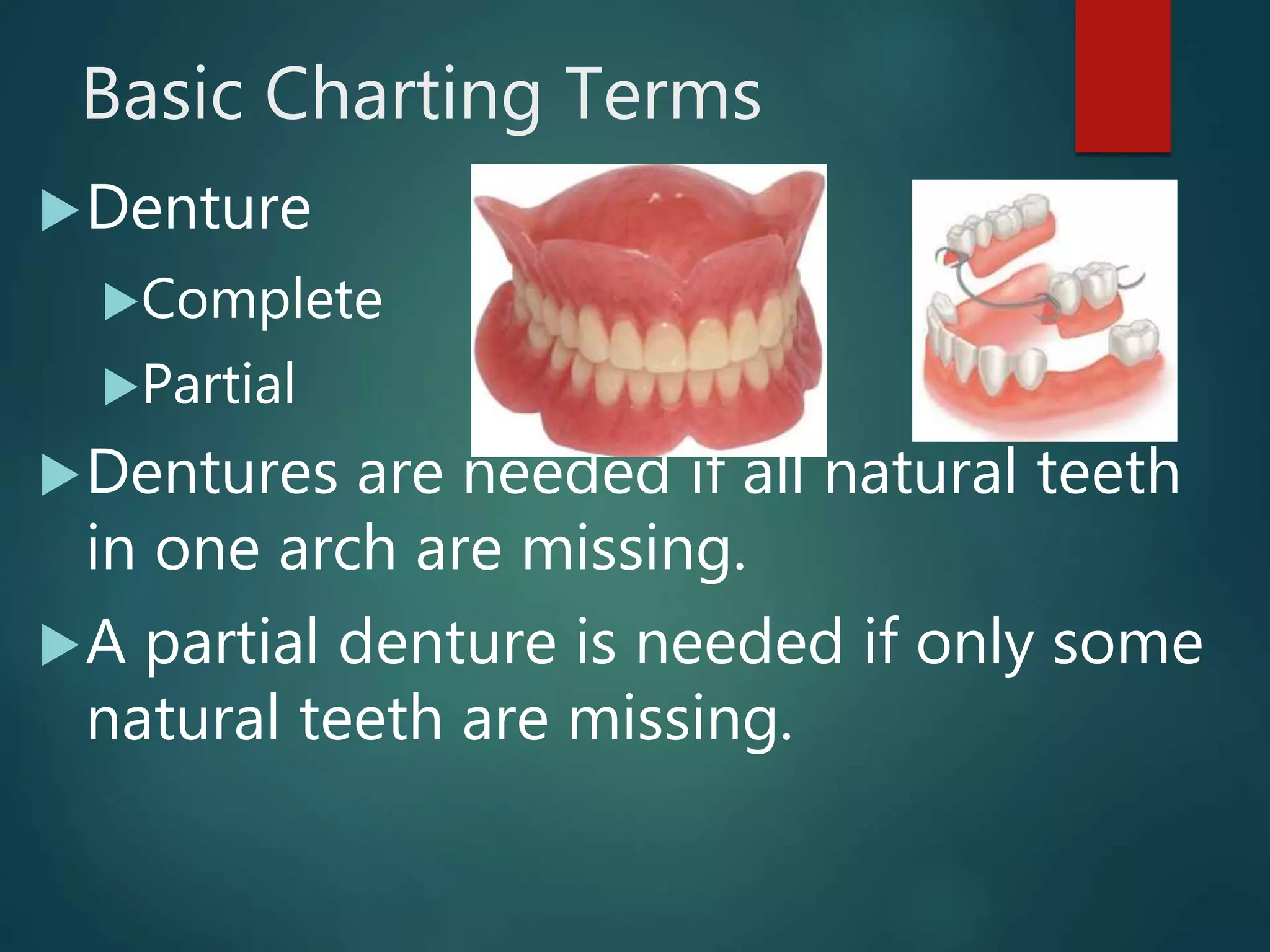
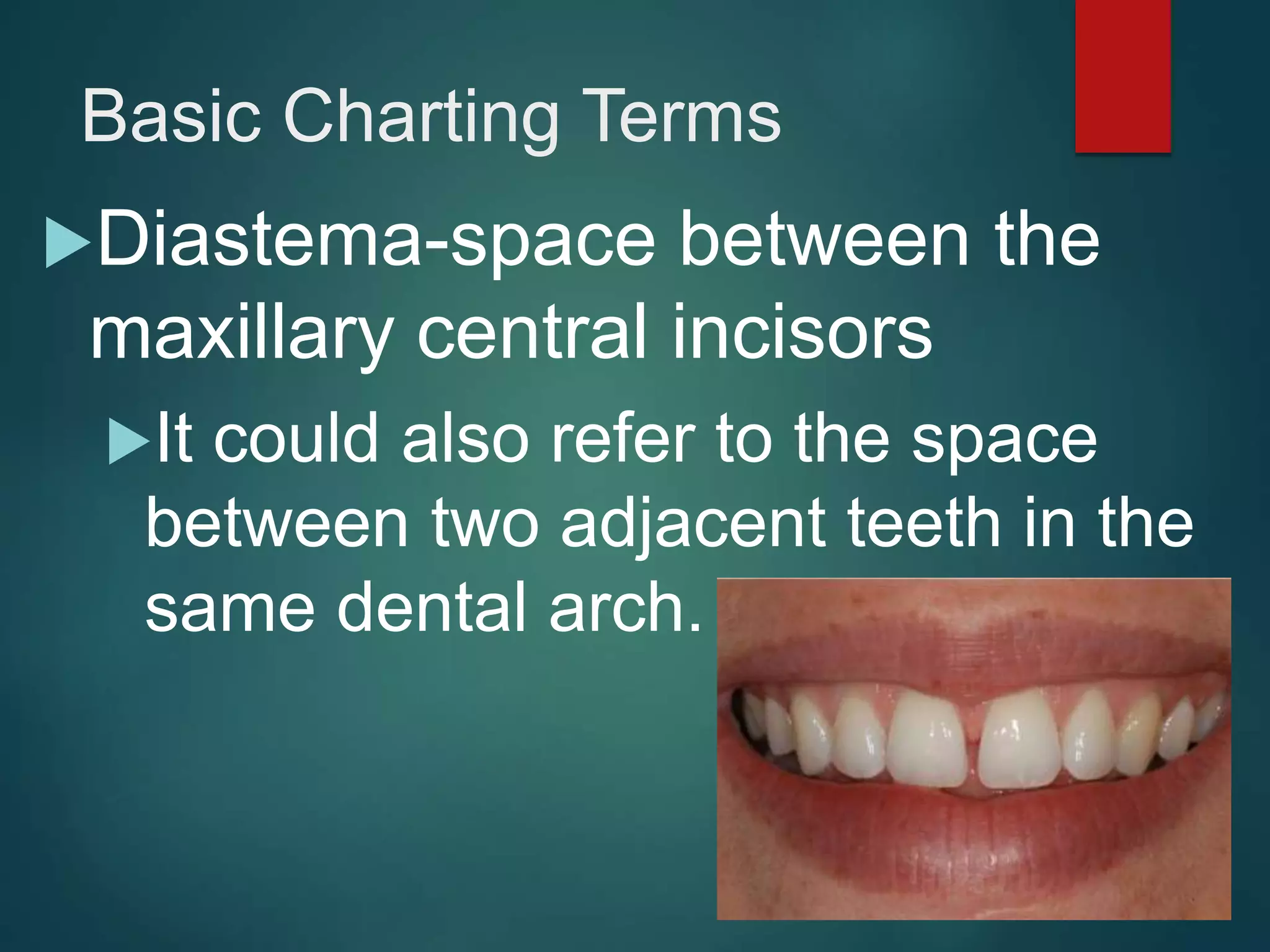
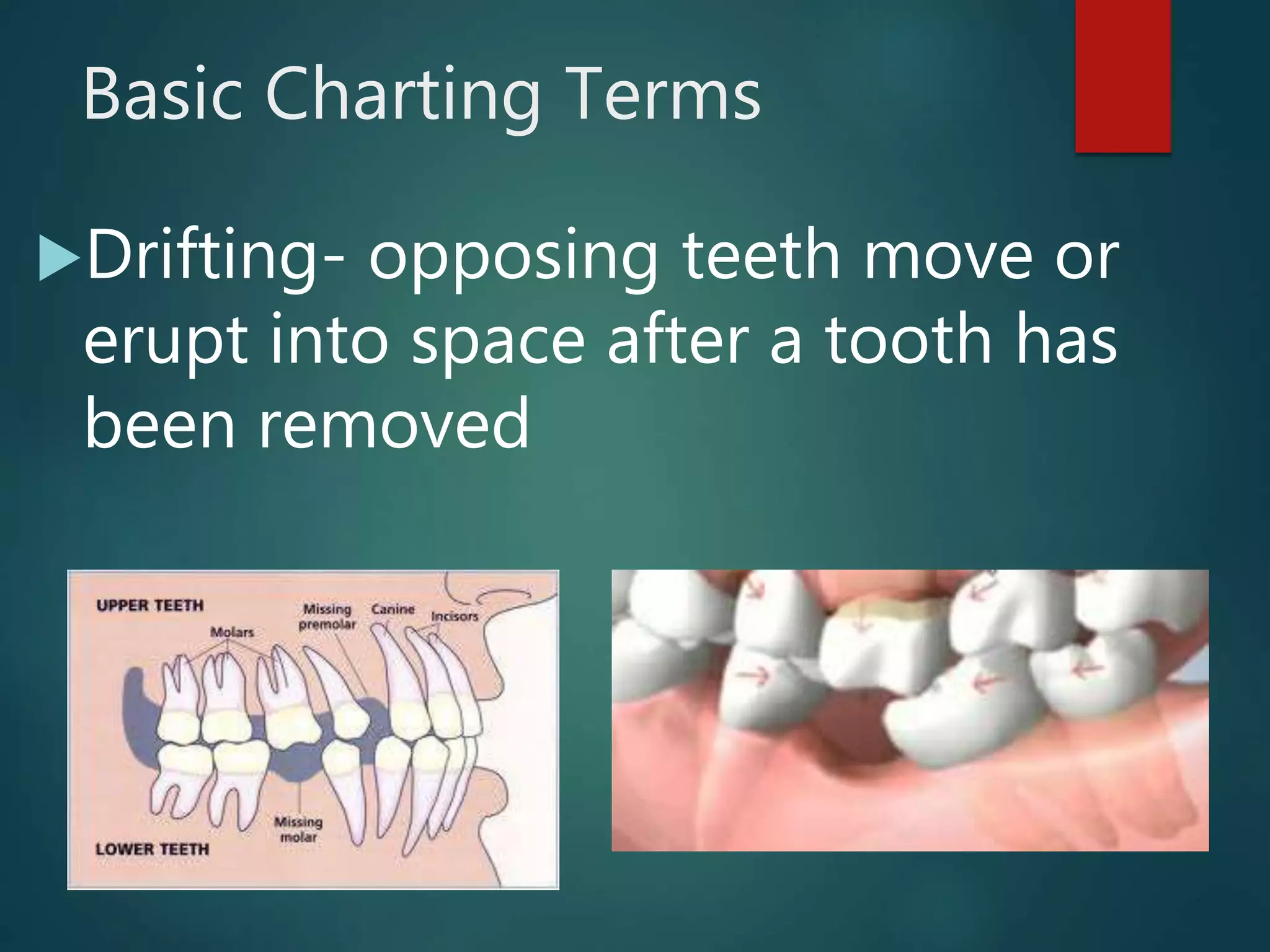
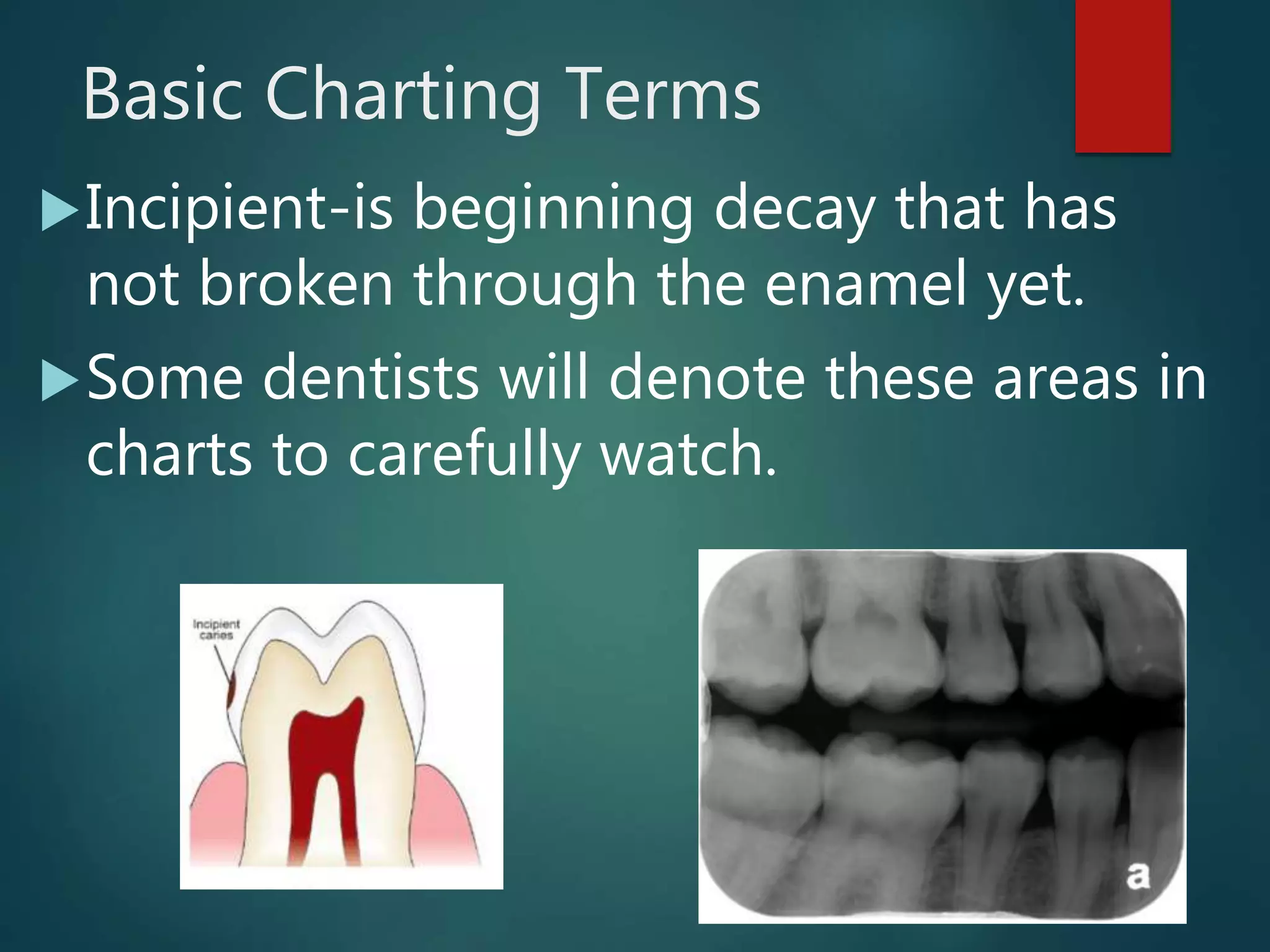
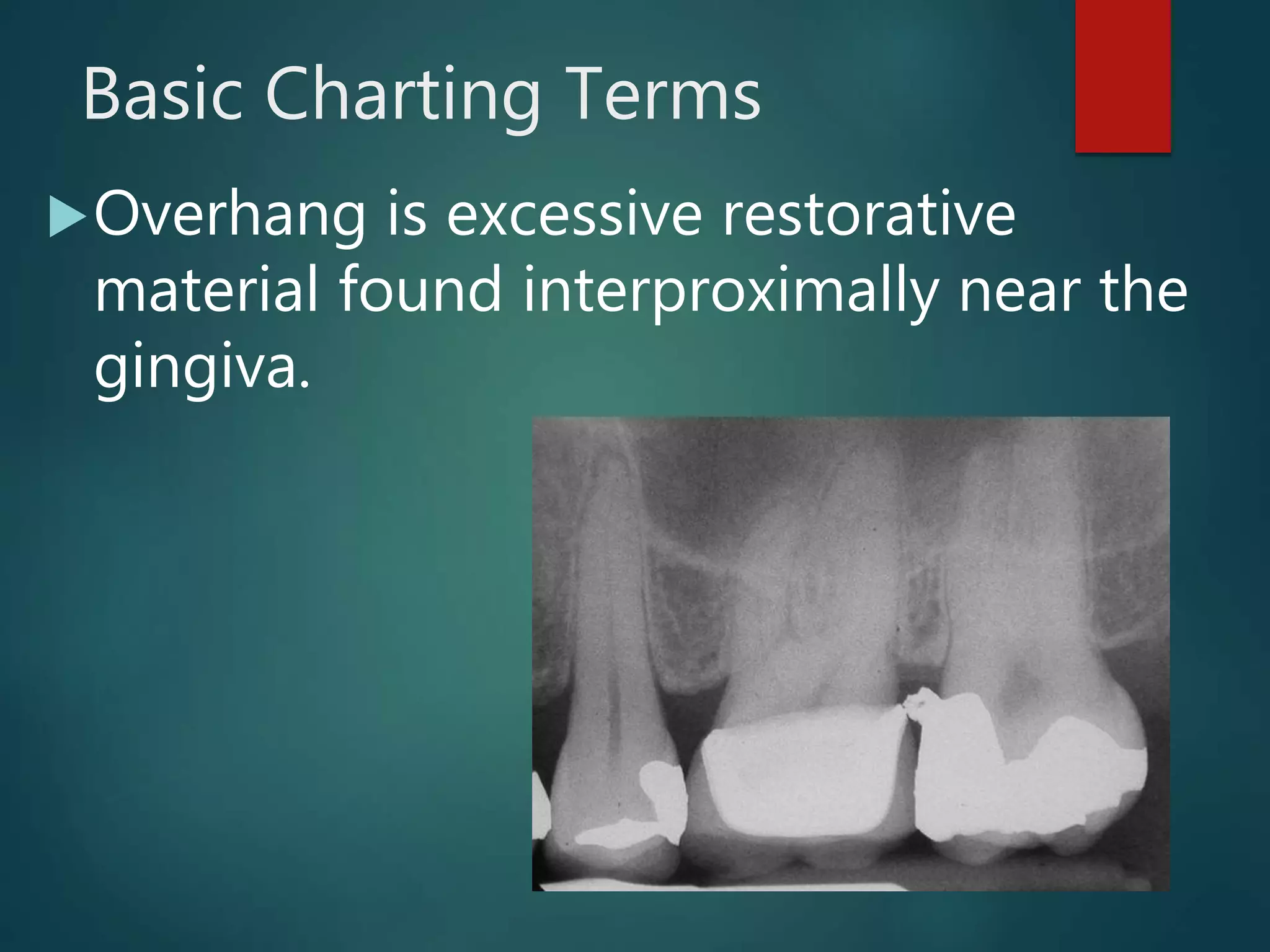
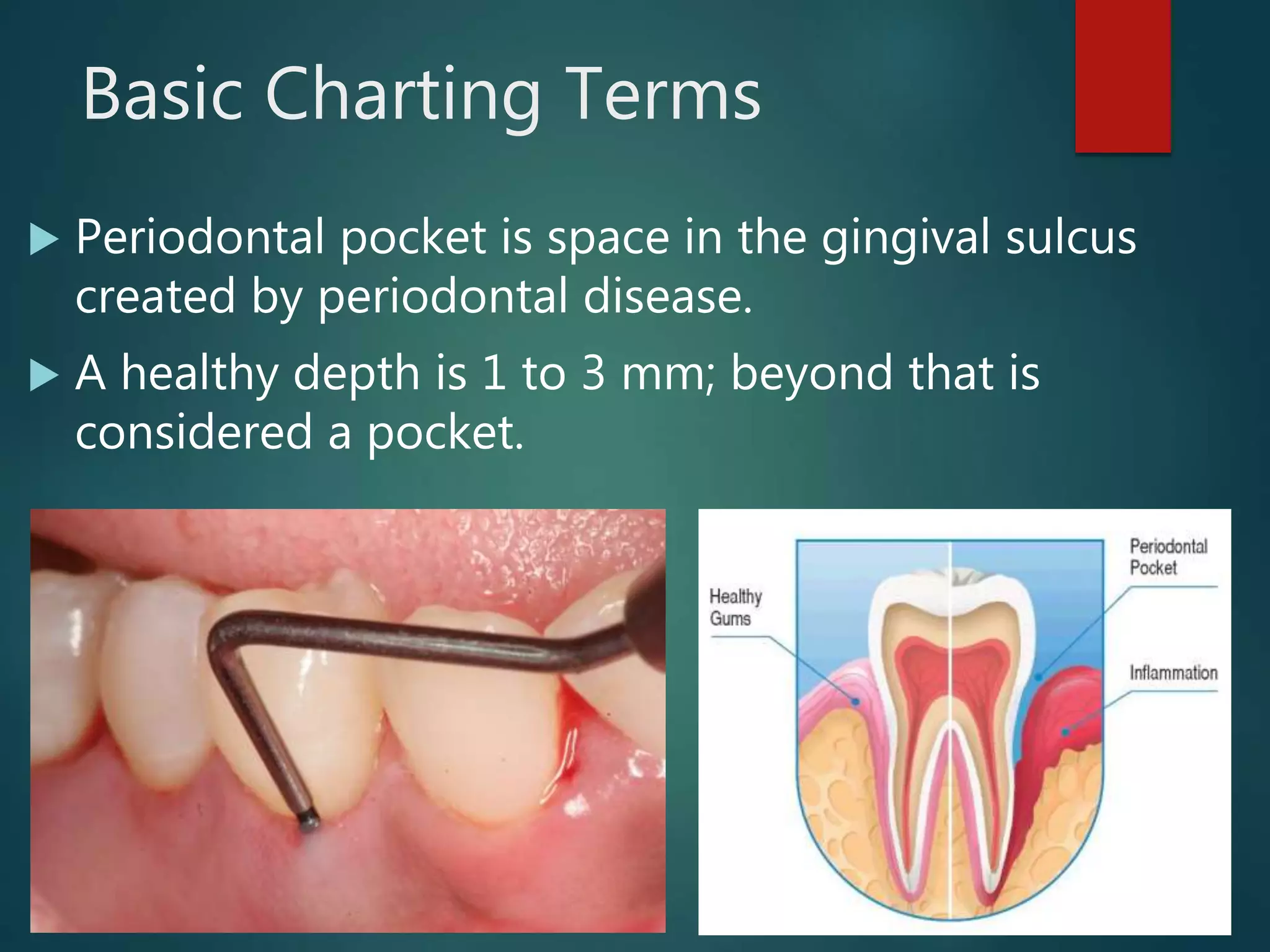
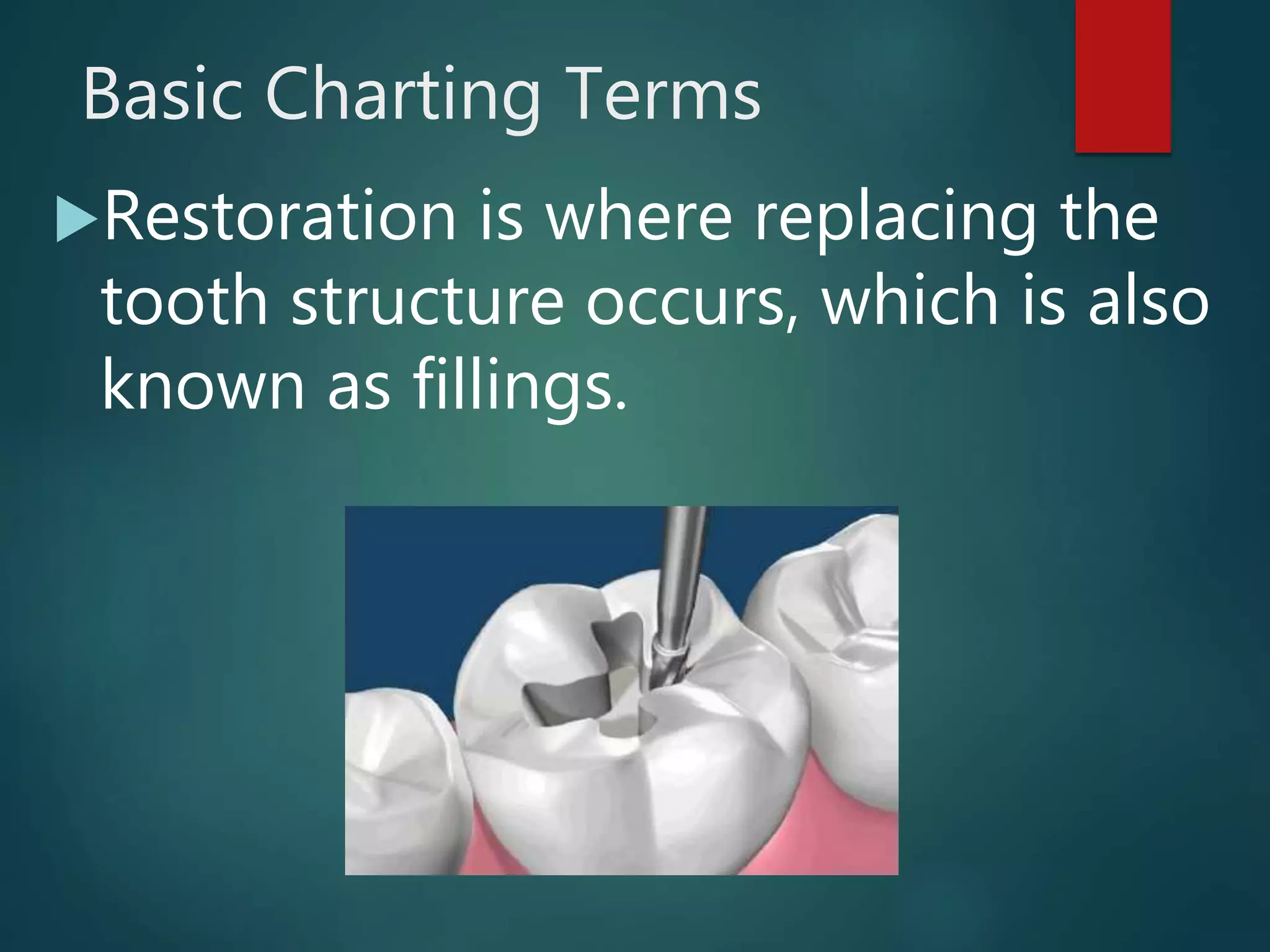
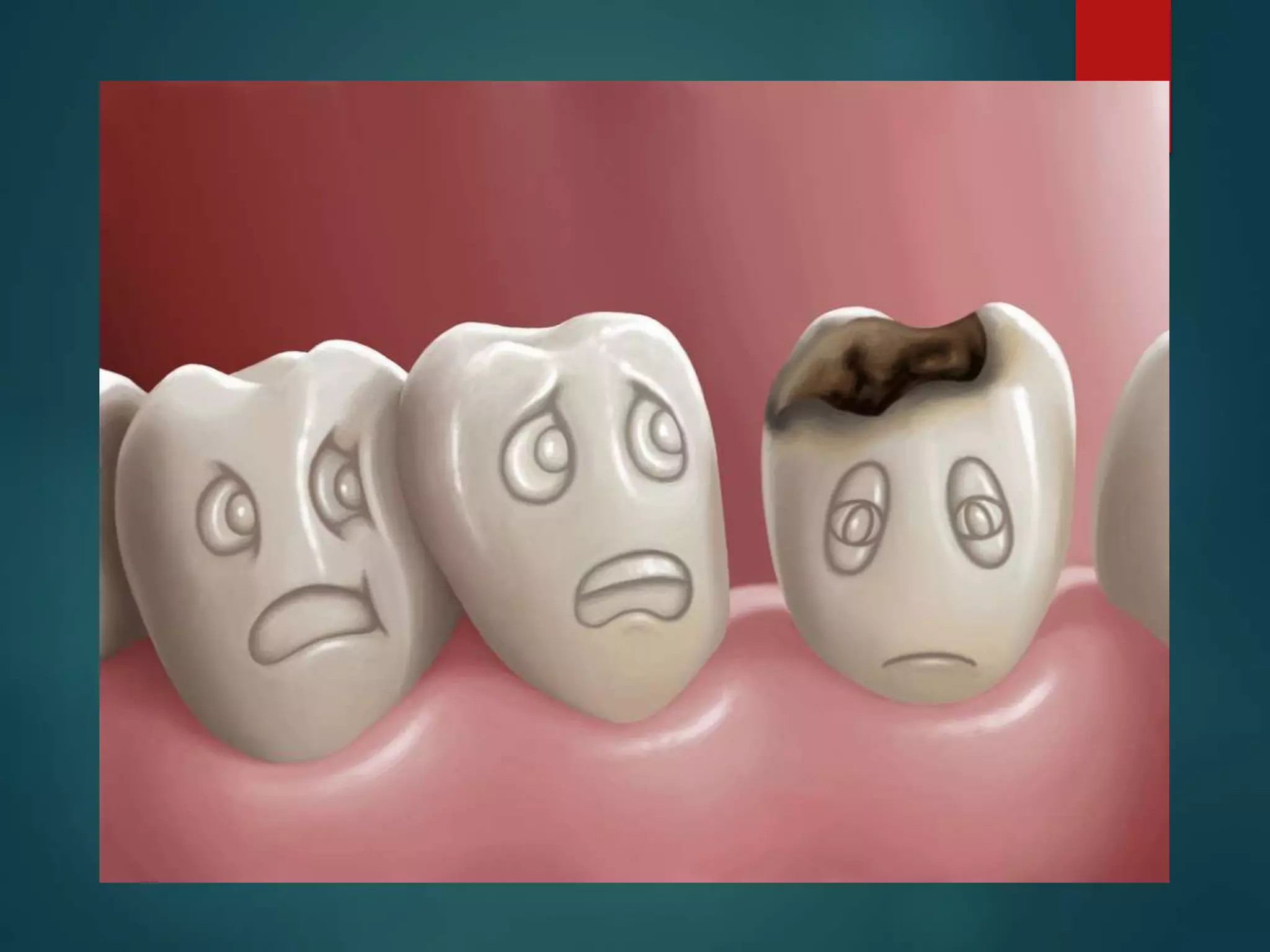
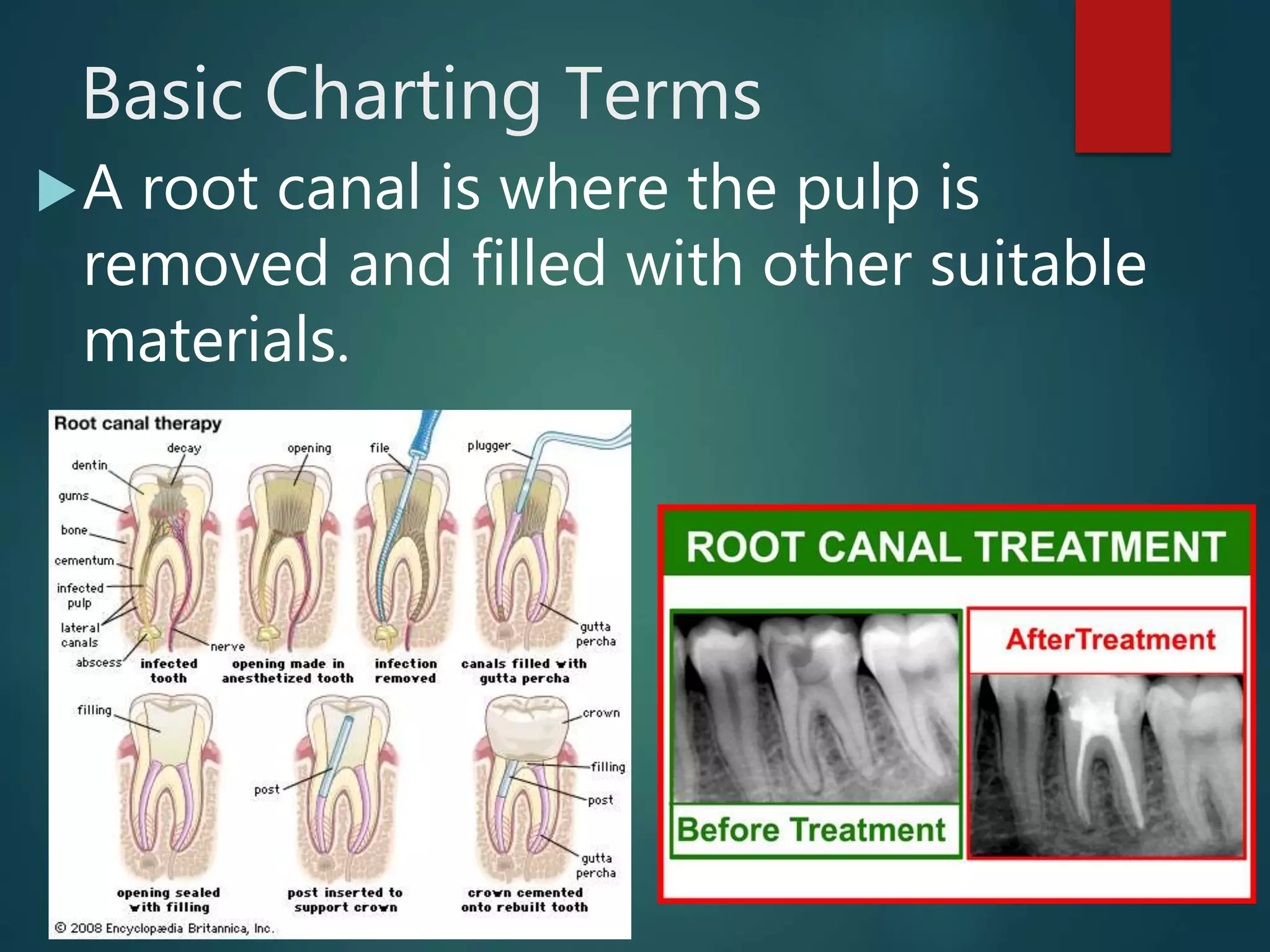
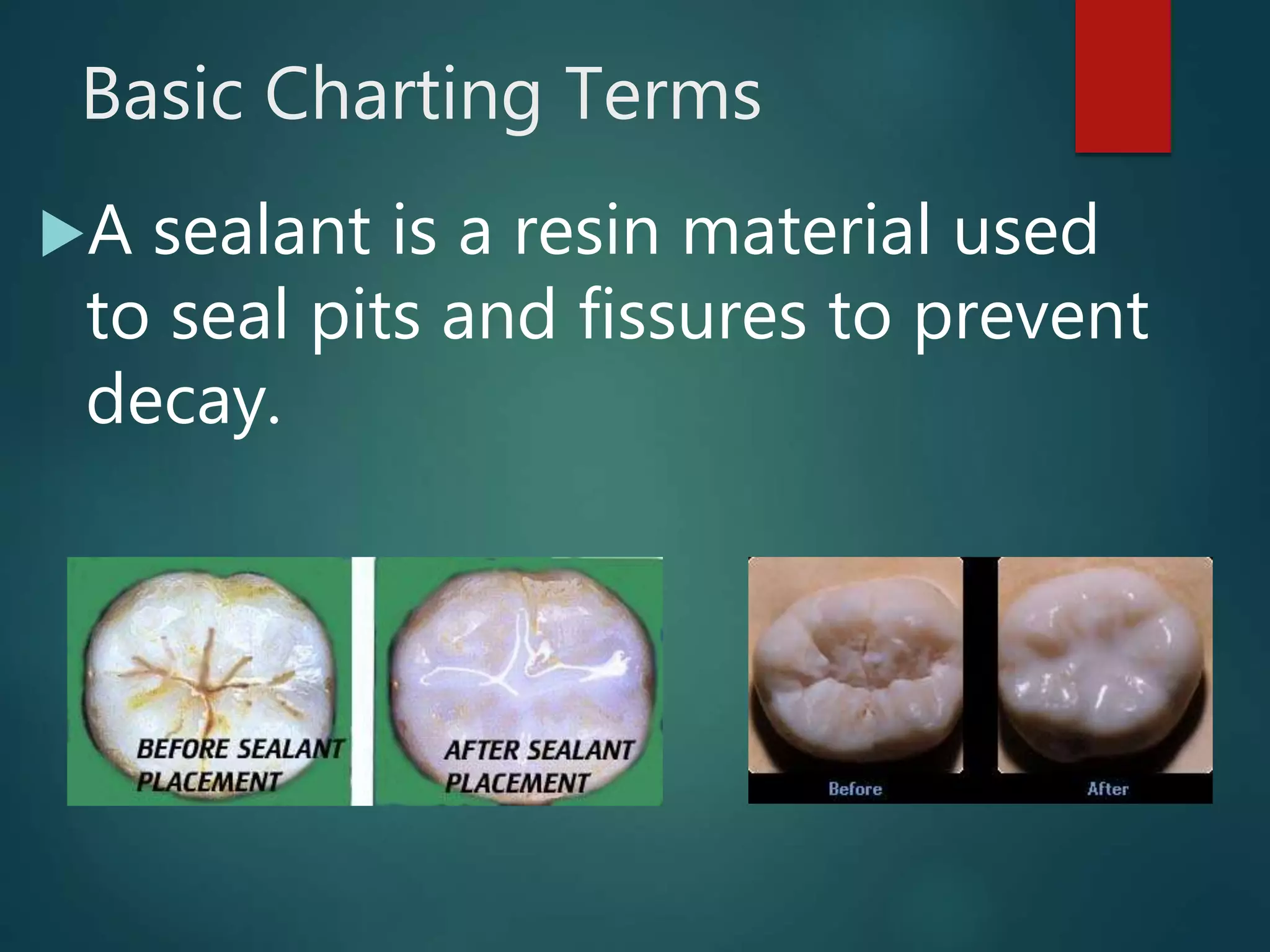
The document discusses dental charting and record keeping, including anatomical versus geometric charting, initial charting procedures, tooth numbering systems, cavity classifications, abbreviations for recording restorations, and basic charting terms such as crowns, bridges, root canals, and periodontal pockets. Computerized charting helps standardize the process and reduces mistakes compared to manual charting. Correct charting is important for documenting a patient's dental records and treatment.