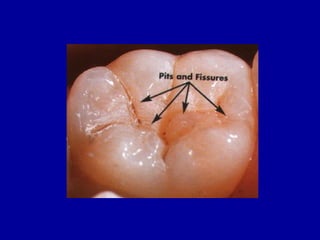
This document provides an introduction to operative dentistry from Dr. Hazem El Ajrami. It defines operative dentistry and discusses its scope, objectives, and indications. Key topics covered include carious and non-carious lesions, tooth histology and occlusion considerations, cavity classifications and nomenclature, and cavity preparation fundamentals. Black's classification system for cavities is explained, detailing the 5 main classes of cavities. Walls and angles of cavities are defined, including the pulpal wall, axial wall, cavo-surface angle, dentino-enamel junction, enamel wall, and dentin wall. References on operative dentistry and preclinical course materials from Cairo University are also listed.