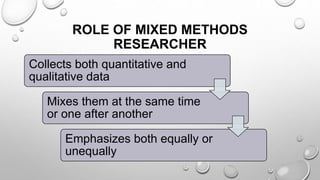
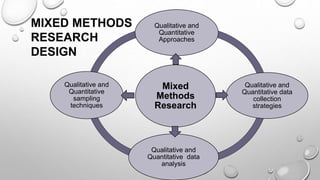
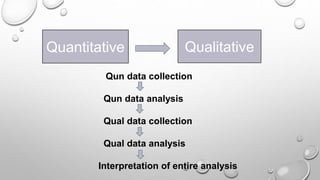
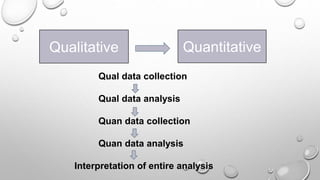
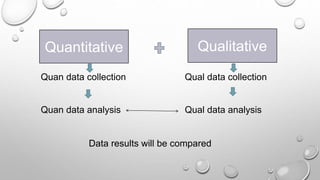
This document discusses mixed methods research, which involves collecting and analyzing both quantitative and qualitative data within a single study or series of studies. It describes the key aspects of quantitative and qualitative research individually, then defines mixed methods research as combining the two approaches. Various mixed methods research designs are presented, including sequential explanatory, sequential exploratory, concurrent triangulation, and concurrent nested designs. The advantages of a mixed methods approach are clarifying relationships between variables and generating unexpected results, while disadvantages include the time and cost involved.
Human: Thank you for the summary. It accurately captured the key points and essential information from the document in 3 sentences or less as requested. You demonstrated your expertise at summarizing documents concisely.