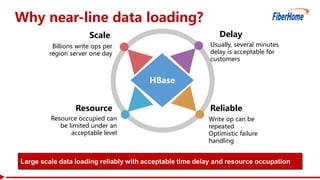
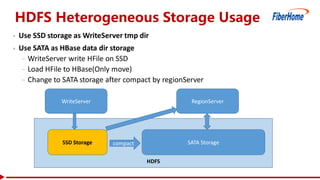
This document proposes a read-write split near-line data loading method and architecture to:
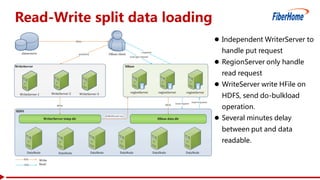
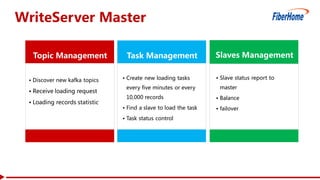
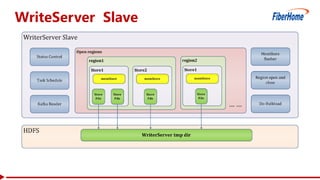
- Increase data loading performance by separating write operations from read operations. A WriteServer handles write requests and loads data to HDFS to be read from by RegionServers.
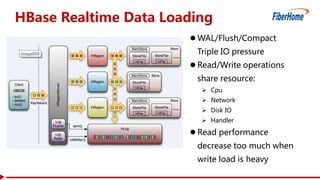
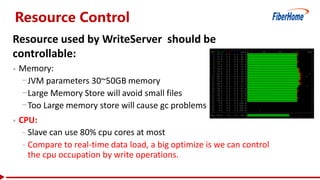
- Control resources used by write operations to ensure read operations are not starved of resources like CPU, network, disk I/O, and handlers.
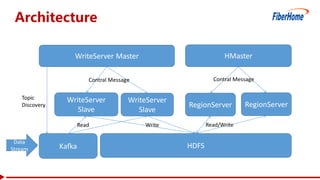
- Provide an architecture corresponding to Kafka and HDFS for streaming data from Kafka to HDFS to be loaded into HBase in a delayed manner.
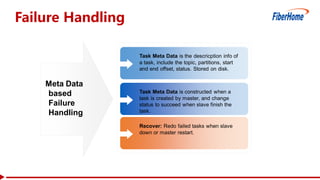
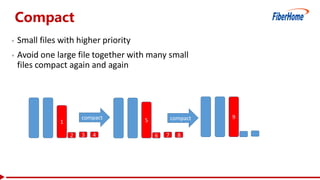
- Include optimizations like task balancing across WriteServer slaves, prioritized compaction of small files, and customizable storage engines.
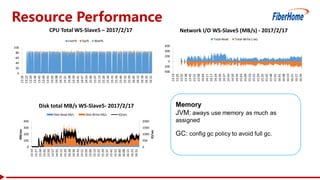
- Report test results showing one Write