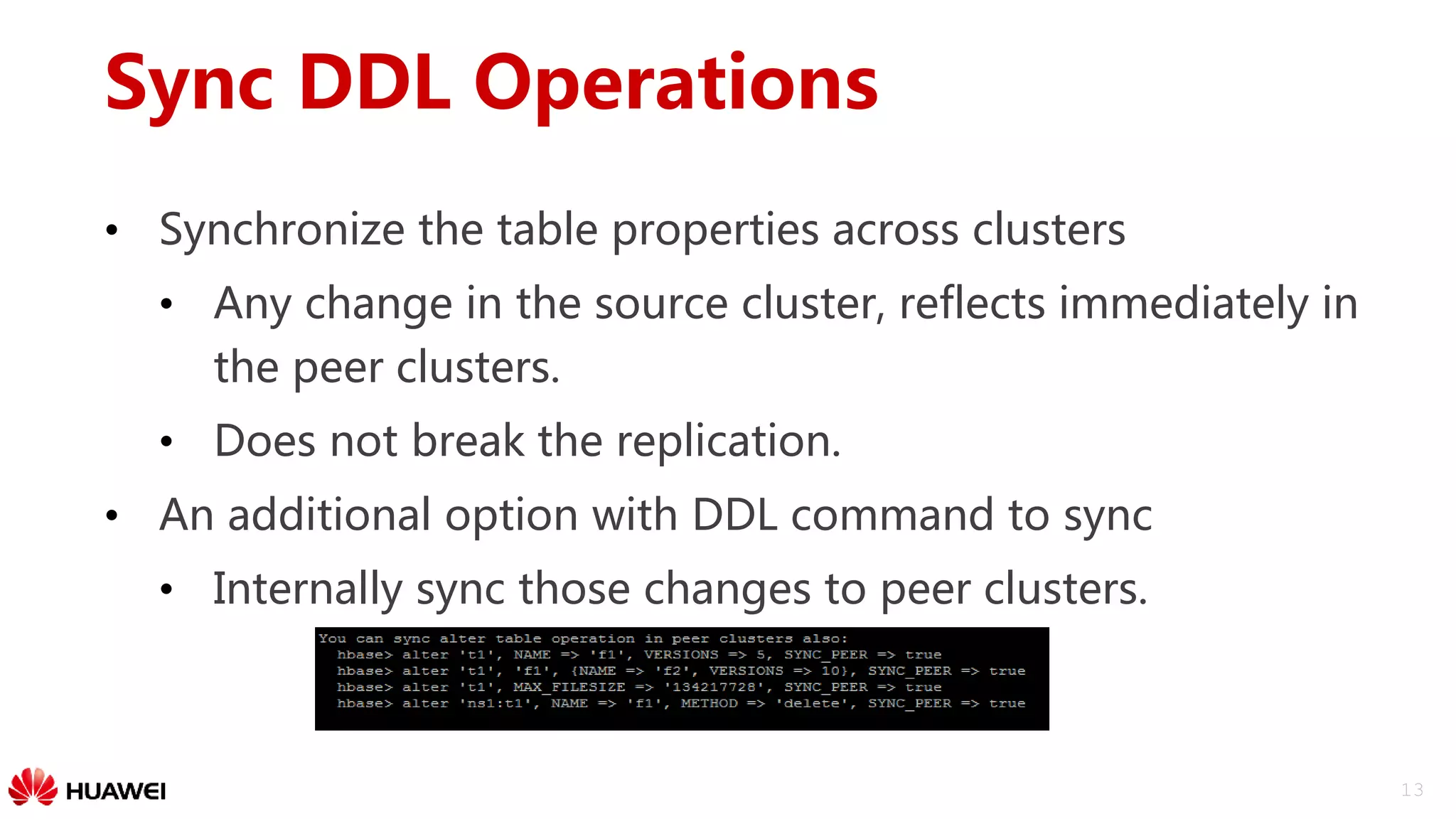
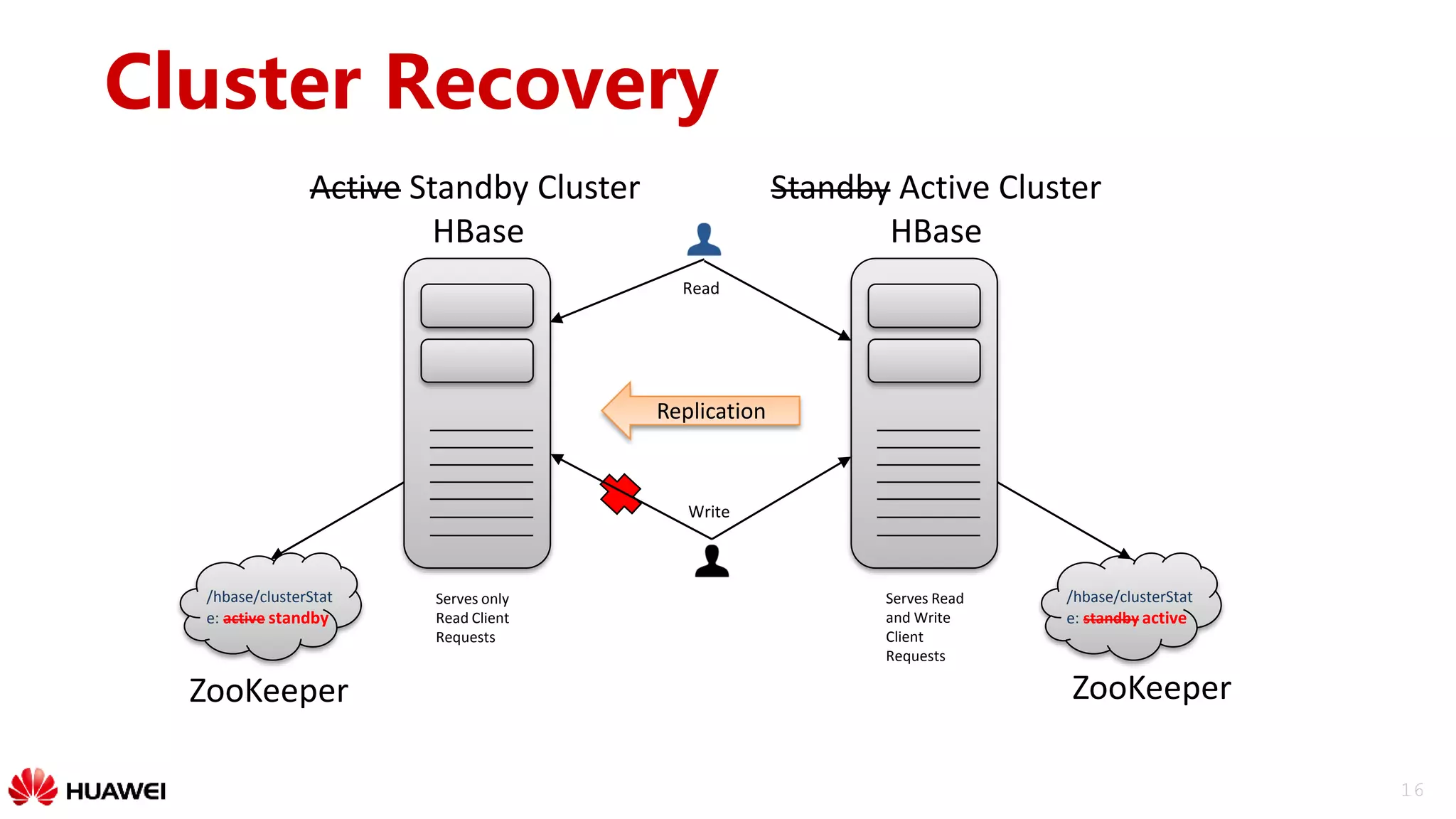
The document outlines a disaster recovery solution for HBase, emphasizing the importance of disaster recovery and the differences between backup and recovery processes. It details the implementation of data replication over WAN, strategies for active-standby clusters, and synchronization of data across clusters. Future work includes improving replication tracking and data locality for better performance.








![12
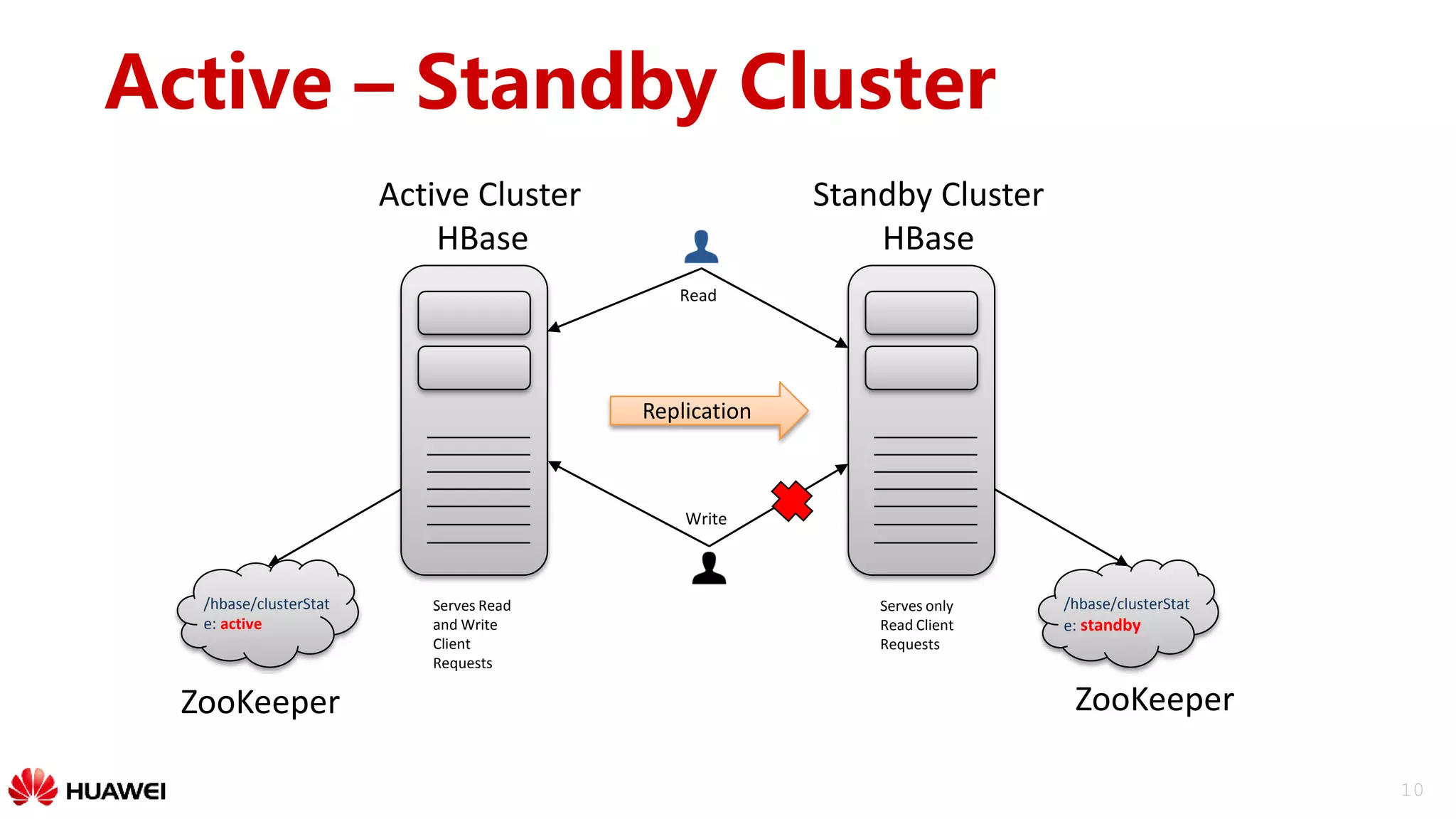
Replication
WAL
1
1
2
Region Server
Replication
Source/End Point
Replication
Source/End Point
Replication Source
Manager
Region Server
…/peers/
…/rs/
…/hfile-refs/
Source Cluster Peer Cluster 1 [tableCfs - 1]
1
3 1
Table
Batch
1
Replication Sink
1
Bulk load
Region Server
TableReplication Sink
Peer Cluster 2 [tableCfs - ]
12
1
Batch
Bulk load
12
1
1
Batch
Bulk load
ZooKeeper](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/track1-6-170807123847/75/hbaseconasia2017-HBase-Disaster-Recovery-Solution-at-Huawei-12-2048.jpg)