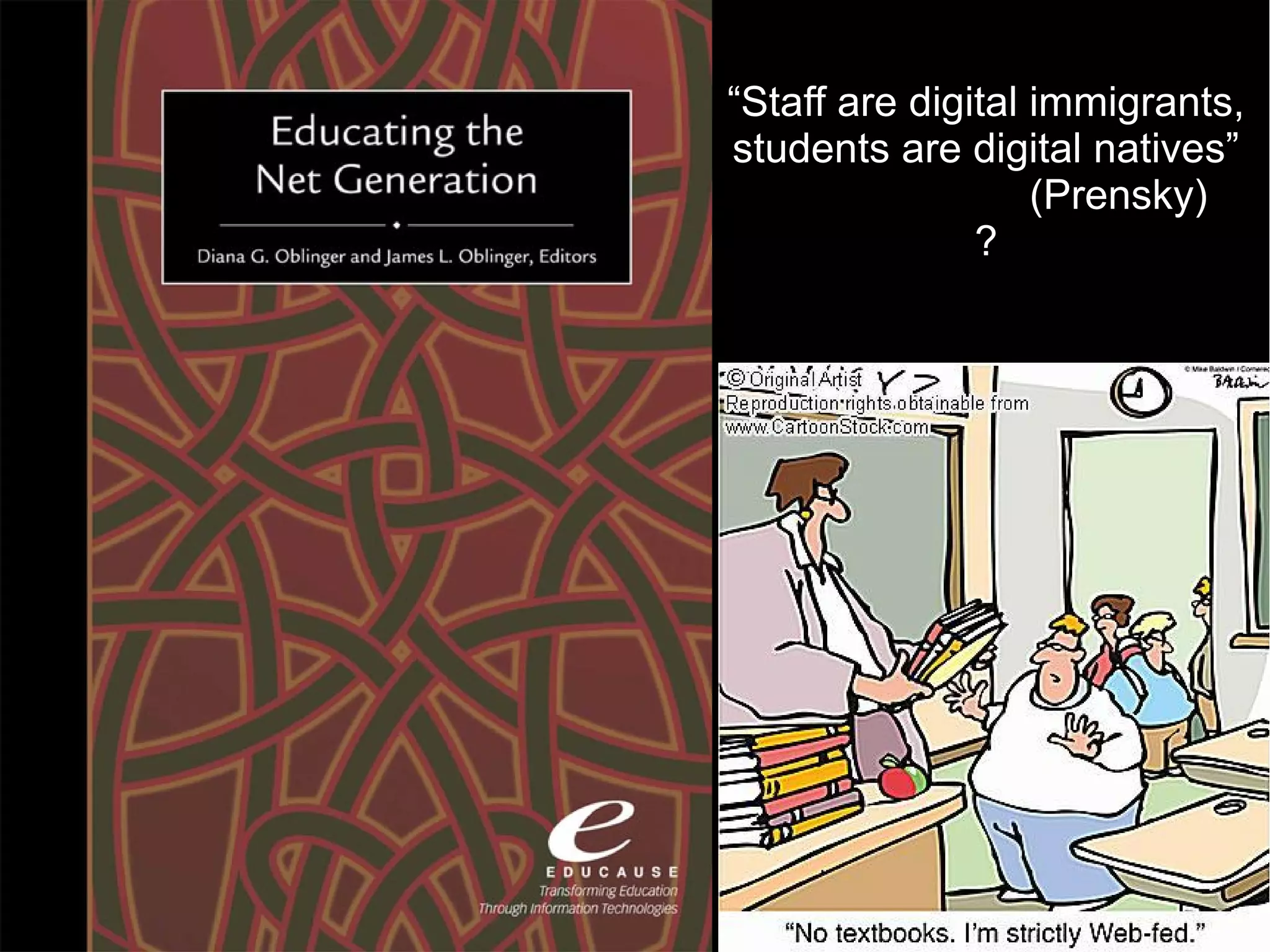
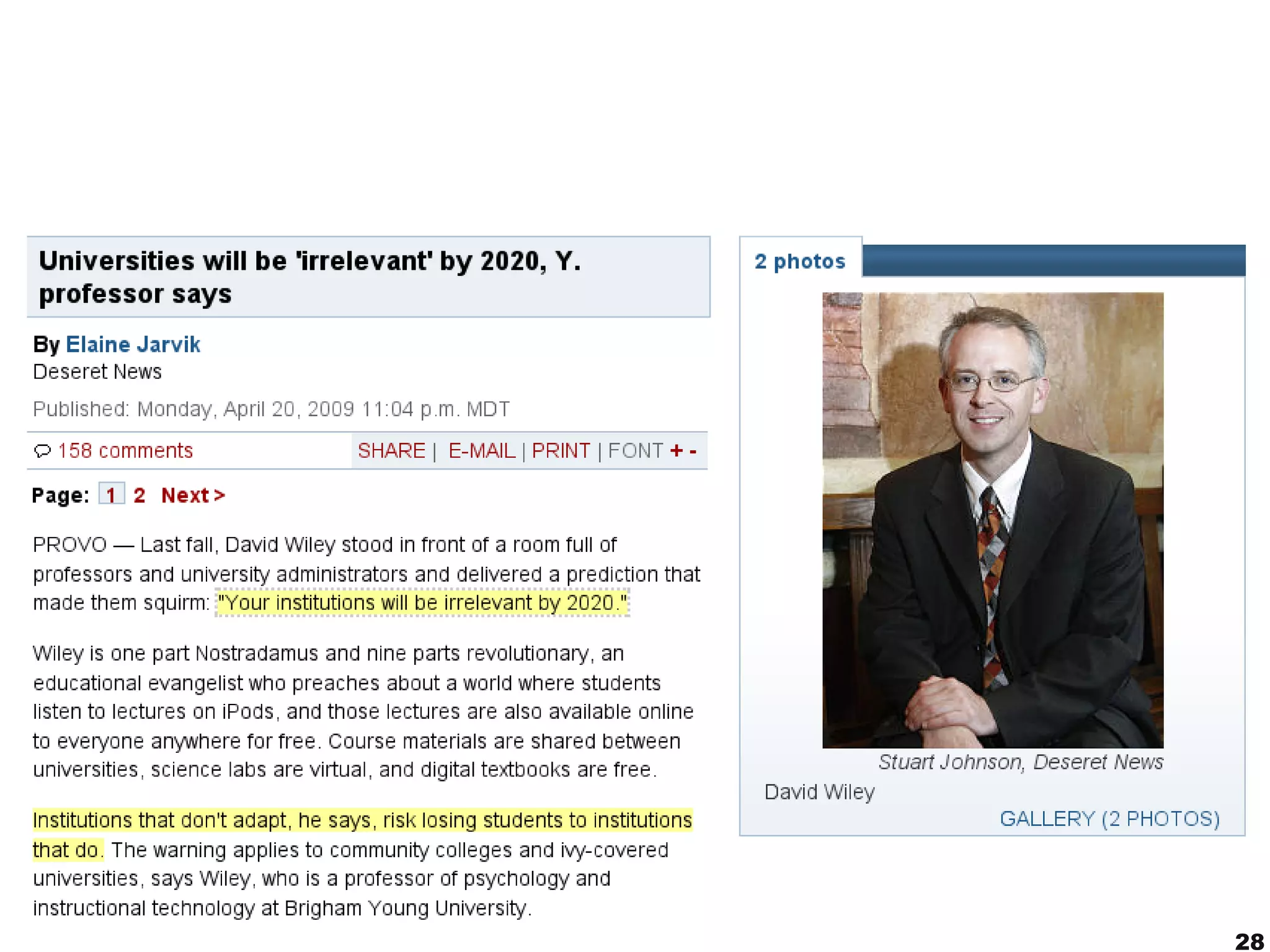
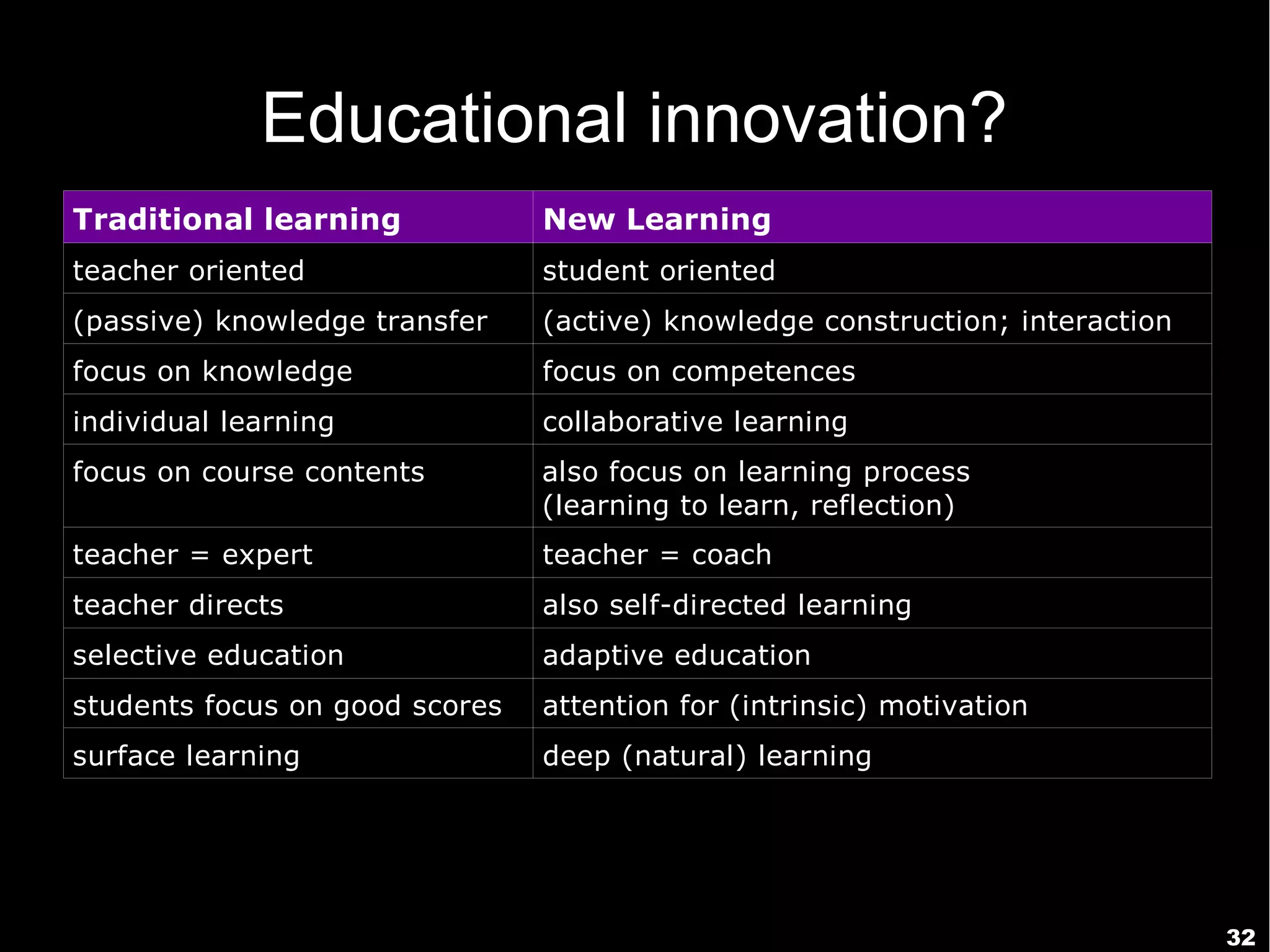
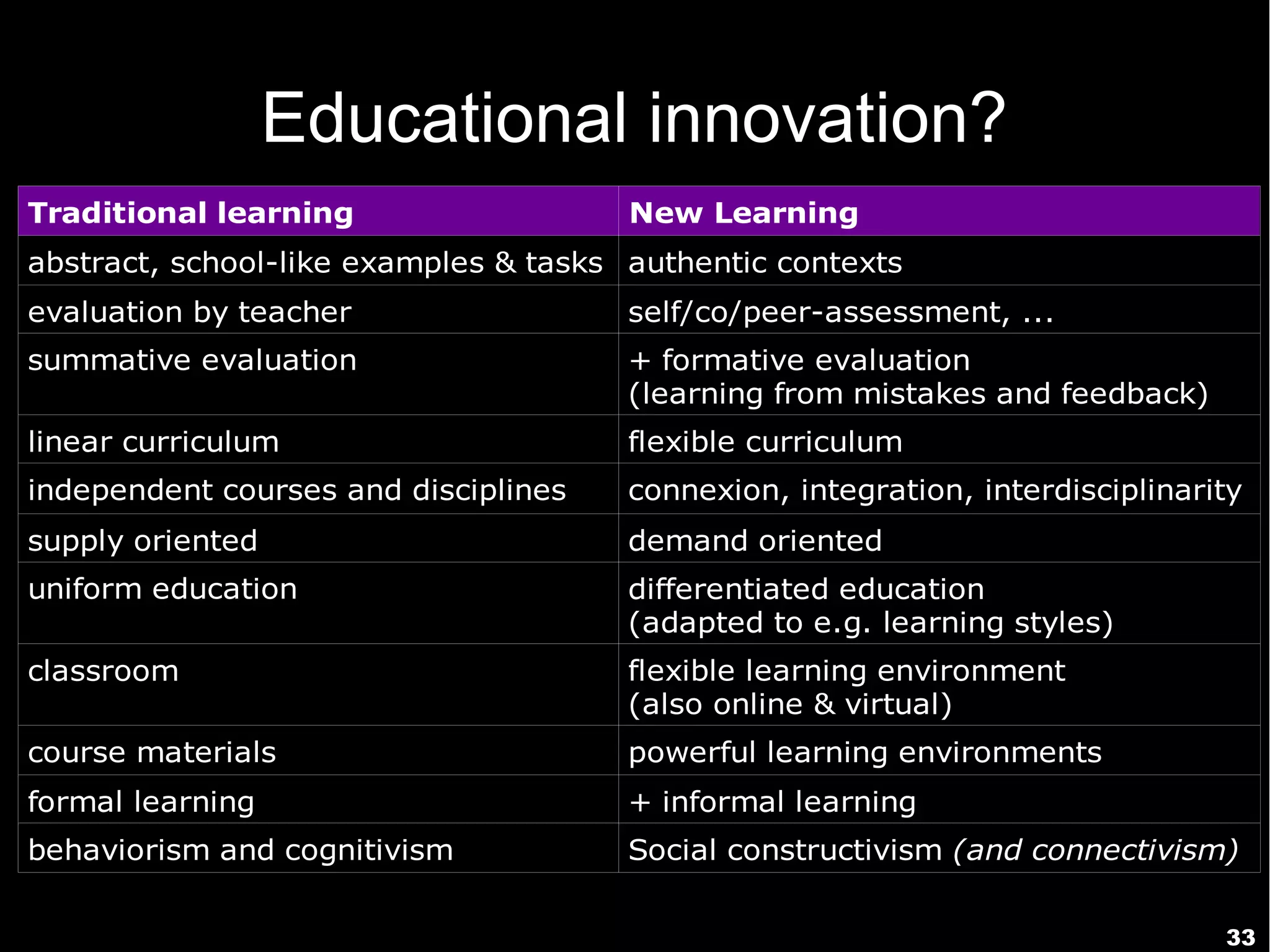
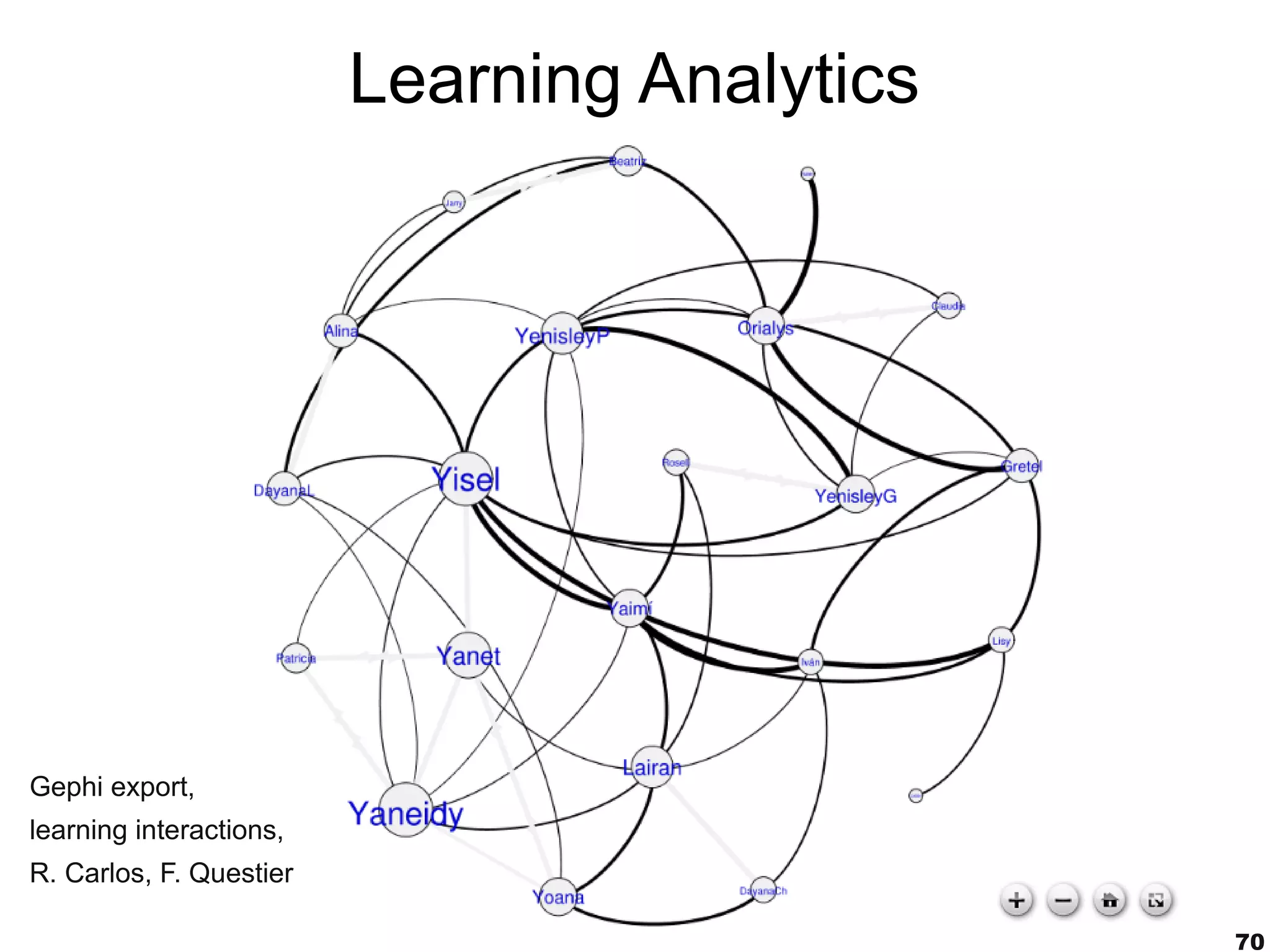
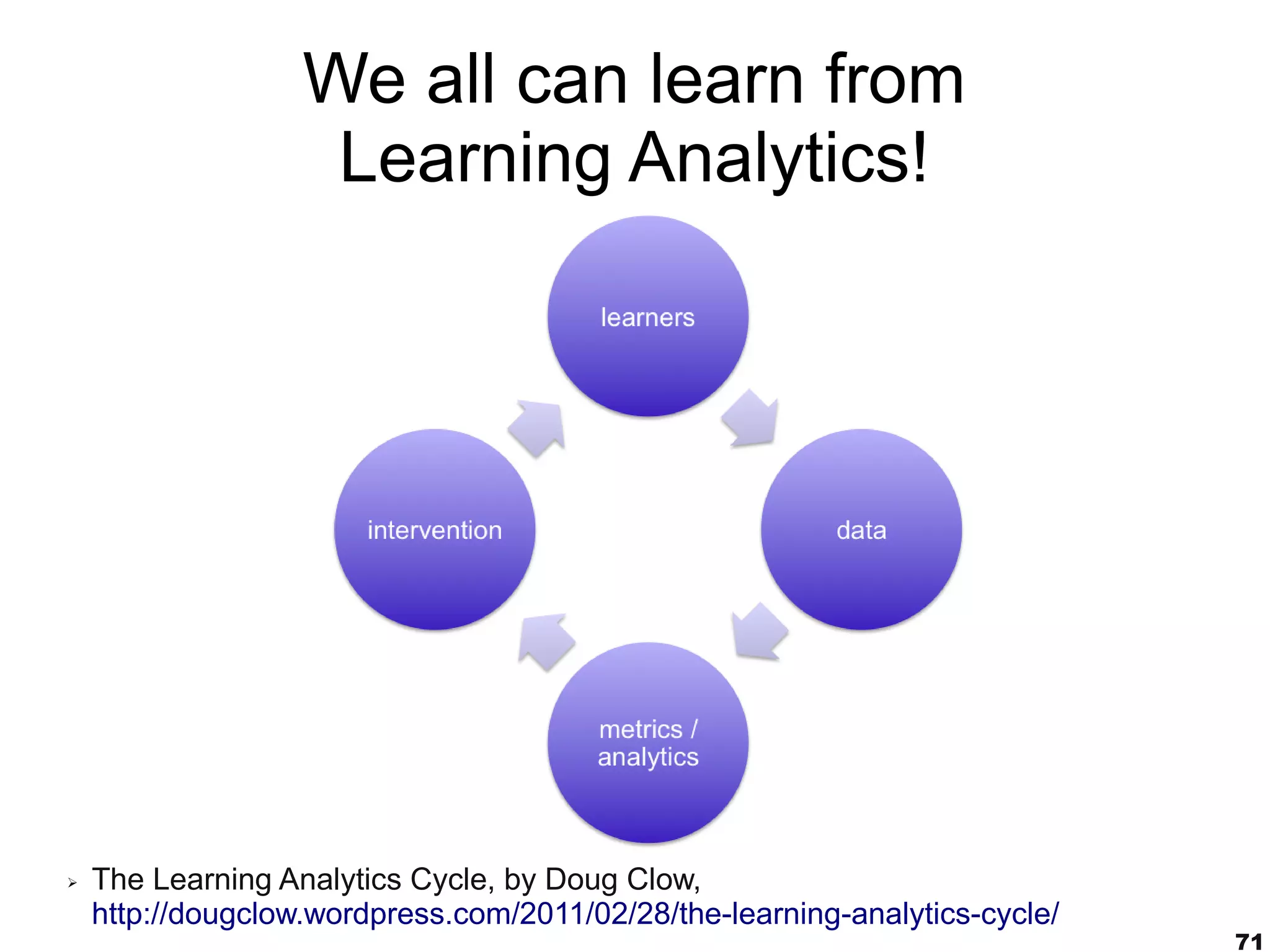
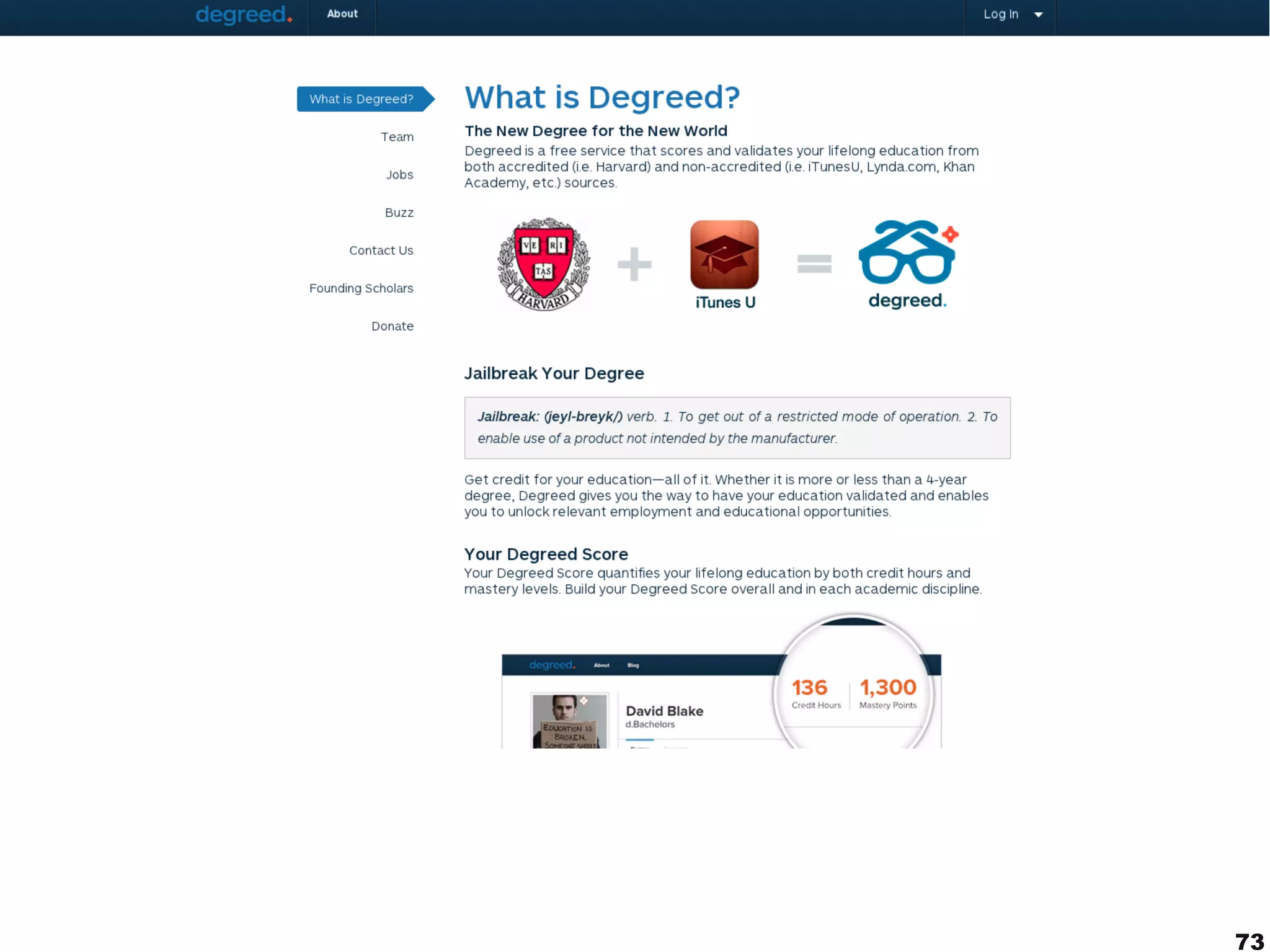
The document discusses innovative approaches to education, emphasizing the need to adapt teaching methods to prepare students for an unknown future. It highlights the shift from traditional knowledge transfer to a focus on competencies and collaborative, contextualized learning in the digital age. Additionally, it stresses the importance of integrating technology in teaching while recognizing the role of educators in facilitating this transformation.