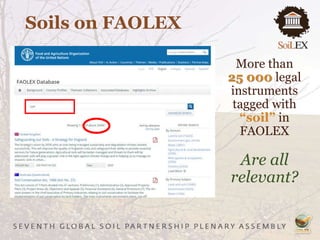
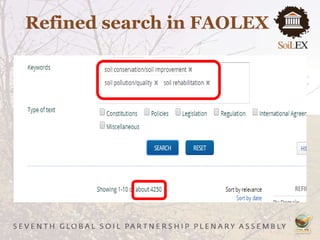
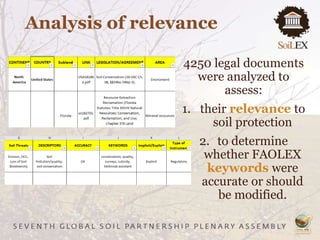
The document outlines recommendations to strengthen soil governance, emphasizing the need for informed policy development and regular assessments of soil conditions. It discusses the FAOLEX database, which contains over 25,000 legal instruments related to soil, and highlights the need for improved legal frameworks to address soil pollution and erosion. Key actions include raising awareness of existing laws and enhancing the effectiveness of legislative approaches to protect and manage soils sustainably.

![Strengthen soil governance
• Recommendation 1: Politicians, policy advisors,
decision makers and associated agencies should
be informed to better appreciate the true
societal value of soil […] in order to encourage
the development of enabling frameworks for soil
protection or sustainable management in line
with the goals of the World Soil Charter
• Recommendation 2: Policy development
should be supported by regular and
harmonised assessments of the state of soil,
associated pressures, their impacts and trends to
prioritise and target interventions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5gsp7pasoilex-190607144952/85/SoilLEX-2-320.jpg)