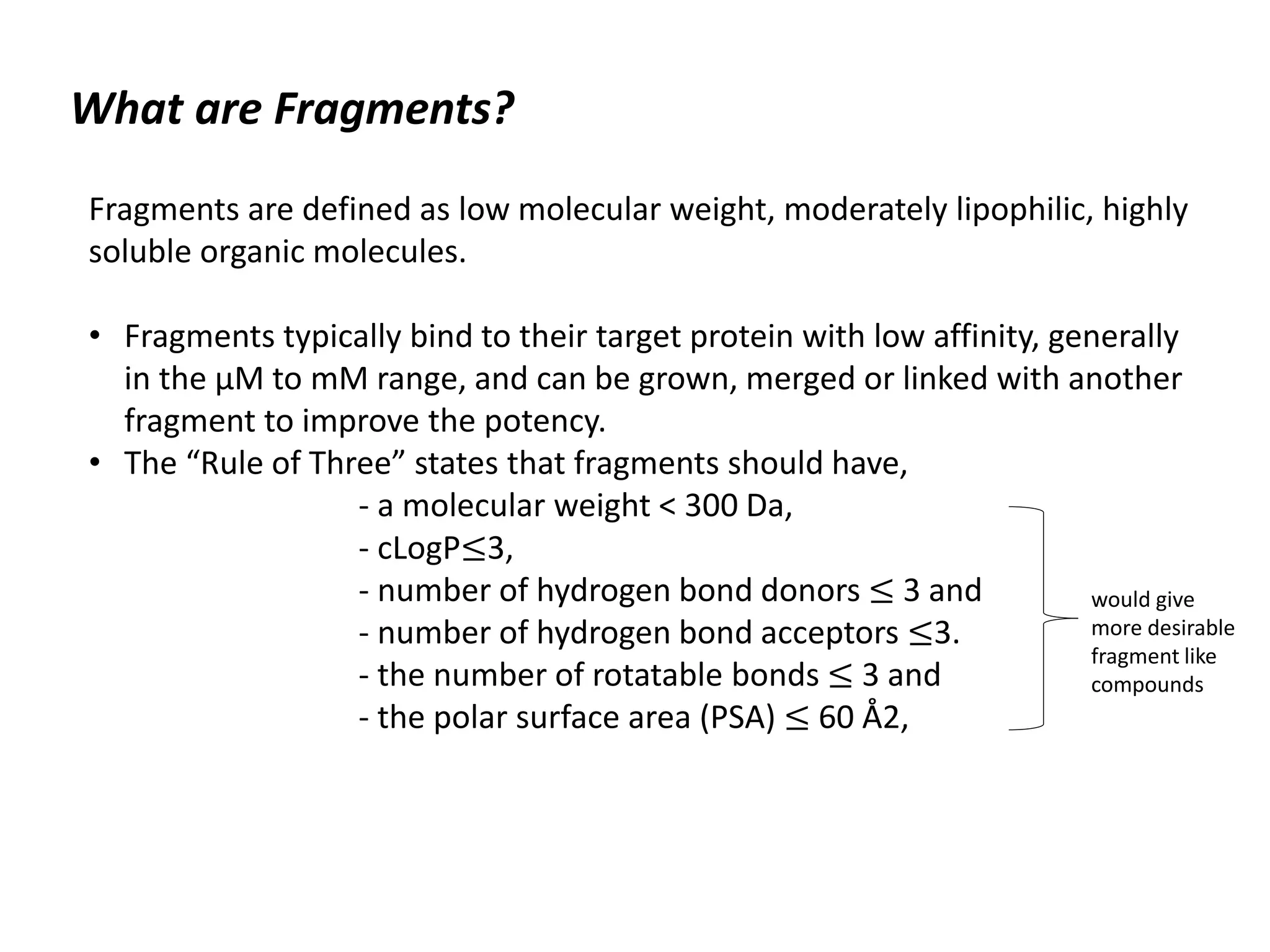
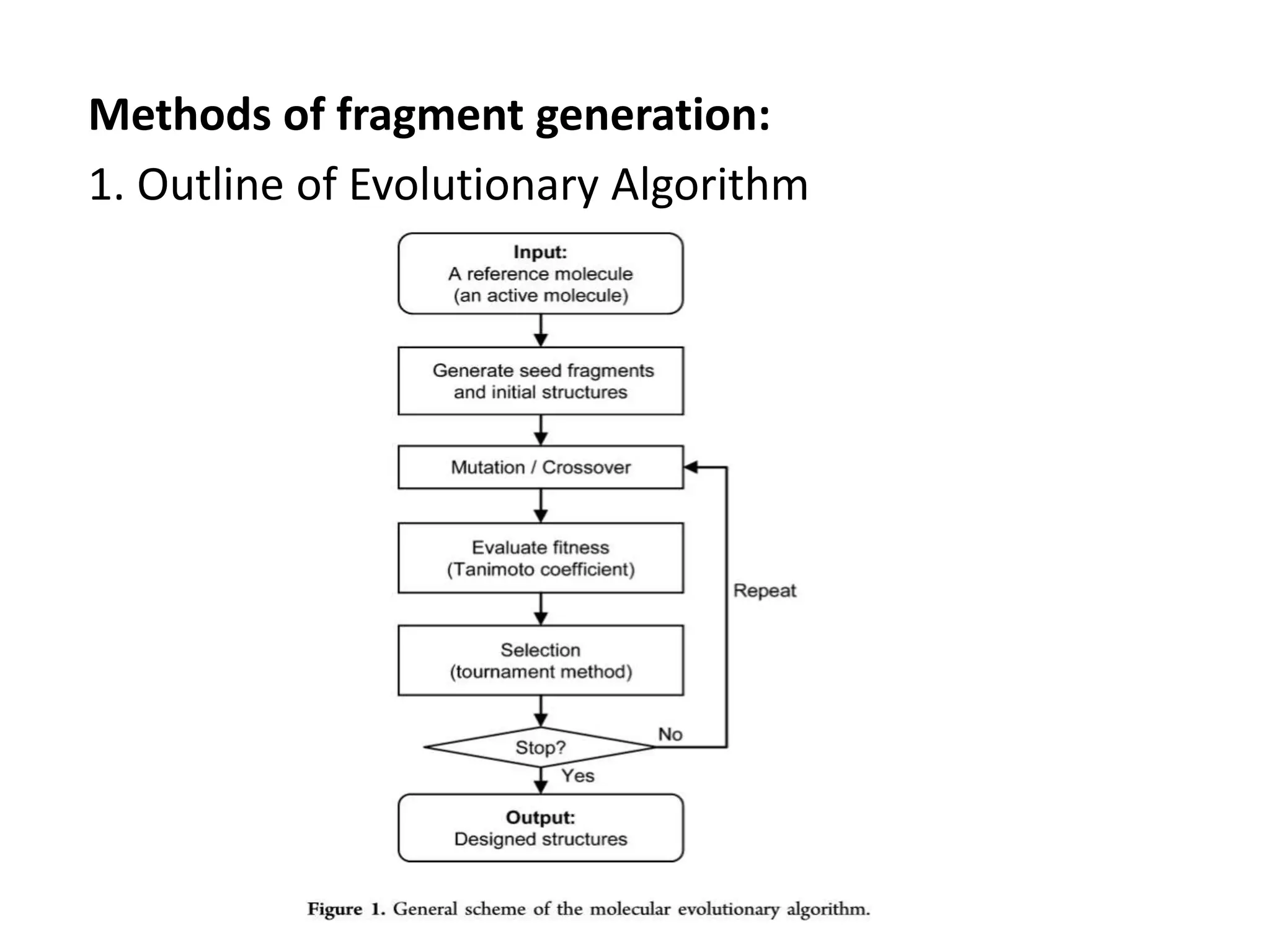
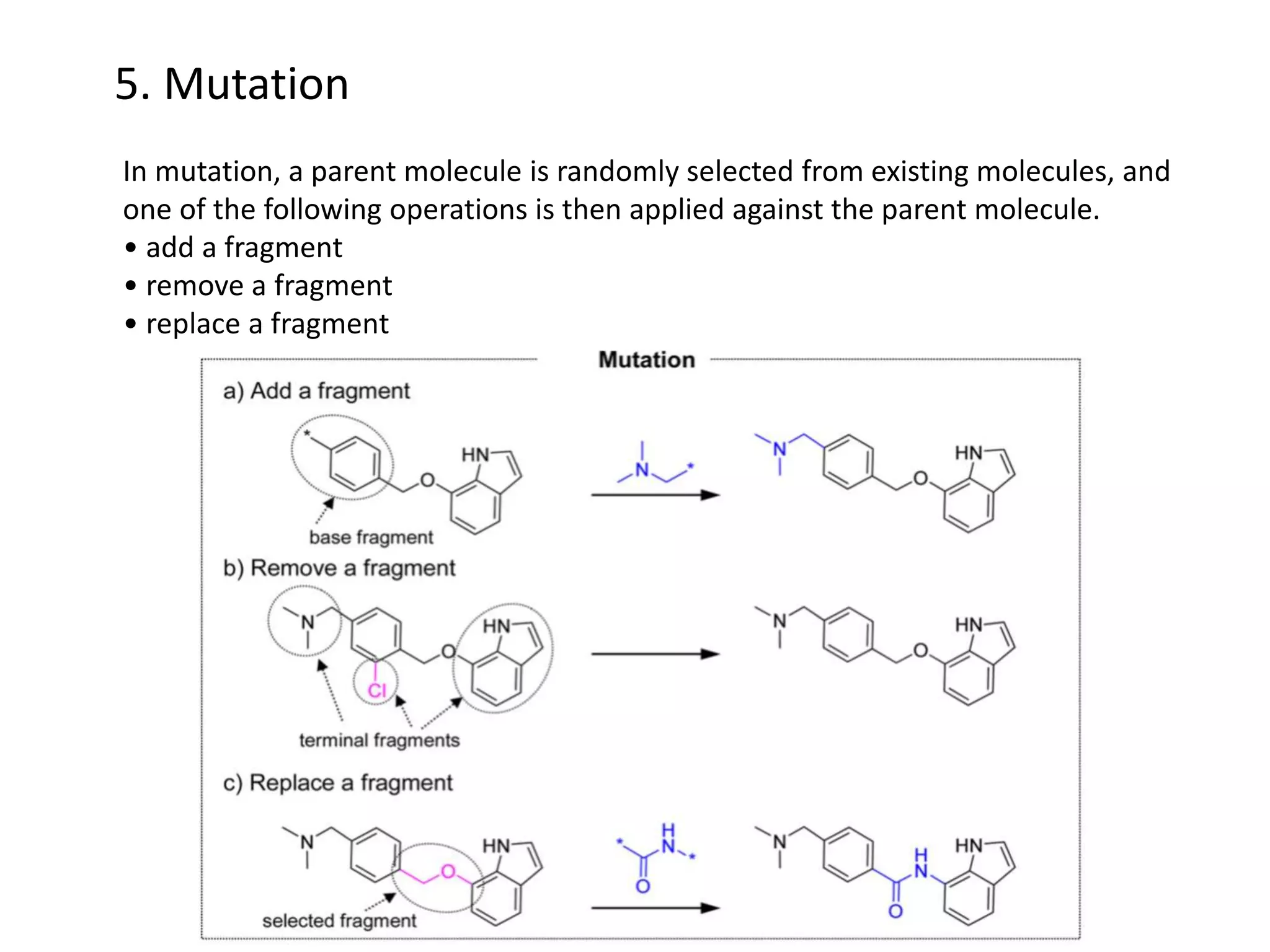
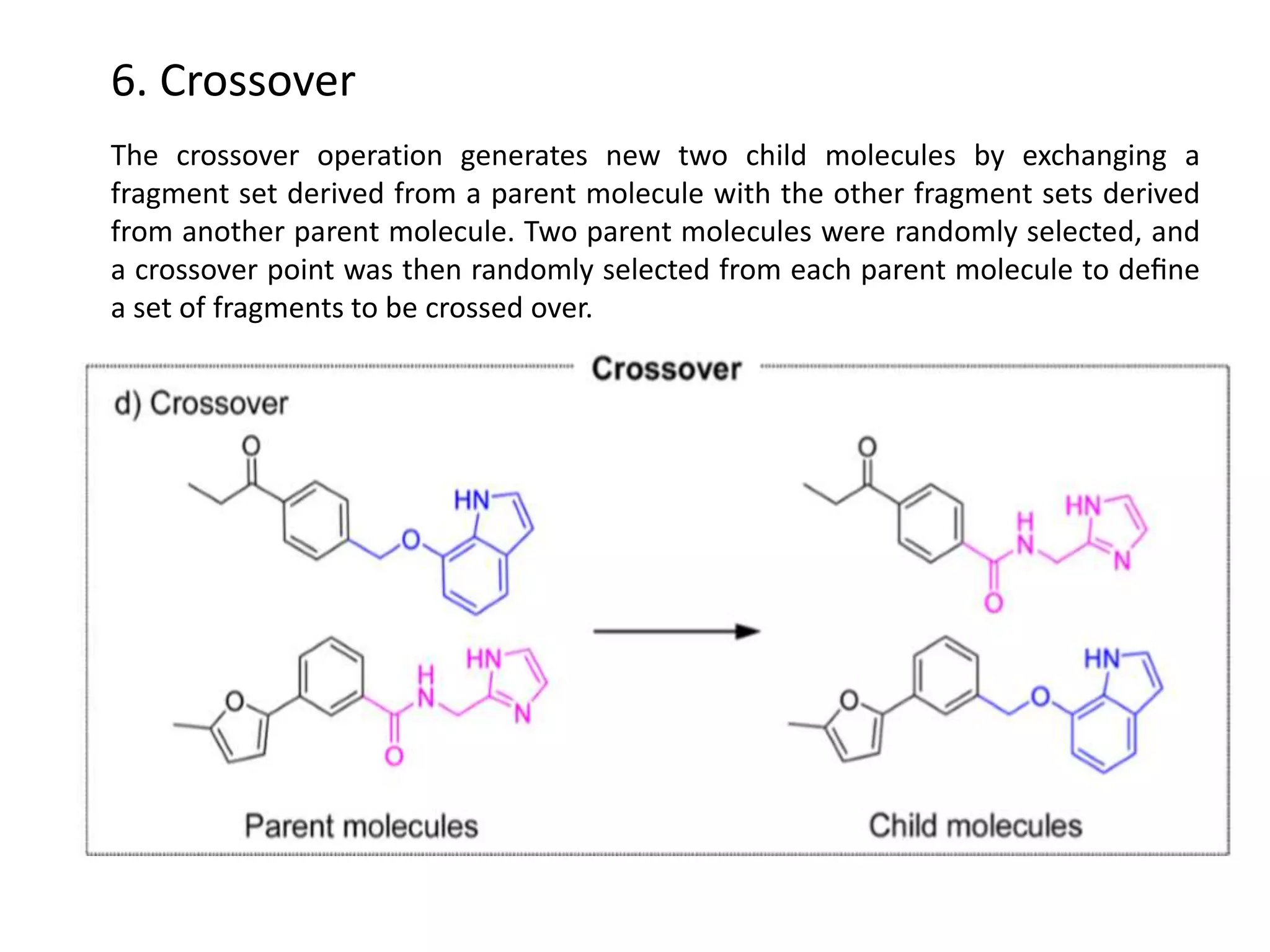
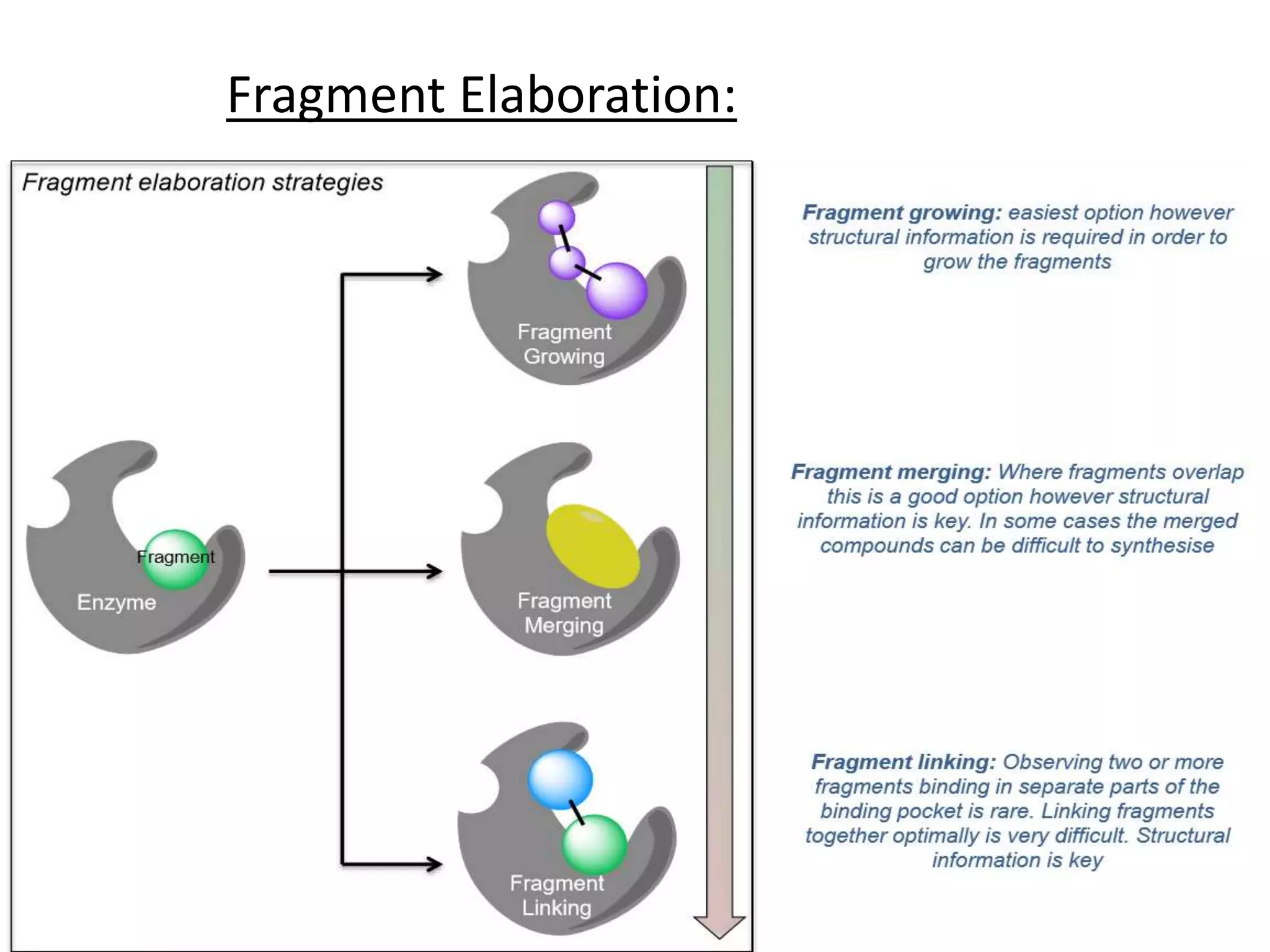
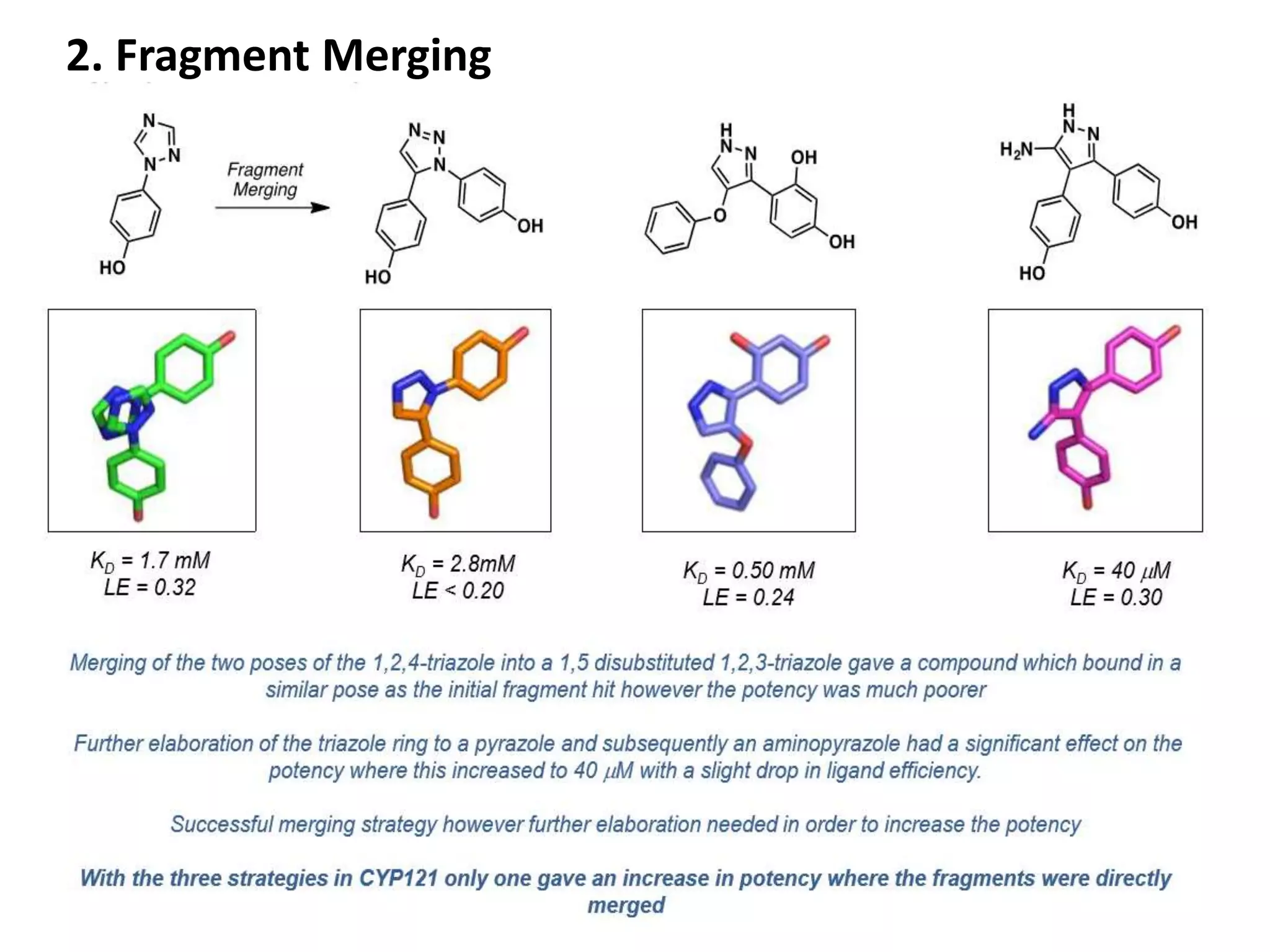
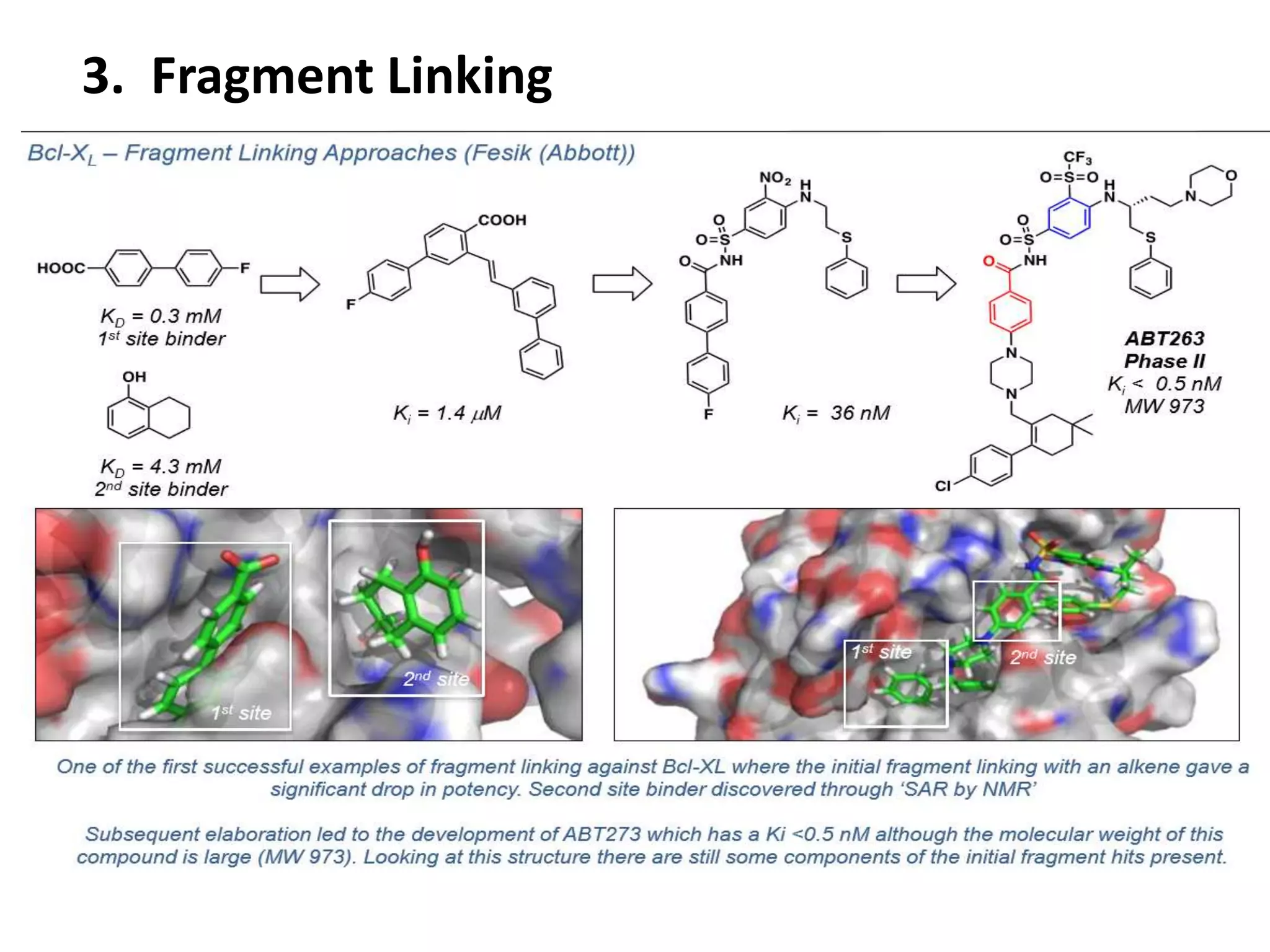
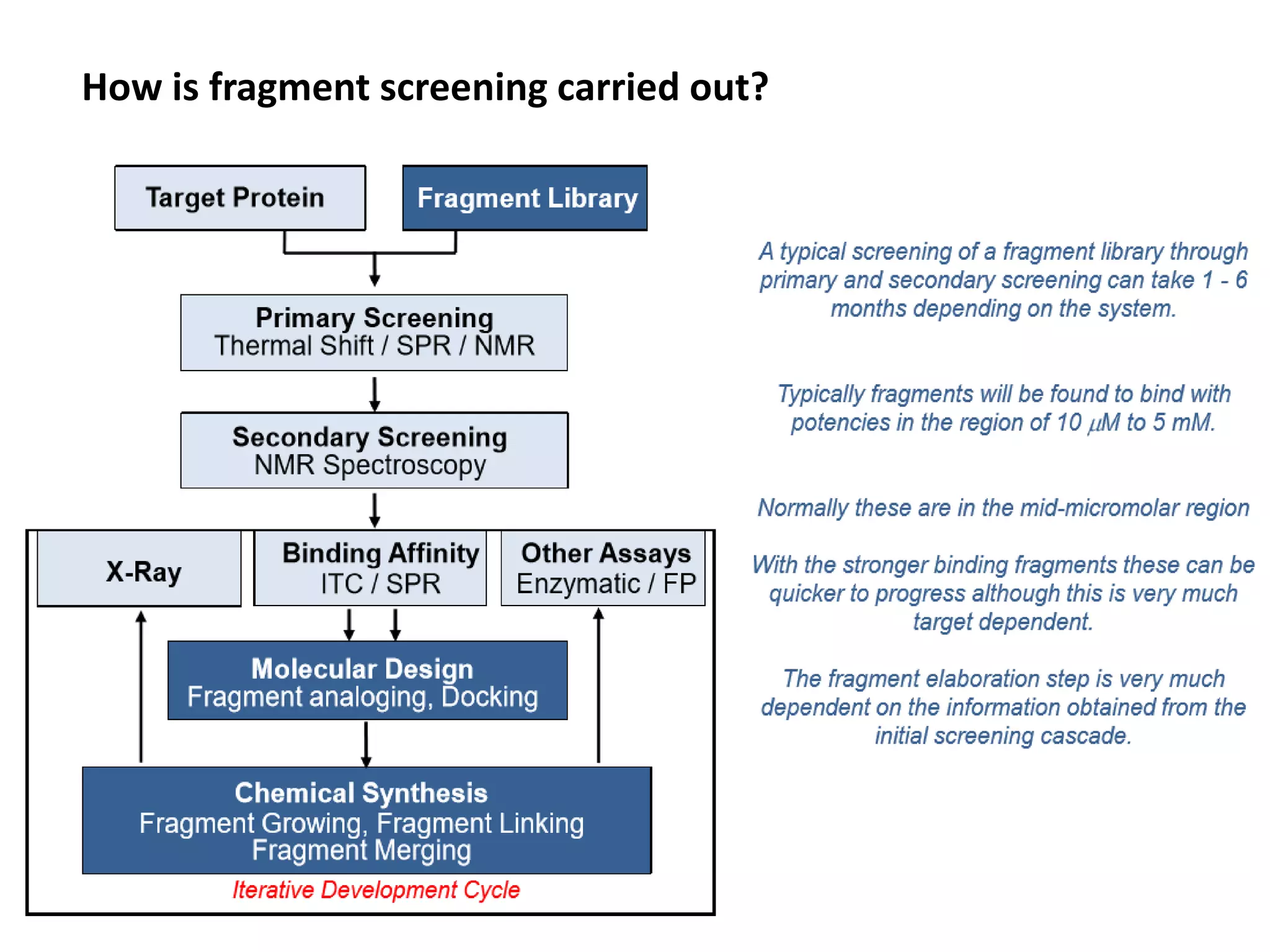
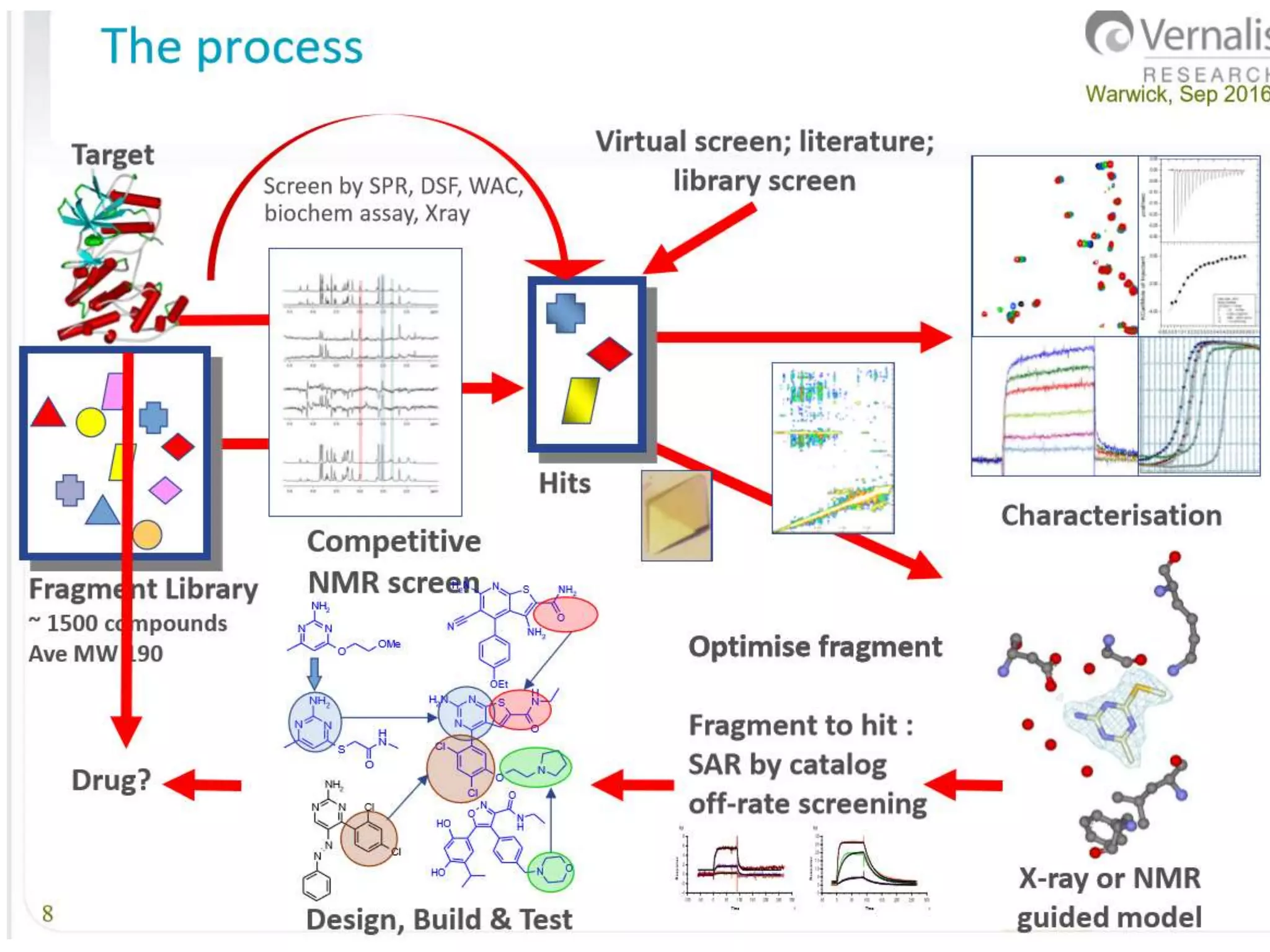
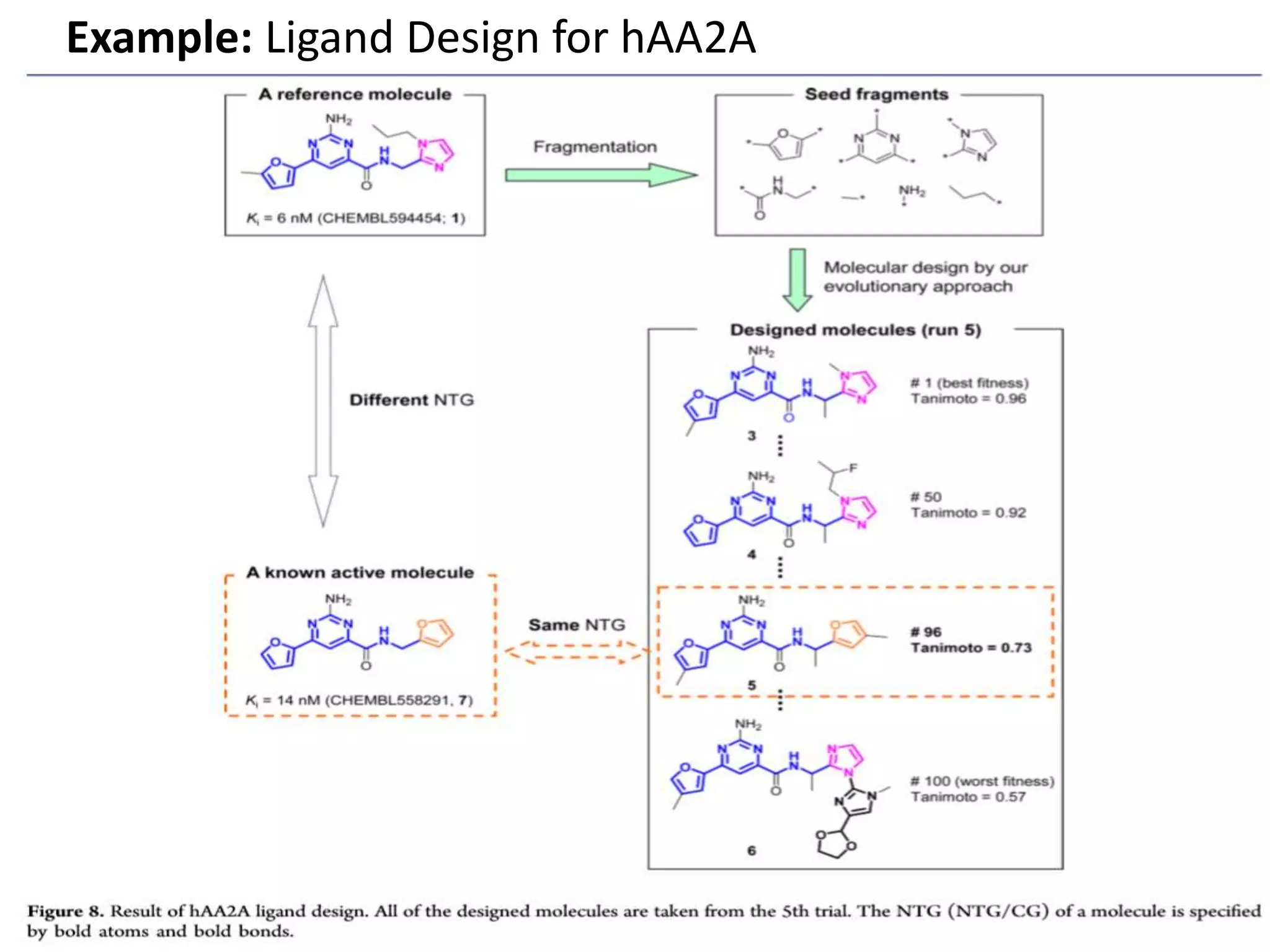
Fragment-based drug design (FBDD) uses small molecular fragments that bind weakly to a target protein's binding site. These fragments can then be grown, merged, or linked to improve binding affinity. FBDD provides starting points for challenging targets like protein-protein interactions. It increases the use of biophysics to characterize compound binding. FBDD also gives small research groups access to tools for identifying chemical probes of biological systems.